Tested Applications
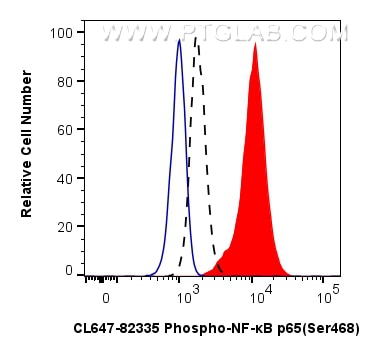
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | Calyculin A treated NIH/3T3 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.25 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL647-82335 targets Phospho-NF-κB p65 (Ser468) in FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 65 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 75 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC011603 |
| Gene Symbol | NF-κB p65 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5970 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 647 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 654 nm / 674 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q04206 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Nuclear factor kB (NF-kB) is a collective term for a small family of dimeric transcription factors [comprising p65 (RelA) and RelB, c-Rel, p50/p105 (NF-κB1), and p52/p100 (NF-κB2)]. All NF-κB proteins share a Rel homology domain (RHD), which is responsible for DNA binding and dimerization. Only p65, RelB, and c-Rel contain potent transactivation domains within sequences from the C-terminal to the RHD. Exterior signals lead to the phosphorylation and degradation of the inhibitory complex IκB, which is modulated by the IκB kinase (IKK), and its degradation allows for the release of the typical NF-κB heterodimer, p65/p50, to translocate into the nucleus. NF-κB binds to its cognate DNA elements and can transcriptionally activate different target genes among which 200-500 genes have been implicated in cell survival/apoptosis, cell growth, immune response, and inflammation.