- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-NUSAP1
NUSAP1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain et plus (2)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 12024-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
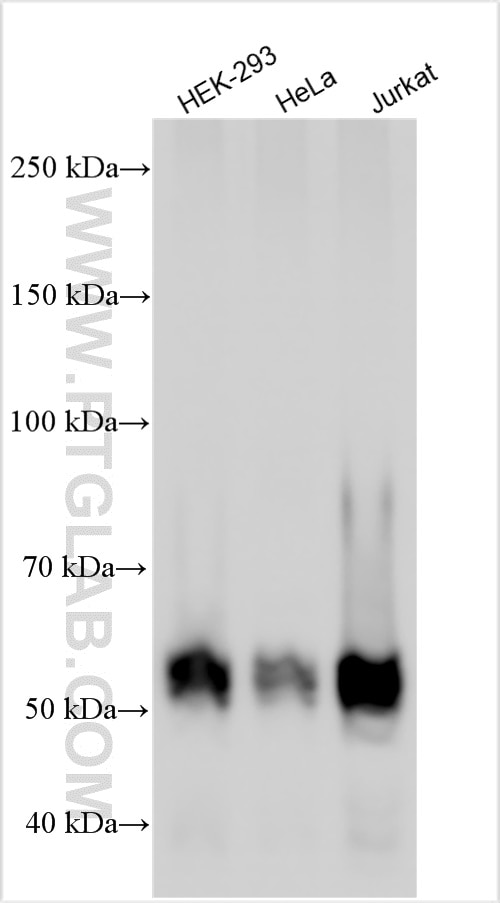
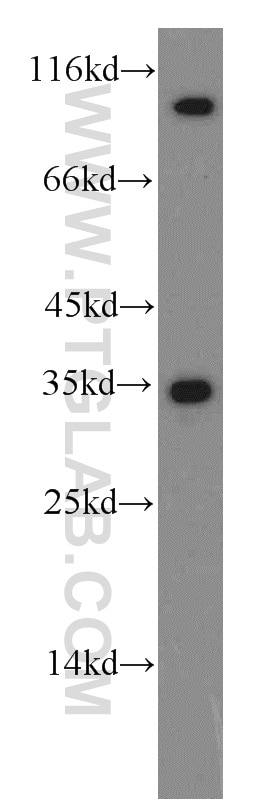
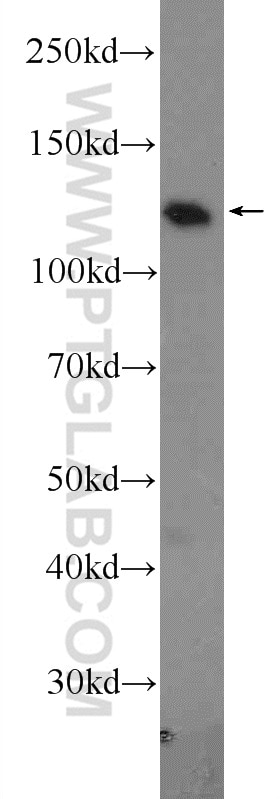
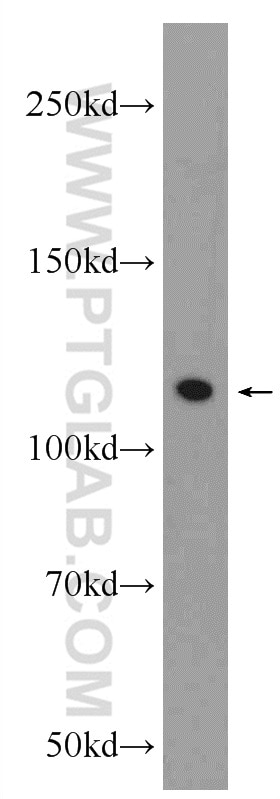
