Anticorps Monoclonal anti-NCAM1/CD56
NCAM1/CD56 Monoclonal Antibody for IF, IHC, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, porc, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1E8C9
N° de cat : 60238-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
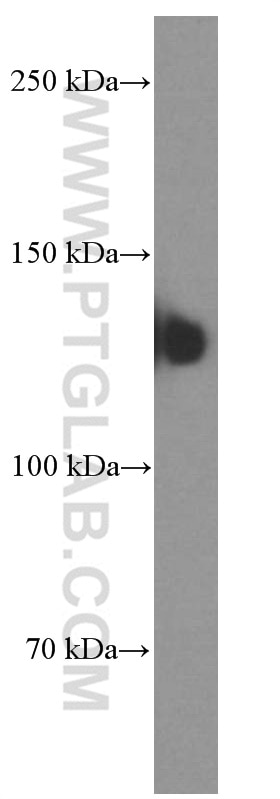
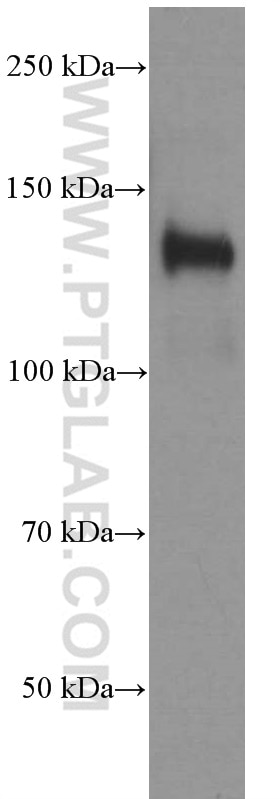
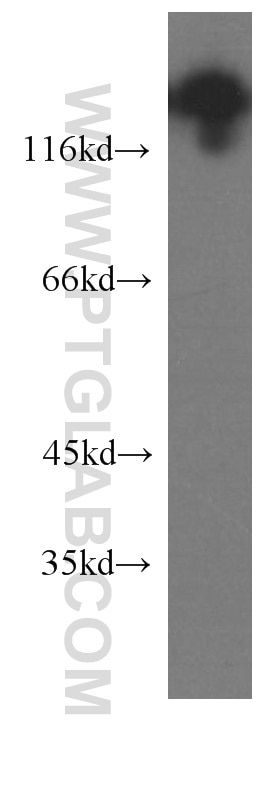
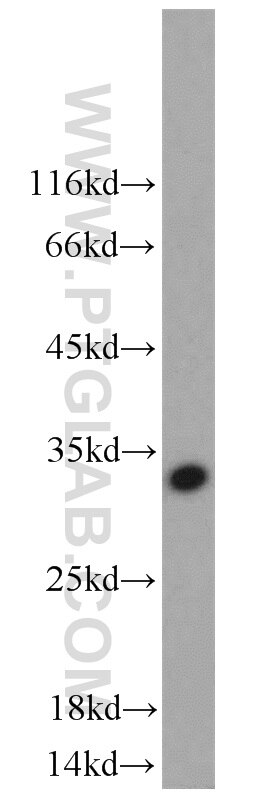
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu cérébral humain fœtal, cellules C6, tissu cérébral de porc, tissu cérébral humain |
