Tested Applications
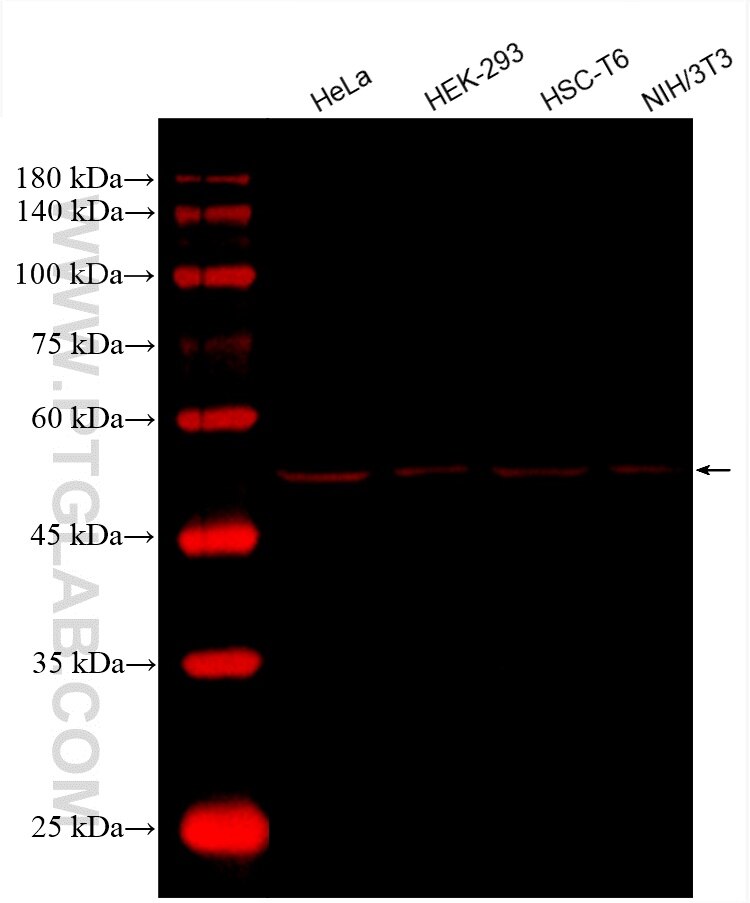
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, HEK-293 cells, HSC-T6 cells, NIH/3T3 cells |
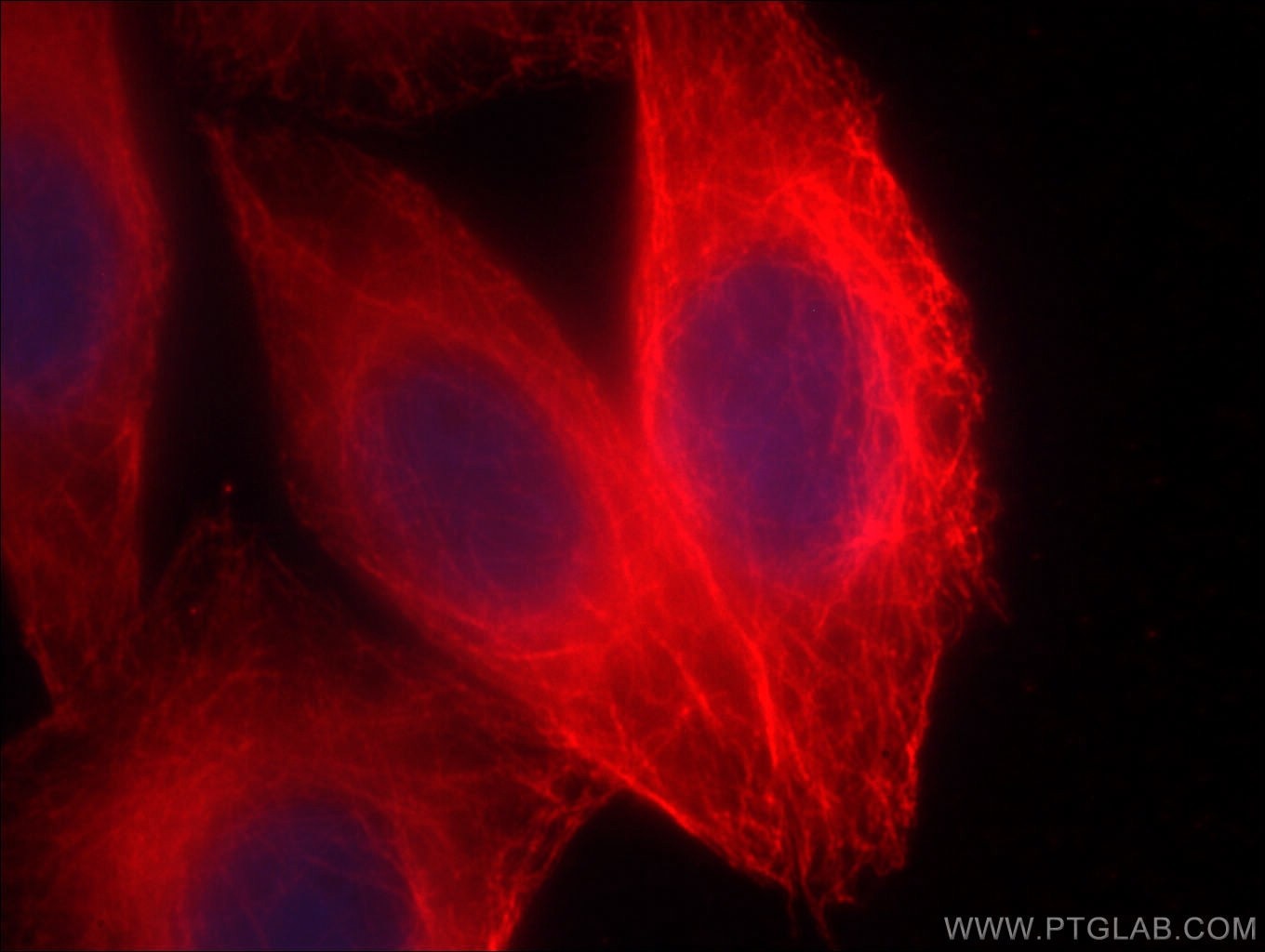
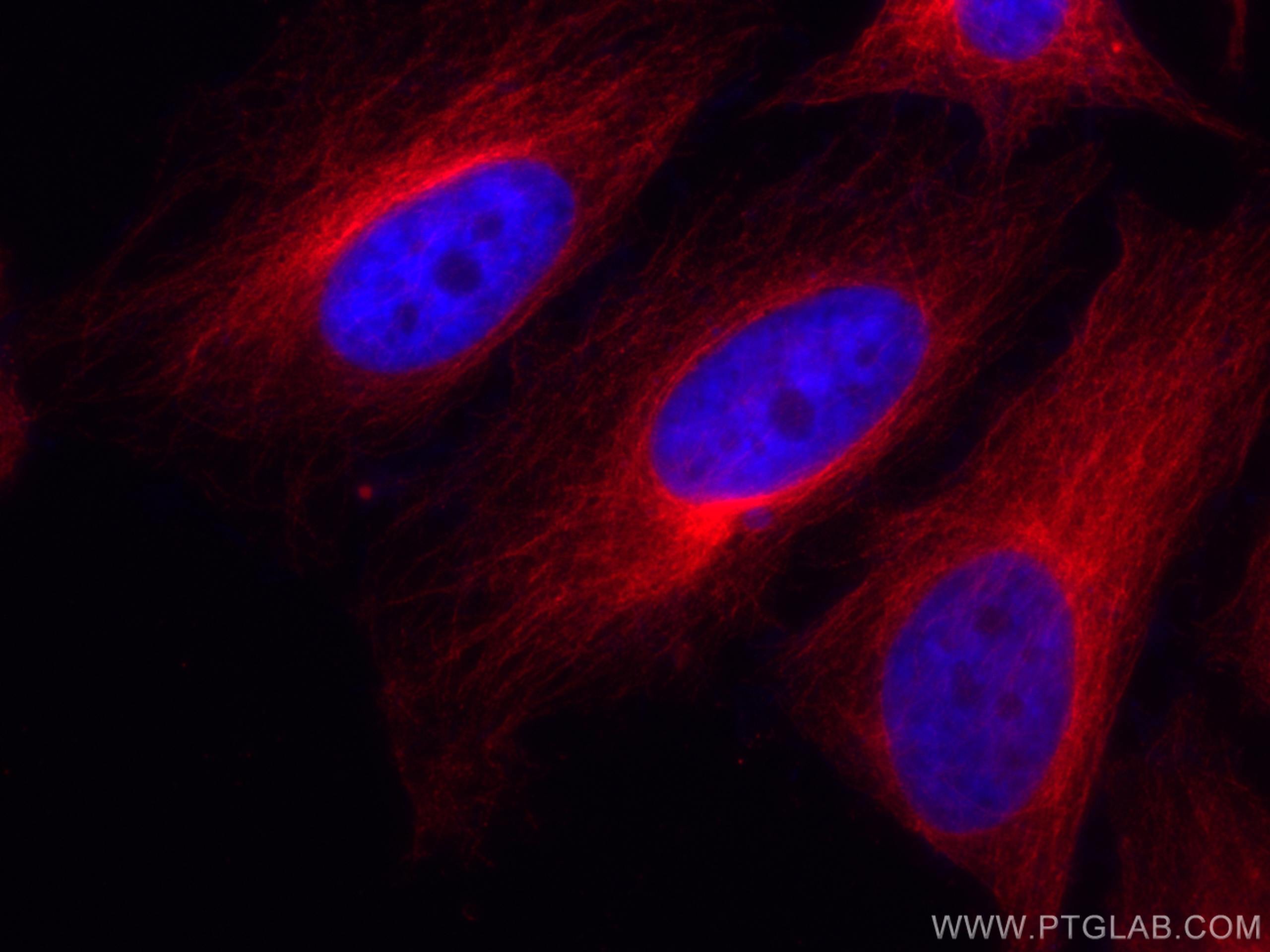
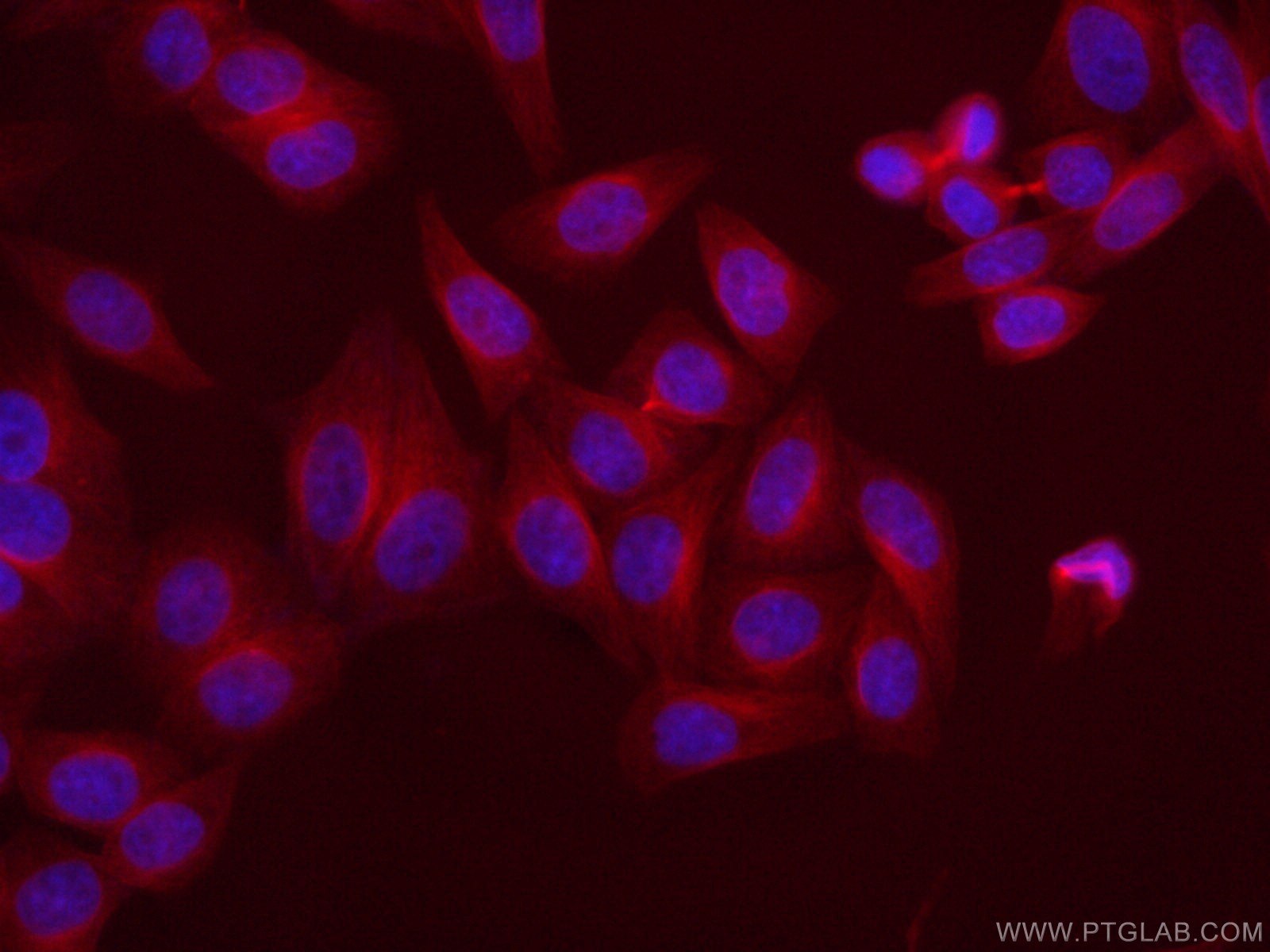
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells, HeLa cells |
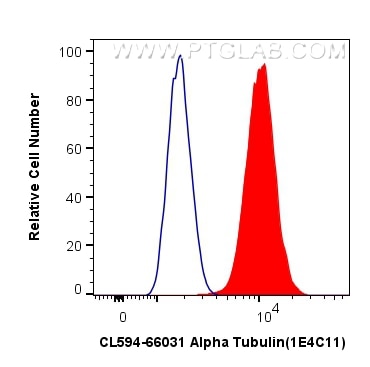
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:300-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.80 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| IF | See 5 publications below |
Product Information
CL594-66031 targets Alpha Tubulin in WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, canine samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, canine |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag18034 Product name: Recombinant human Tubulin-Alpha protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-451 aa of BC009314 Sequence: MRECISIHVGQAGVQIGNACWELYCLEHGIQPDGQMPSDKTIGGGDDSFNTFFSETGAGKHVPRAVFVDLEPTVIDEVRTGTYRQLFHPEQLITGKEDAANNYARGHYTIGKEIIDLVLDRIRKLADQCTGLQGFLVFHSFGGGTGSGFTSLLMERLSVDYGKKSKLEFSIYPAPQVSTAVVEPYNSILTTHTTLEHSDCAFMVDNEAIYDICRRNLDIERPTYTNLNRLISQIVSSITASLRFDGALNVDLTEFQTNLVPYPRIHFPLATYAPVISAEKAYHEQLSVAEITNACFEPANQMVKCDPRHGKYMACCLLYRGDVVPKDVNAAIATIKTKRSIQFVDWCPTGFKVGINYQPPTVVPGGDLAKVQRAVCMLSNTTAIAEAWARLDHKFDLMYAKRAFVHWYVGEGMEEGEFSEAREDMAALEKDYEEVGVDSVEGEGEEEGEEY Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | tubulin, alpha 1b |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 50 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC009314 |
| Gene Symbol | Alpha Tubulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10376 |
| RRID | AB_2883483 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| Excitation Laser | Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm) |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P68363 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
What is the function of alpha tubulin?
Alpha-tubulin belongs to a large superfamily of tubulin proteins. There are a number of different subtypes that have a molecular weight of ~50kDa and are able to bind to beta-tubulin, forming a heterodimer that polymerises to microtubules as part of the cytoskeleton. These maintain cell structure, provide platforms for intracellular transport and are also involved in cell division.
Where is alpha-tubulin expressed?
Alpha tubulin is highly conserved and is present in nearly all eukaryotic cells as one of the building blocks of microtubules. The ubiquitous nature of this protein has led to its common use as a control protein for many tissue types as well as highlighting the structure of the cytoskeleton.
What are the post-translational modifications of alpha tubulin?
The function and properties of microtubules are drastically affected by the post-translational modifications undergone by tubulin, which may occur to the tubulin dimer directly or to the polymerised mictotubule. For example, the first modification to be identified was detyrosination1, as most alpha-tubulins have a tyrosine at their terminus. This process affects microtubules more than dimers and leads to patches of detyronisation along the structure, regulating protein interactions and allowing subcellular compartments to be defined.2,3 Polyglutamylation also occurs on several sites within the carboxy-terminal tails. However, to date, the most-studied alpha tubulin modification is related to acetylation of lysine 40 (K40).
1. Gundersen, G. G., Khawaja, S. & Bulinski, J. C. Postpolymerization detyrosination of alpha-tubulin: a mechanism for subcellular differentiation of microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 105, 251-64 (1987).
2. Galjart, N. Plus-End-Tracking Proteins and Their Interactions at Microtubule Ends. Curr. Biol. 20, R528-R537 (2010).
3. Jiang, K. & Akhmanova, A. Microtubule tip-interacting proteins: a view from both ends. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23, 94-101 (2011).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for CL594 Alpha Tubulin antibody CL594-66031 | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CL594 Alpha Tubulin antibody CL594-66031 | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for CL594 Alpha Tubulin antibody CL594-66031 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Exp Mol Med Identification of novel rheumatoid arthritis-associated MiRNA-204-5p from plasma exosomes. | ||
Biology (Basel) Effects of IGF-1 on the Three-Dimensional Culture of Ovarian Preantral Follicles and Superovulation Rates in Mice. | ||
Cell Death Discov KIFC1 depends on TRIM37-mediated ubiquitination of PLK4 to promote centrosome amplification in endometrial cancer | ||
bioRxiv A Cell Type-Specific Role for Tubb6 in Ciliogenesis of Xenopus Epidermal Multiciliated Cells | ||
Int J Mol Sci Overexpression of Tfap2a in Mouse Oocytes Impaired Spindle and Chromosome Organization |