- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-PPARA
PPARA Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris et plus (5)
Applications
WB, IP, IF, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
179
N° de cat : 15540-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
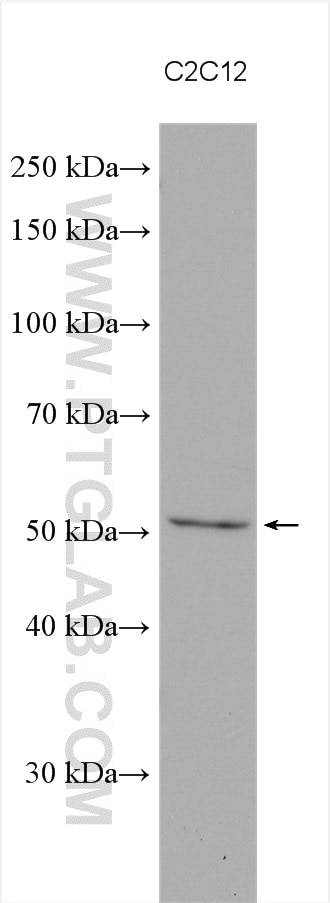
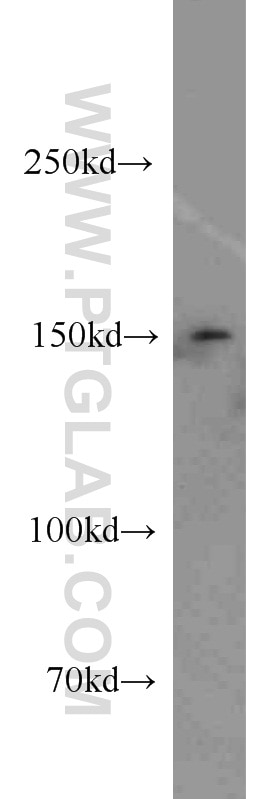
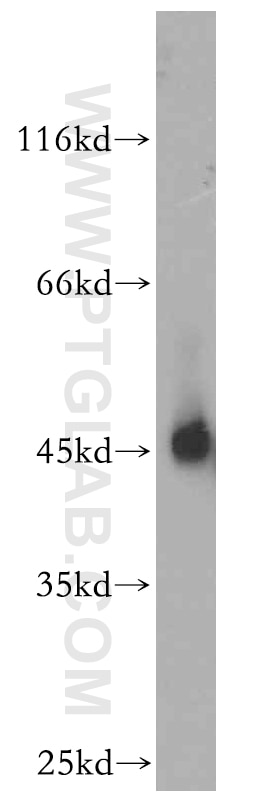
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules C2C12, |
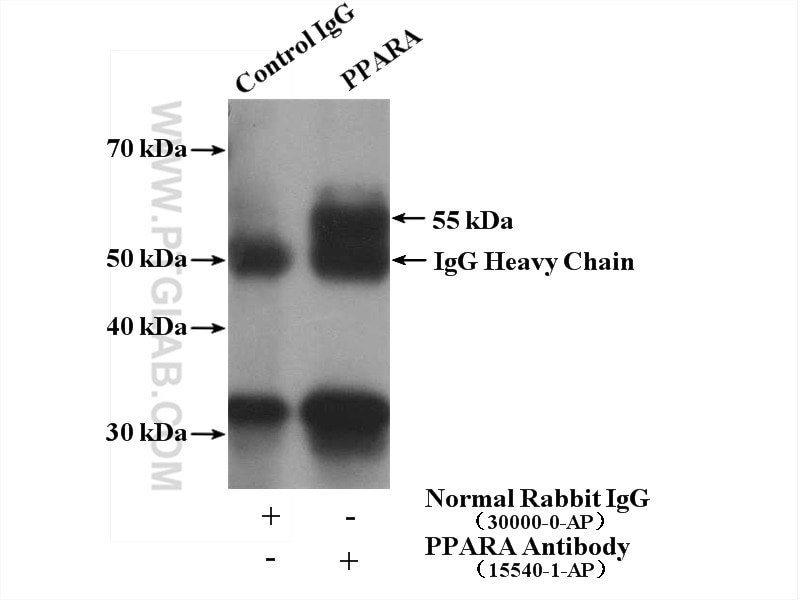
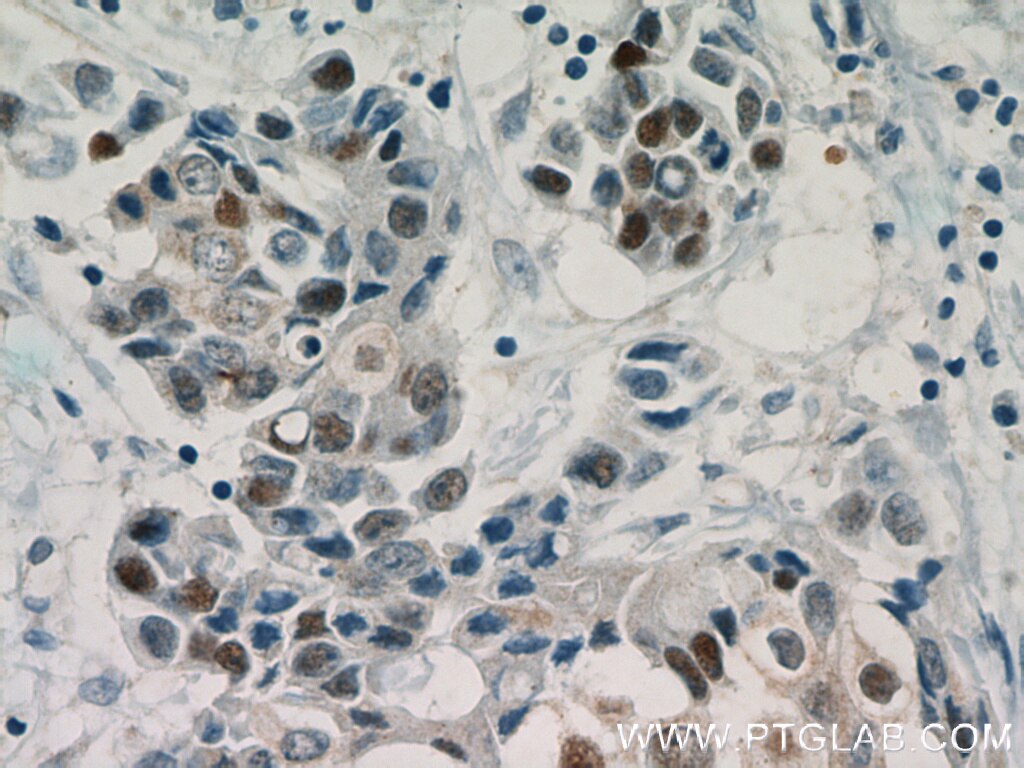
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules U-937, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 13 publications below |
| WB | See 169 publications below |
| IF | See 13 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
15540-1-AP cible PPARA dans les applications de WB, IP, IF, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, bovin, Chèvre, Humain, porc, poulet, souris, Hamster |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | PPARA Protéine recombinante Ag7896 |
| Nom complet | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 52 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 52 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC000052 |
| Symbole du gène | PPARA |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 5465 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARA) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that belongs to the PPAR nuclear receptor superfamily. PPARA is essential in the modulation of lipid transport and metabolism, mainly through activating mitochondrial and peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation pathways. In addition, PPARA seems to decrease inflammation