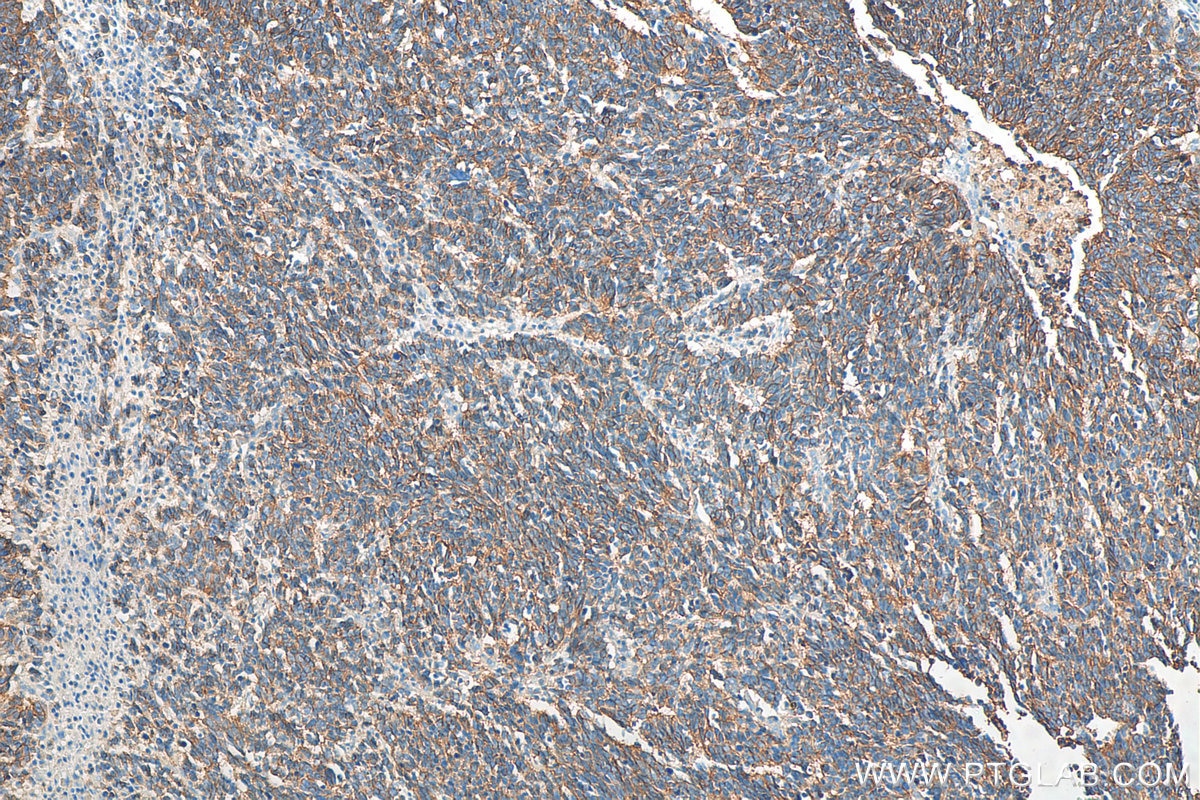
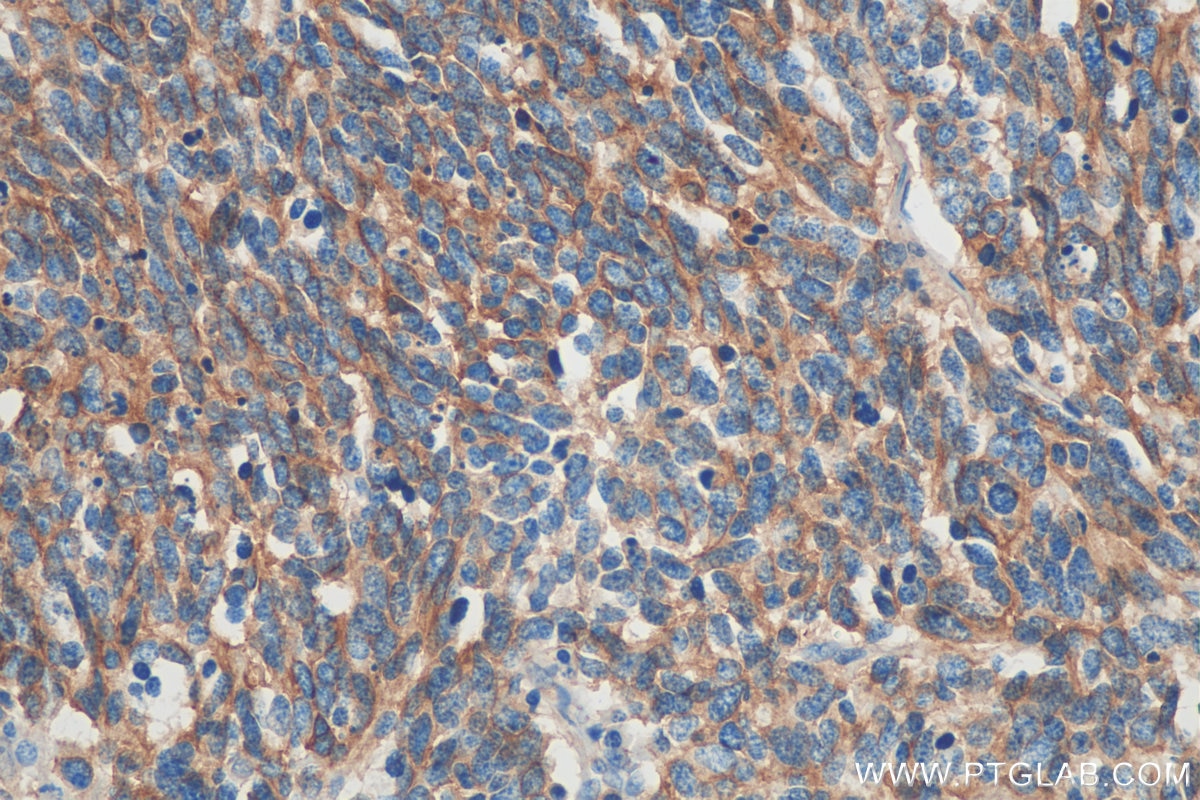
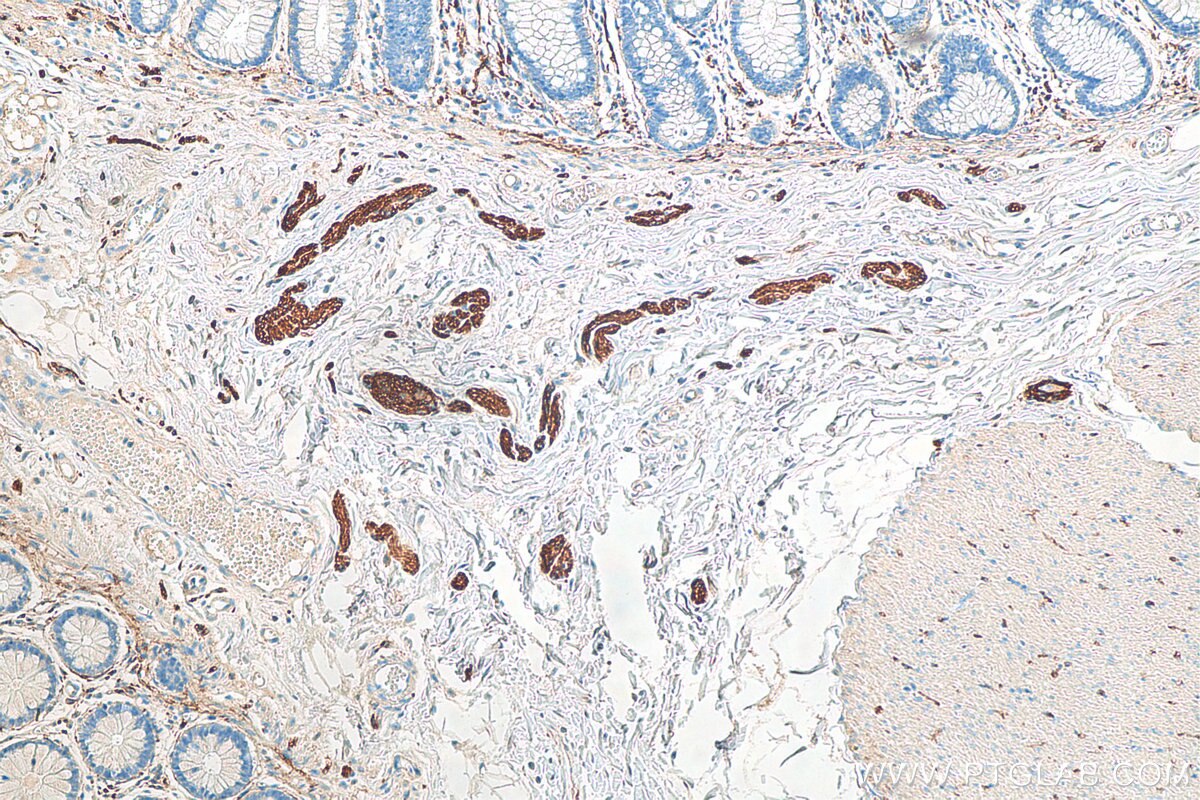
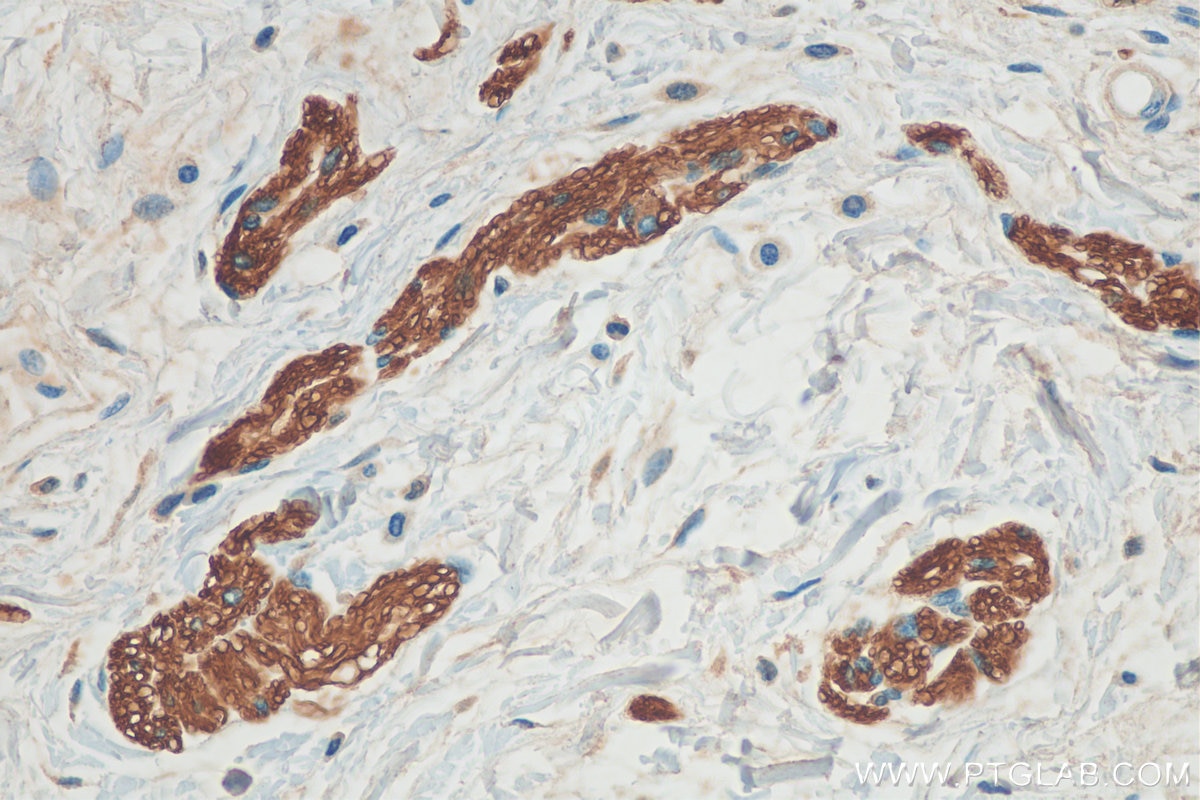
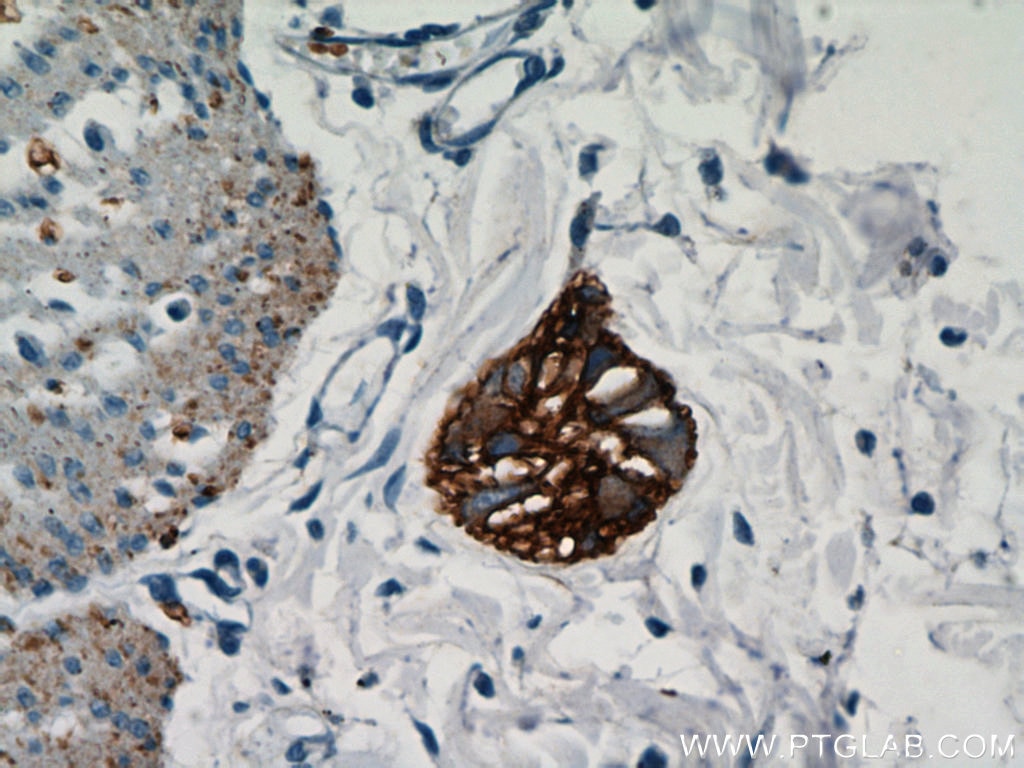
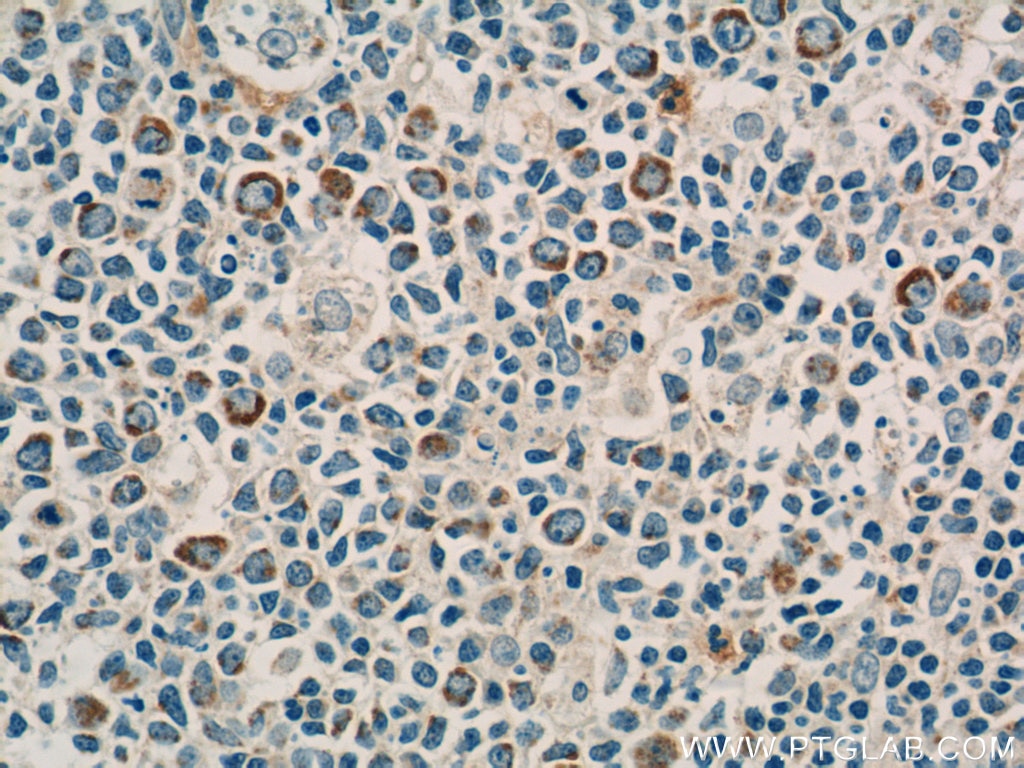
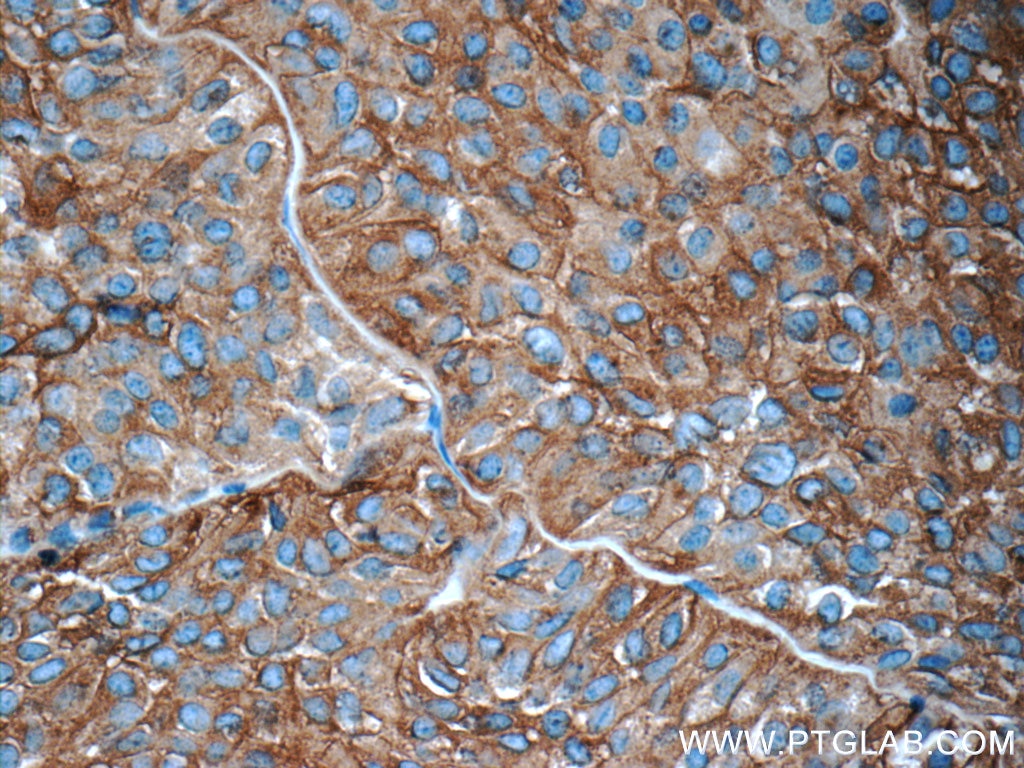
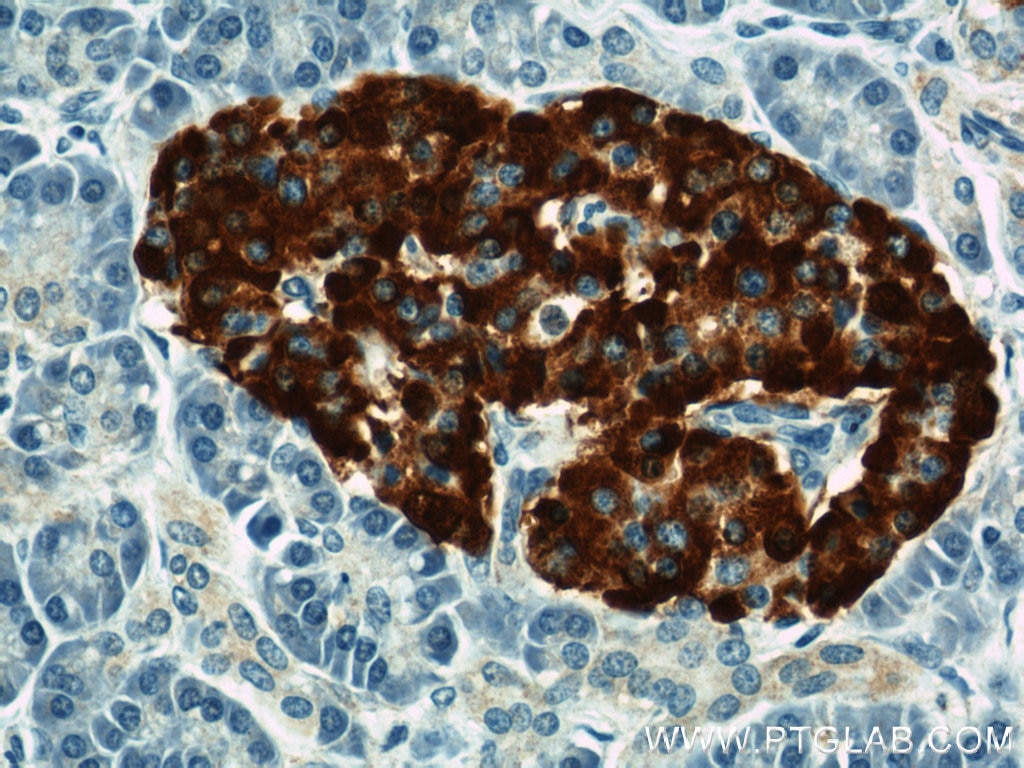
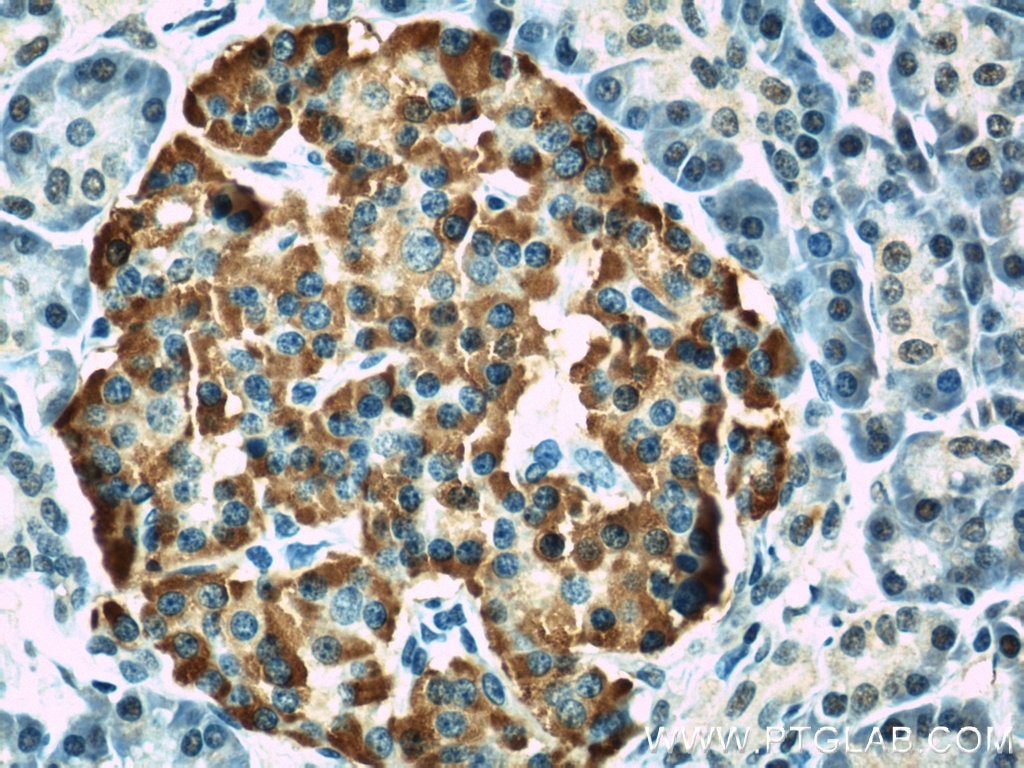
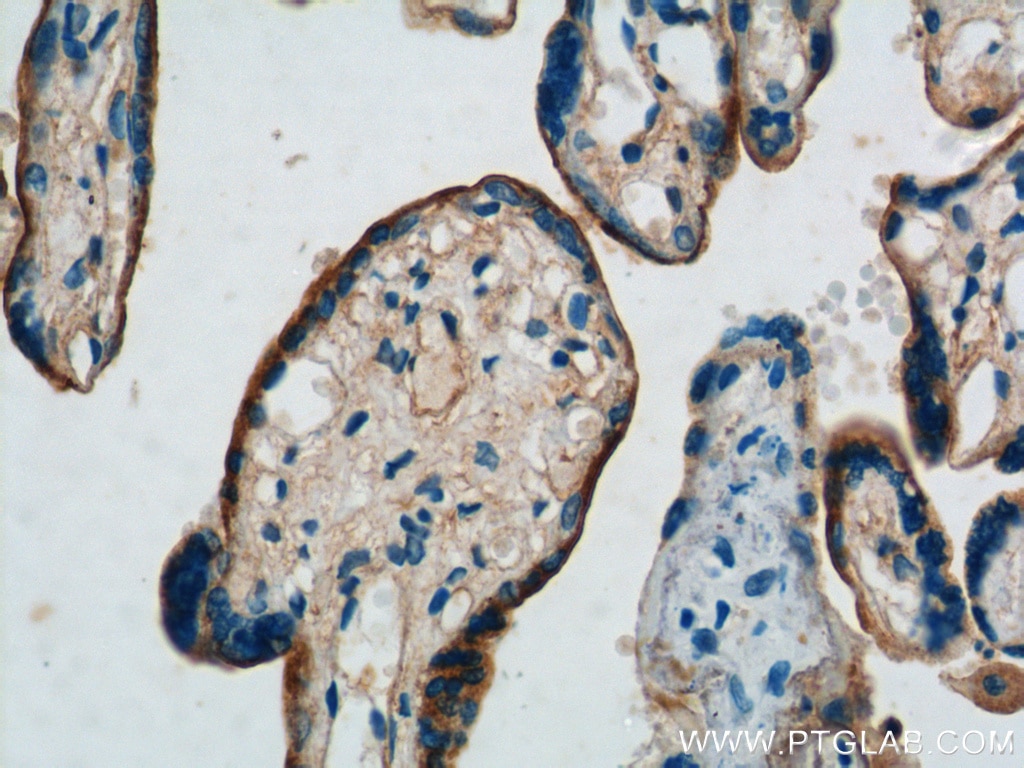
