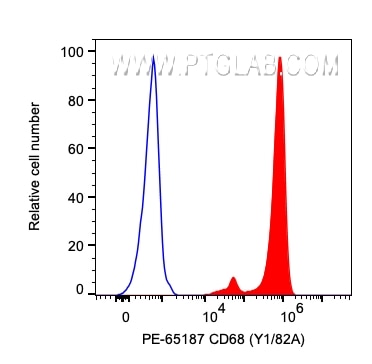
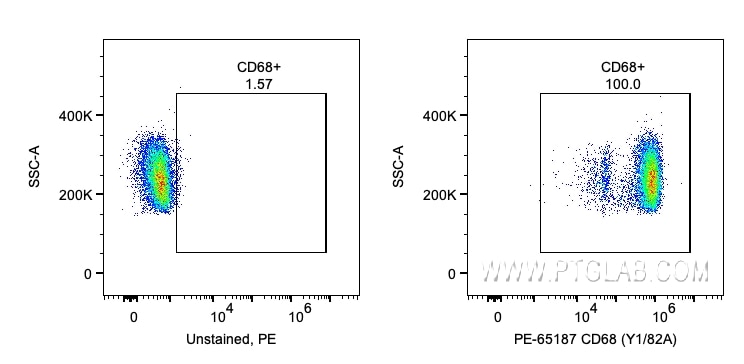
Tested Applications
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | human PBMCs |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 5 ul per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| IF | See 2 publications below |
| FC | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
PE-65187 targets CD68 in IF, FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b, kappa |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Lysosomal contents of lung macrophages Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | CD68 molecule |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 37 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC015557 |
| Gene Symbol | CD68 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 968 |
| RRID | AB_2883957 |
| Conjugate | PE Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 496 nm, 565 nm / 578 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | The purified antibody is conjugated with R-phycoerythrin (PE) under optimum conditions. The conjugate is purified by size-exclusion chromatography. |
| UNIPROT ID | P34810 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide and 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for PE CD68 antibody PE-65187 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cancer Sci Homeobox A7 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through C-C motif chemokine ligand 2-mediated tumor-associated macrophage recruitment | ||
Sci Adv Atf3-mediated metabolic reprogramming in hepatic macrophage orchestrates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis | ||
Int Immunopharmacol OTUD4-mediated inhibition of YAP1 signaling pathway in ovarian cancer: Implications for macrophage polarization and recruitment | ||
Am J Cancer Res FTO-mediated m6A modification of QPCT promotes tumorigenesis in lung adenocarcinoma by inducing macrophage chemotaxis and M2 polarization |