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HEK-293, cellules HeLa, cellules Jurkat |
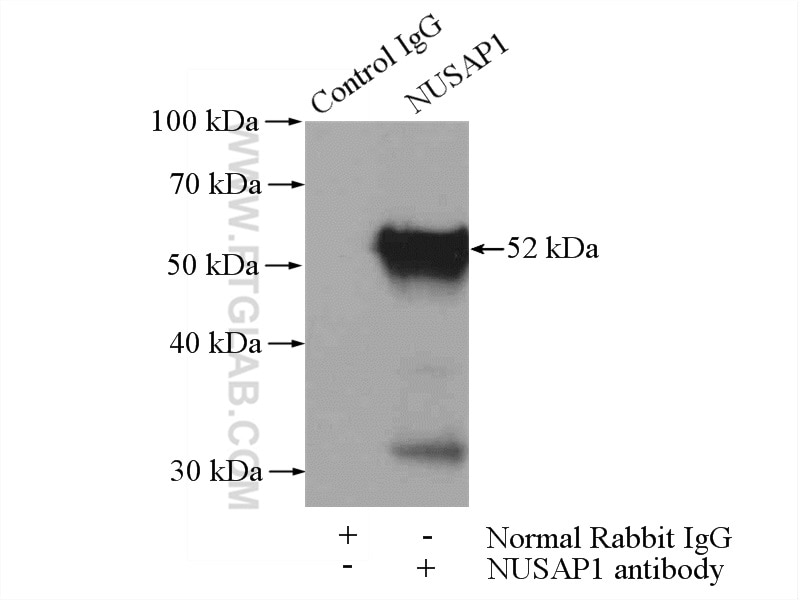
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HeLa |
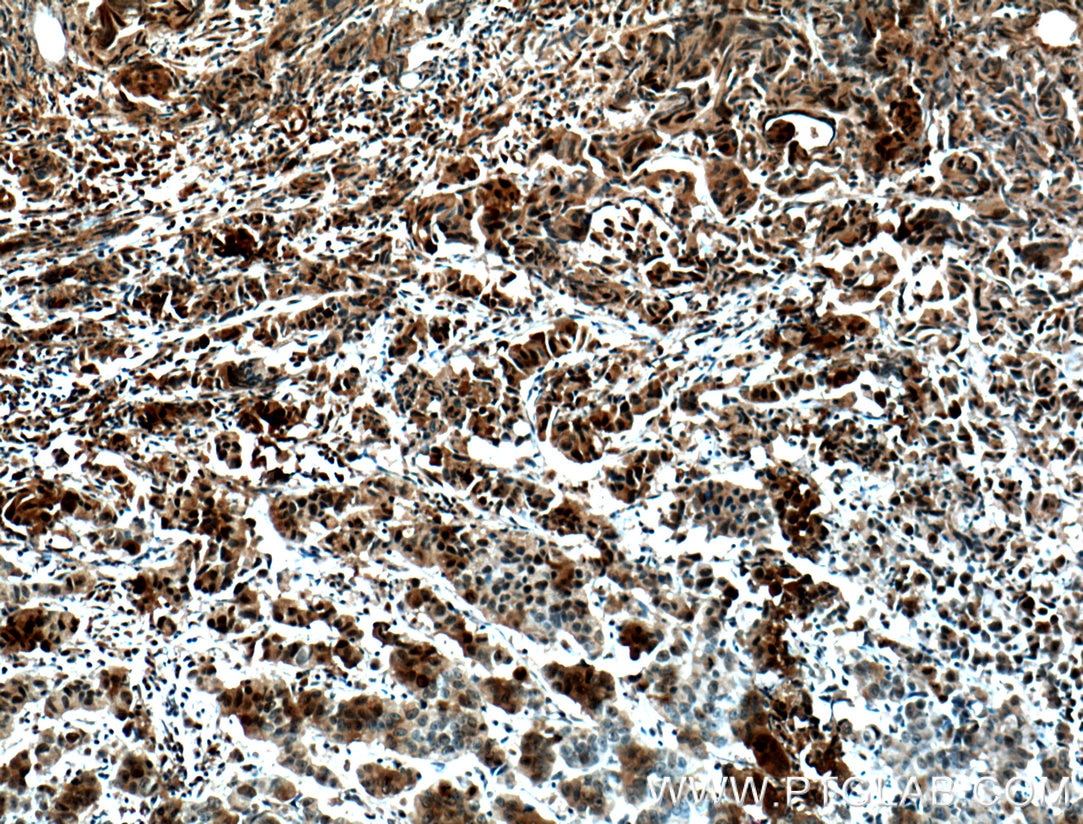
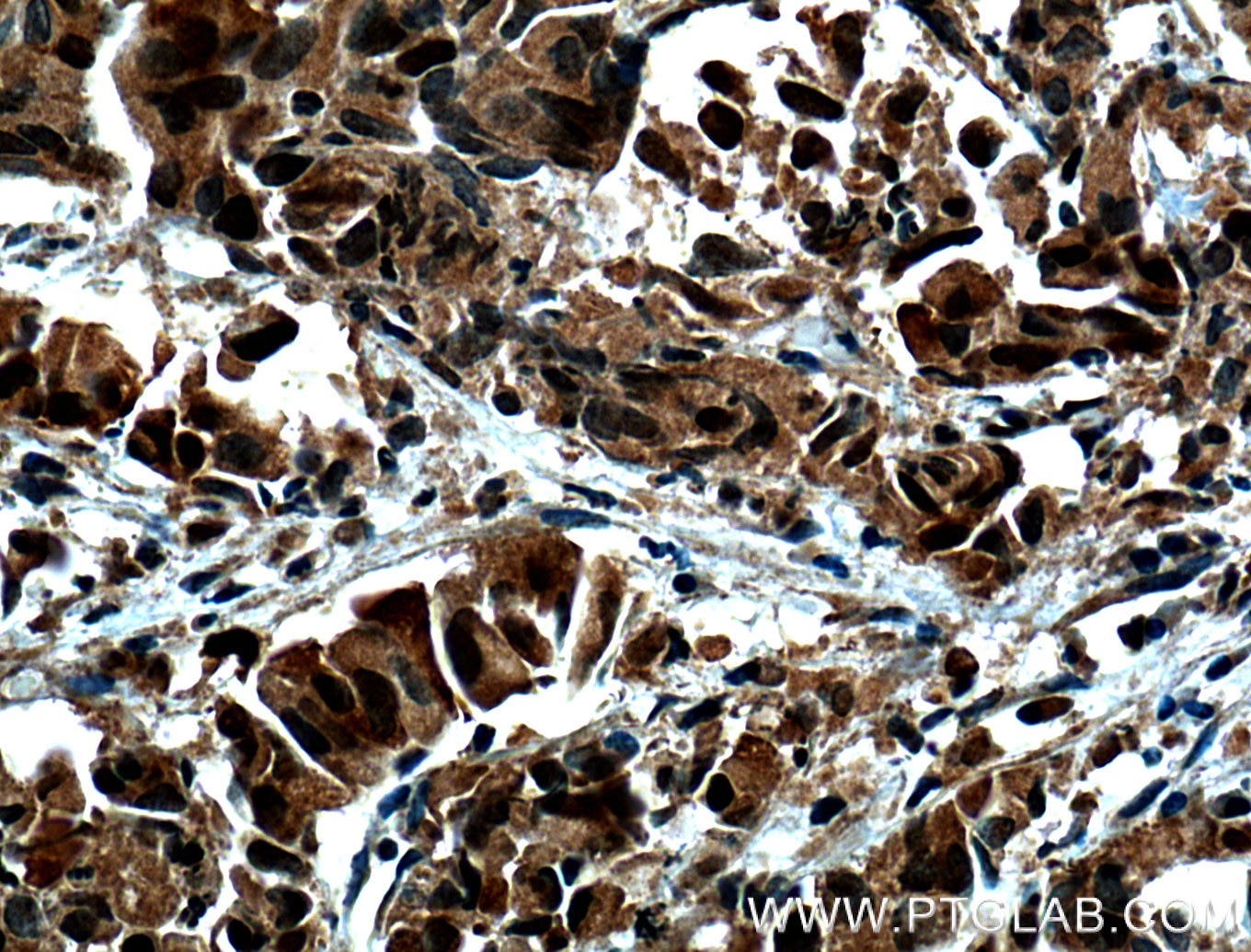
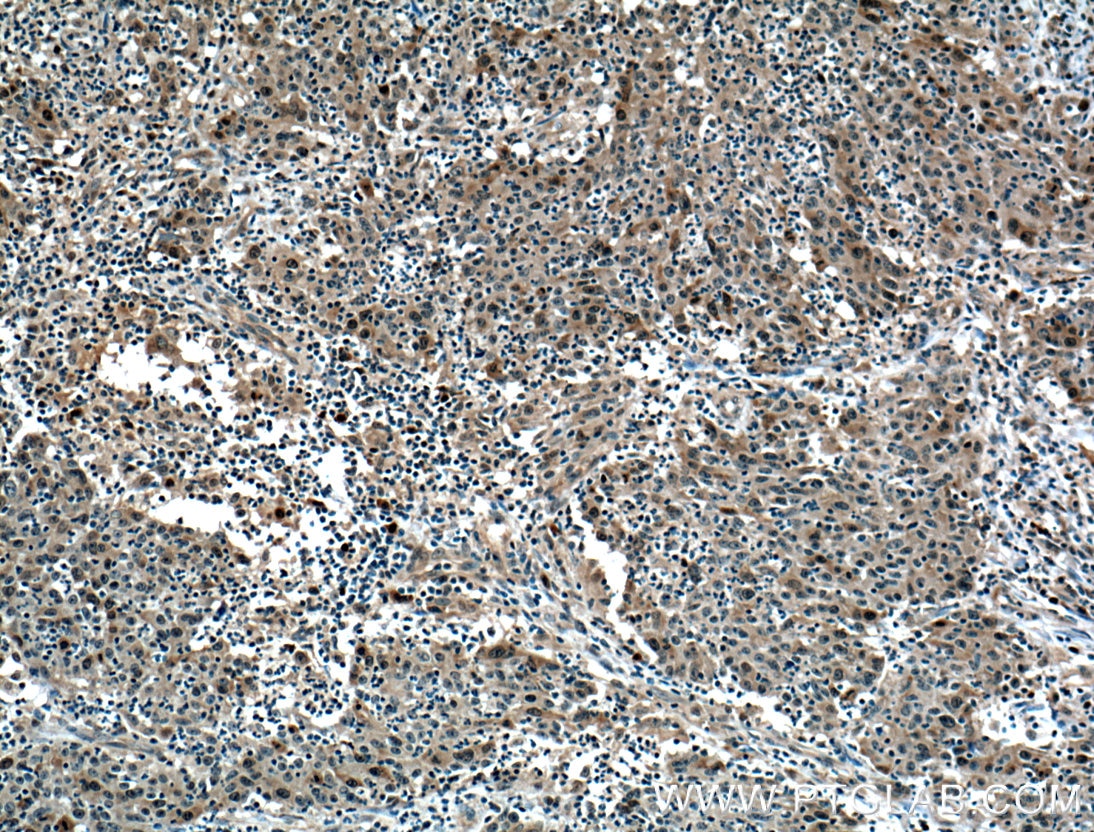
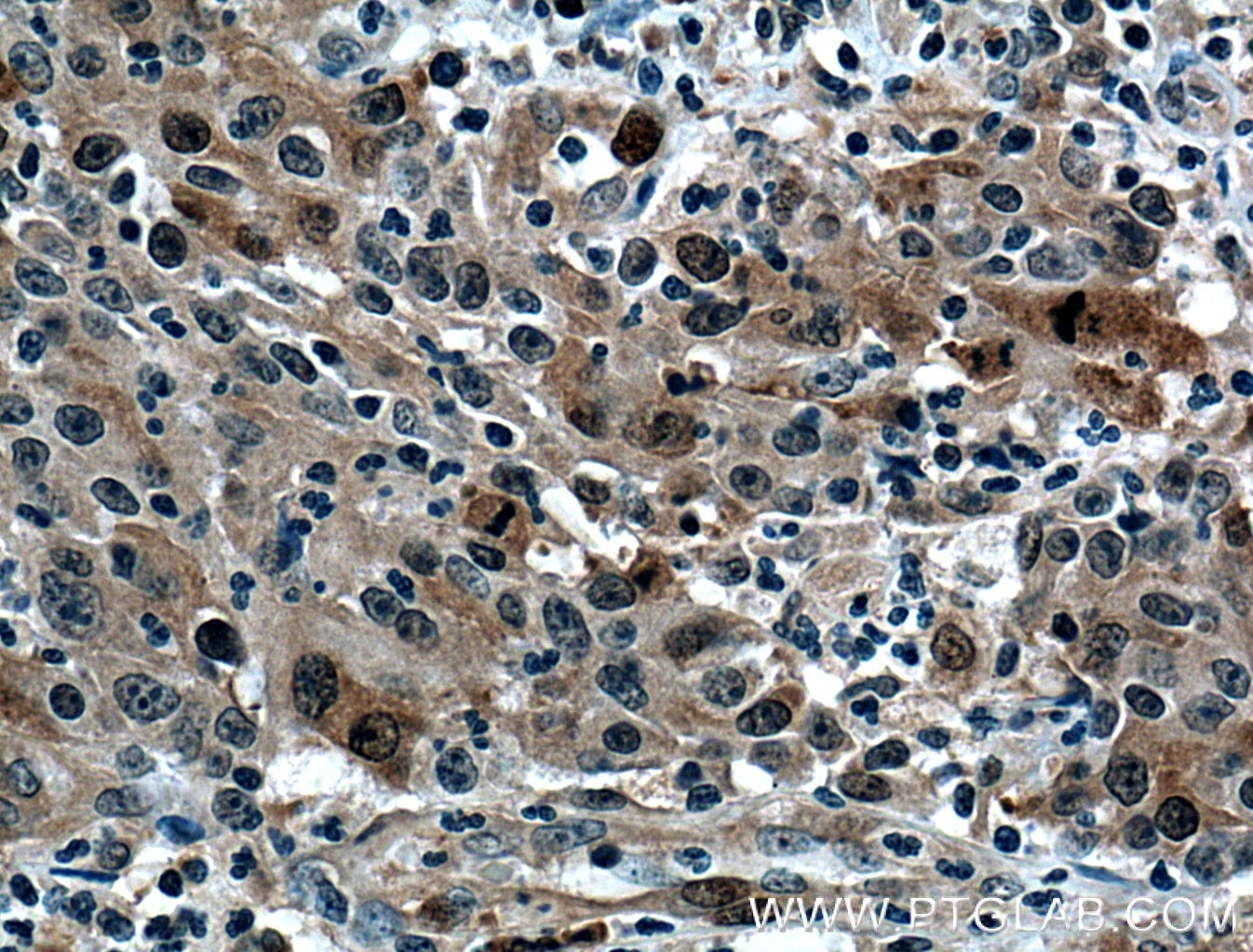
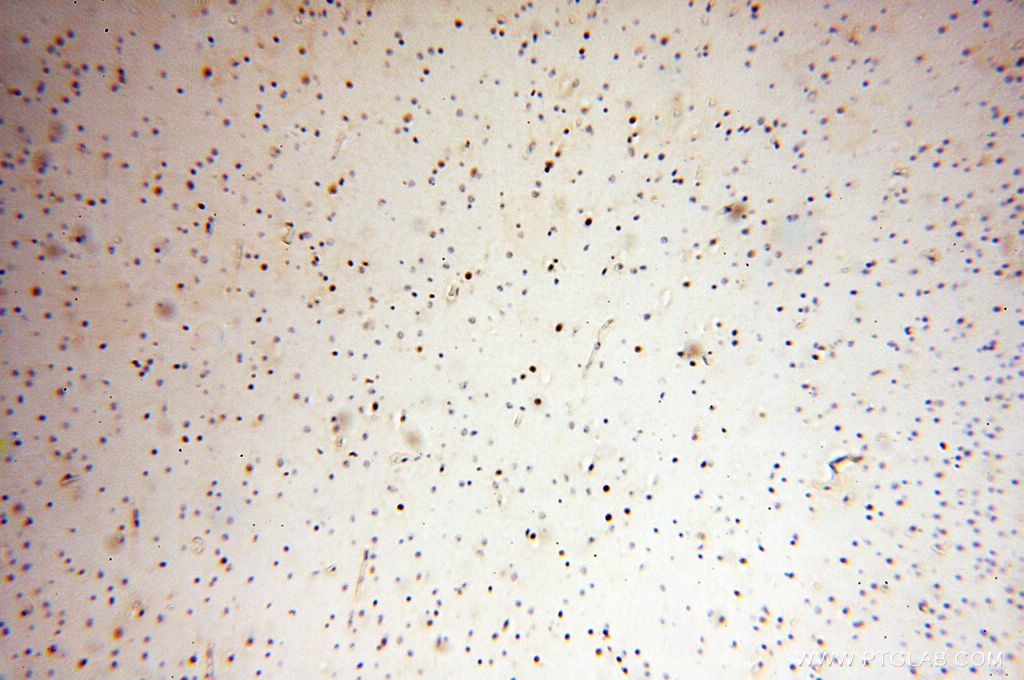
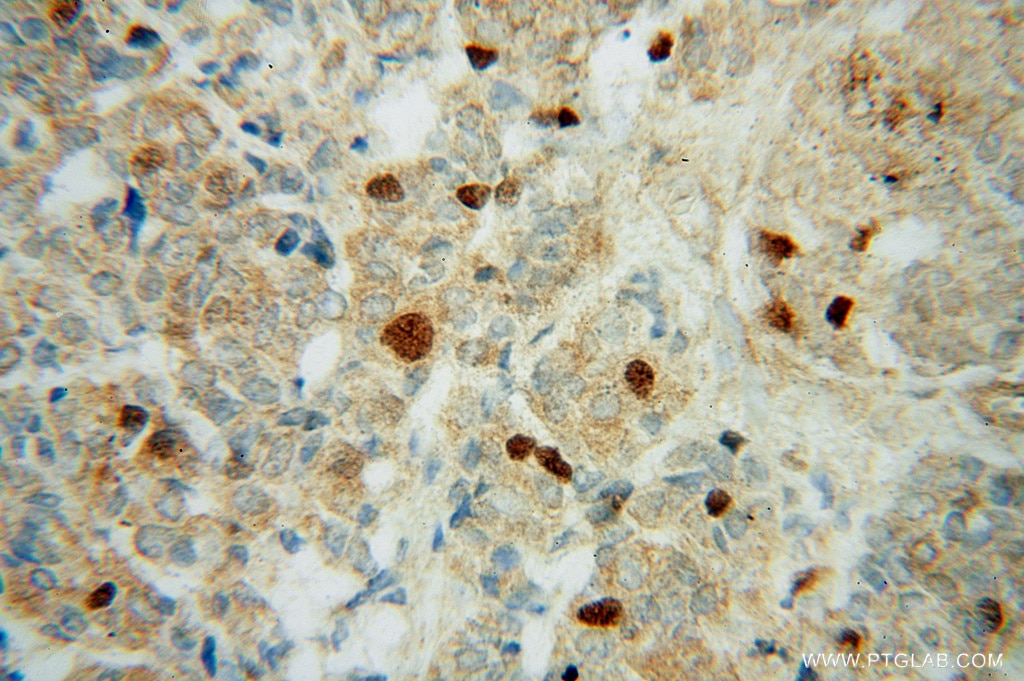