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du poumon humain, tissu de côlon humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
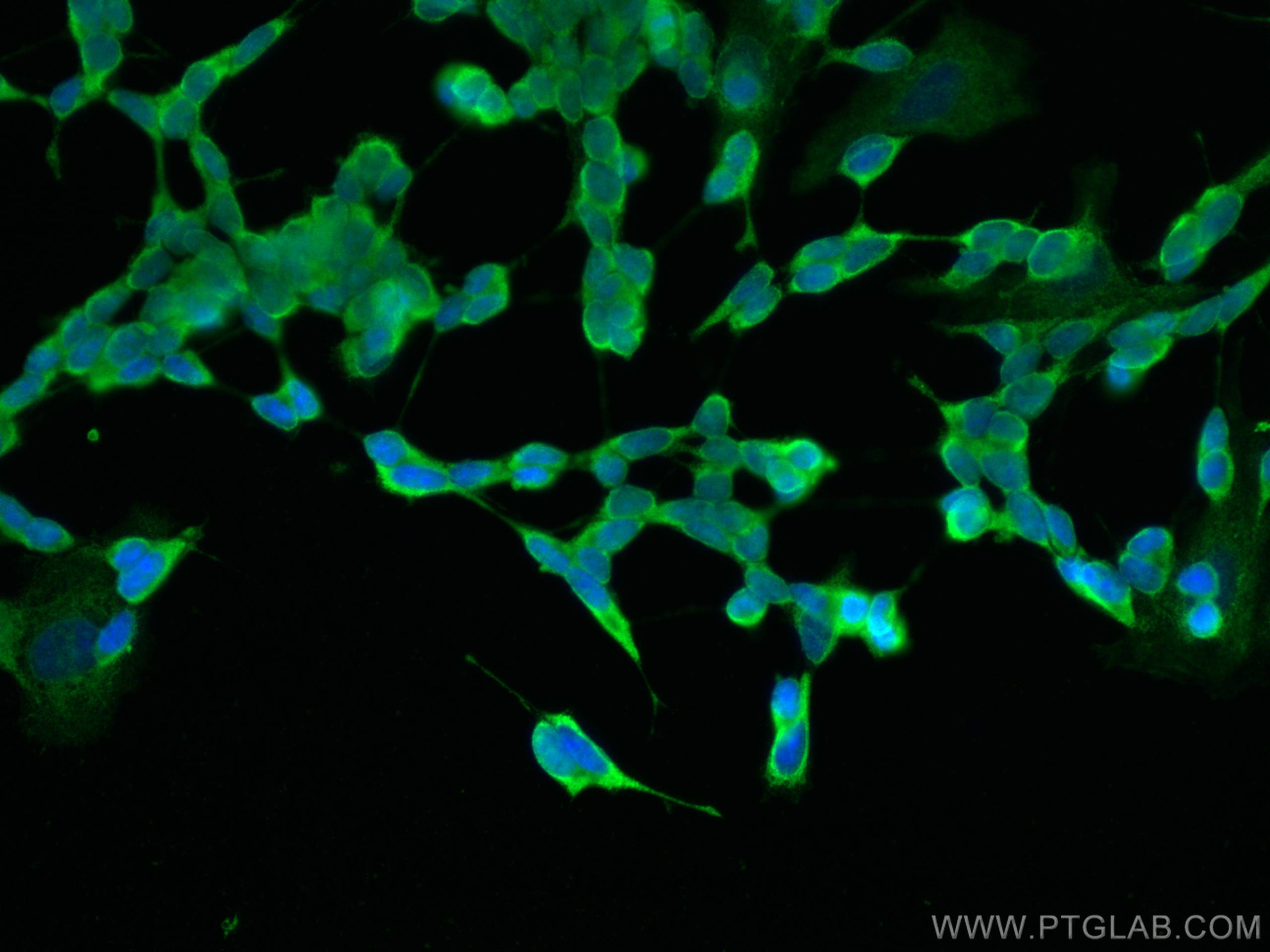
| Résultats positifs en IF | cellules SH-SY5Y, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:2000-1:8000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | IF : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
60238-1-Ig cible NCAM1/CD56 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, porc, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, porc, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | NCAM1/CD56 