mainly through direct interaction with NF-κB, causing inhibition of its signaling pathway or reducing the activated levels of NF-κB and subsequent inflammation. Furthermore, PPARA was implicated in the attenuation of oxidative stress in alcoholic liver disease when treated with polyenephosphatidylcholine through downregulation of ROS-generating enzymes such as ethanol-inducible cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1), acyl-CoA oxidase, and NADPH oxidase. PPARA exists two isoforms and molecular weight of PPARA isoforms are 52 kDa and 22 kDa. The ability of a retinoid X receptor (RXR) to heterodimerize with many nuclear receptors, including LXR, PPAR, NGF1B and RAR, underscores its pivotal role within the nuclear receptor superfamily. Among these heterodimers, PPAR:RXR is considered an important signalling mediator of both PPAR ligands, such as fatty acids, and 9-cis retinoic acid (9-cis RA), an RXR ligand. (PMID: 15103326 ). PPARA can form Heterodimer with RXRA and molecular weight of Heterodimer is about 110 kDa.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PPARA antibody 15540-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for PPARA antibody 15540-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun Hyodeoxycholic acid ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting RAN-mediated PPARα nucleus-cytoplasm shuttling | ||
Sci Adv Small-molecule inhibitor targeting orphan nuclear receptor COUP-TFII for prostate cancer treatment. | ||
Hepatology The histone methyltransferase Suv39h2 contributes to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. | ||
Nat Commun N1-methyladenosine methylation in tRNA drives liver tumourigenesis by regulating cholesterol metabolism. | ||