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer de la prostate humain, tissu de cancer du côlon humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
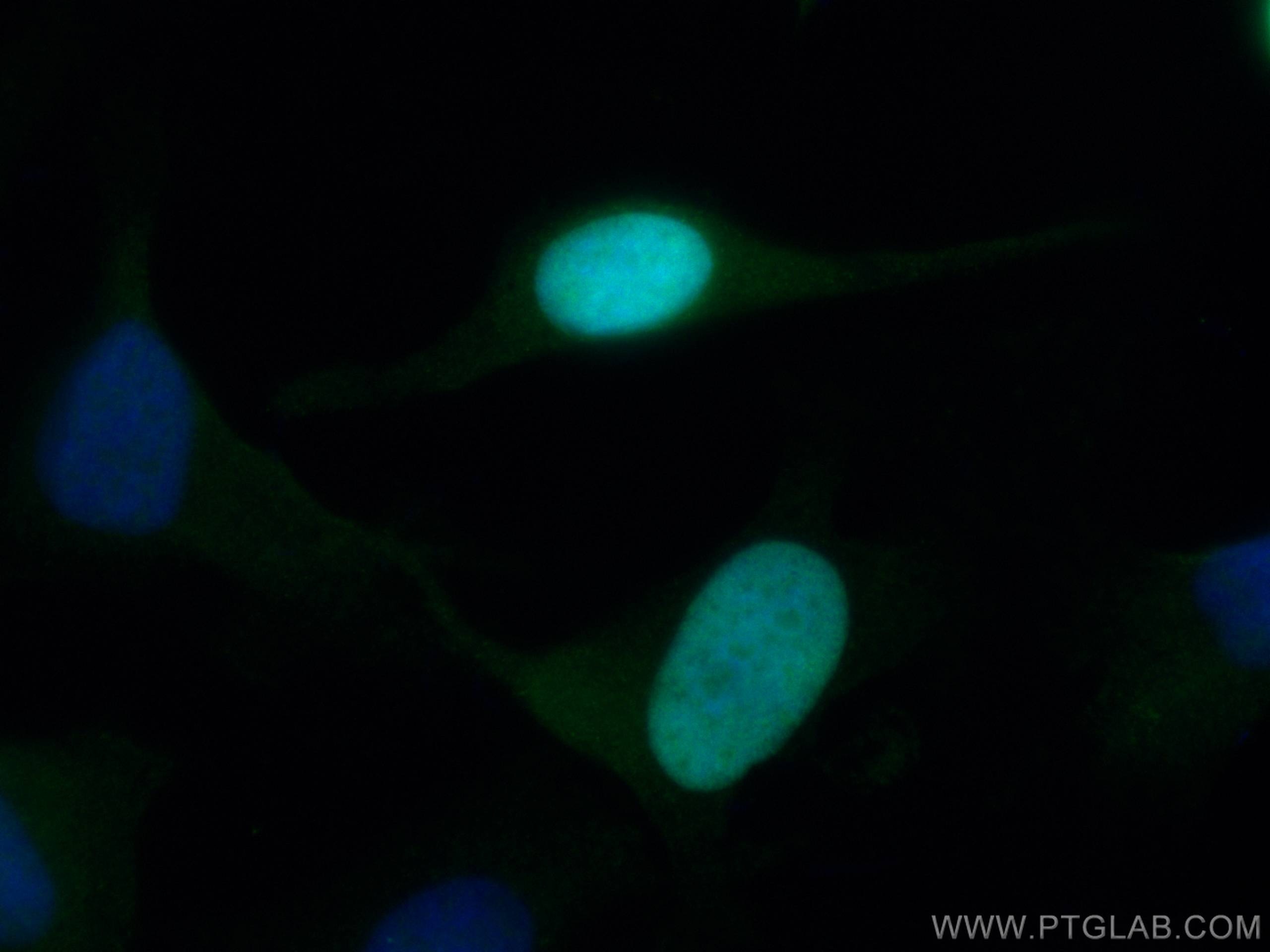
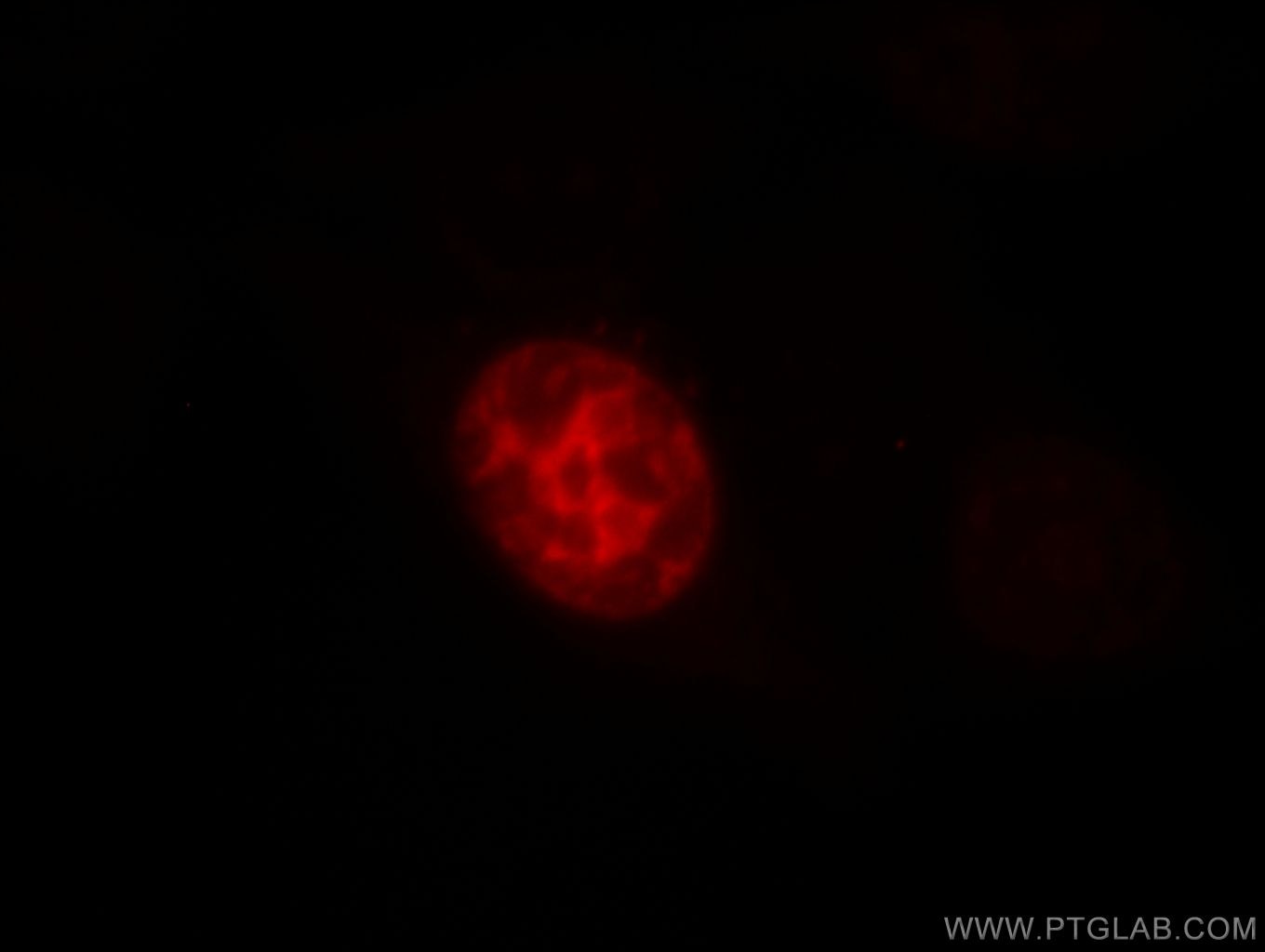
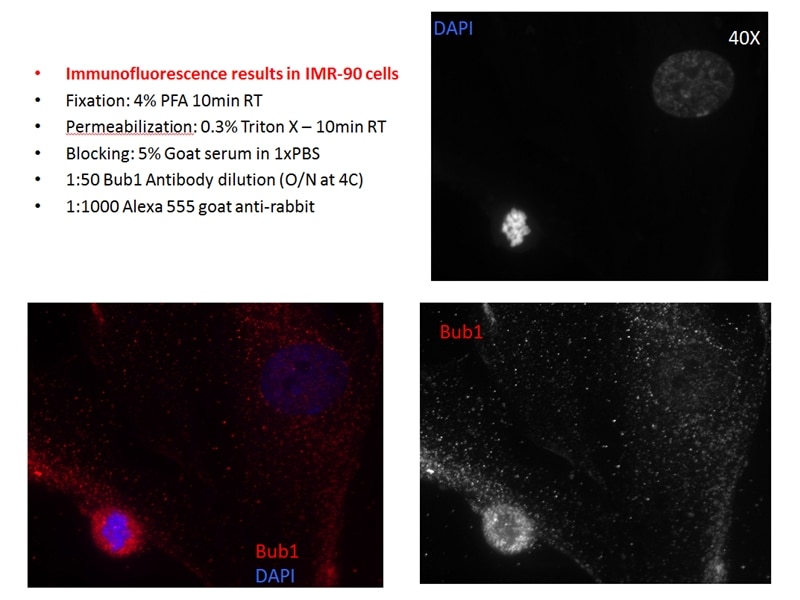
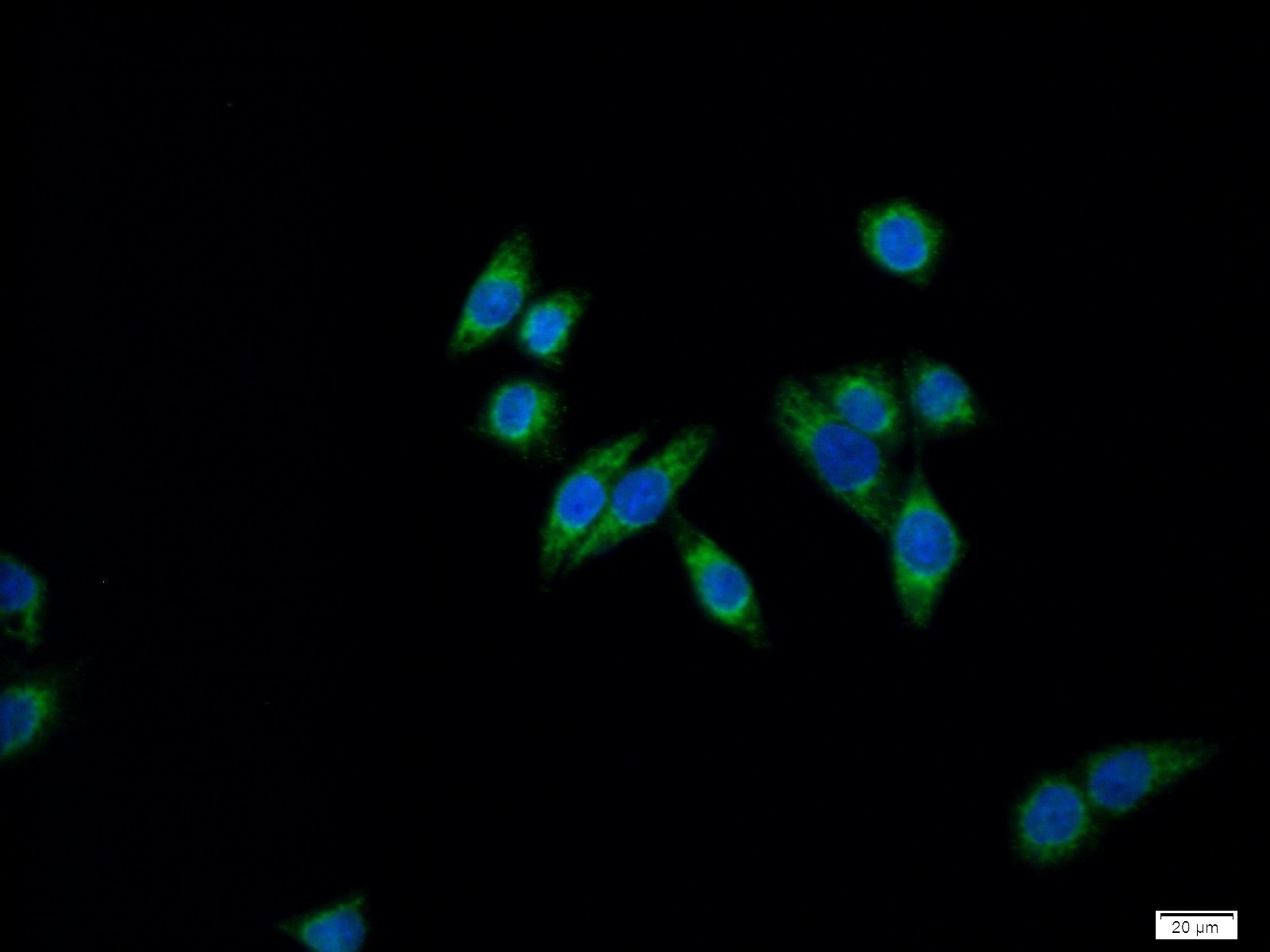
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HeLa, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 7 publications below |
| WB | See 28 publications below |