Protéine recombinante Ag5732 |
| Nom complet | neural cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 95 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 140 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC047244 |
| Symbole du gène | NCAM1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4684 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, also known as CD56) is a cell adhesion glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a multifunction protein involved in synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neurogenesis. NCAM1 is expressed on human neurons, glial cells, skeletal muscle cells, NK cells and a subset of T cells, and the expression is observed in a wide variety of human tumors, including myeloma, myeloid leukemia, neuroendocrine tumors, Wilms' tumor, neuroblastoma, and NK/T cell lymphomas. Three major isoforms of NCAM1, with molecular masses of 120, 140, and 180 kDa, are generated by alternative splicing of mRNA (PMID: 9696812). The glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored NCAM120 and the transmembrane NCAM140 and NCAM180 consist of five Ig-like domains and two fibronection-type III repeats (FNIII). All three forms can be posttranslationally modified by addition of polysialic acid (PSA) (PMID: 14976519). Several other isofroms have also been described (PMID: 1856291).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NCAM1/CD56 antibody 60238-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for NCAM1/CD56 antibody 60238-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for NCAM1/CD56 antibody 60238-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Small Nanobody-Engineered Natural Killer Cell Conjugates for Solid Tumor Adoptive Immunotherapy | ||
J Transl Med Systematic analysis of various RNA transcripts and construction of biological regulatory networks at the post-transcriptional level for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | ||
Stem Cells Dev Effect of the Soluble Factors Released by Dental Apical Papilla-Derived Stem Cells on the Osteo/Odontogenic, Angiogenic, and Neurogenic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Cells. | ||
Jpn J Clin Oncol Identification of distinct genomic features reveals frequent somatic AHNAK and PTEN mutations predominantly in primary malignant melanoma presenting in the ureter. | ||
Hepatology Hepatocyte-derived MASP1-enriched small extracellular vesicles activate HSCs to promote liver fibrosis |