| IHC | See 15 publications below |
| IF | See 5 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
12024-1-AP cible NUSAP1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | NUSAP1 Protéine recombinante Ag2654 |
| Nom complet | nucleolar and spindle associated protein 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 440 aa, 49 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 47-52 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC001308 |
| Symbole du gène | NUSAP1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 51203 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
NUSAP1, also named as ANKT, belongs to the NUSAP family. It is microtubule-associated protein with the capacity to bundle and stabilize microtubules. NUSAP1 may associate with chromosomes and promote the organization of mitotic spindle microtubules around them. NUSAP1 plays a role in connecting apoptosis with cell migration and it is a potentially involved in morphogenesis in vertebrates (PMID:21203972). NUSAP1 is an immunogenic antigen in 65% of patients with AML following allogeneic HCT and suggests a tumor antigen role(PMID:20053754 ). NuSAP1 protein level is tightly regulated by the APC/C ubiquitin ligase complex and NuSAP induces mitotic arrest dependent of its microtubule affinity (PMID:17618083). NUSAP1 is overexpressed in pituitary adenomas.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NUSAP1 antibody 12024-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for NUSAP1 antibody 12024-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for NUSAP1 antibody 12024-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for NUSAP1 antibody 12024-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Gastroenterology microRNA 193a-5p Regulates Levels of Nucleolar- and Spindle-Associated Protein 1 to Suppress Hepatocarcinogenesis. | ||
Mol Cell Regulated degradation of spindle assembly factors by the anaphase-promoting complex. | ||
J Exp Med Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals differential nutrient absorption functions in human intestine. | ||
Acta Neuropathol Transcriptome analysis of MENX-associated rat pituitary adenomas identifies novel molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of human pituitary gonadotroph adenomas. |