- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
AP1,JUN,P39 Polyklonaler Antikörper
AP1,JUN,P39 Polyklonal Antikörper für ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10024-2-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
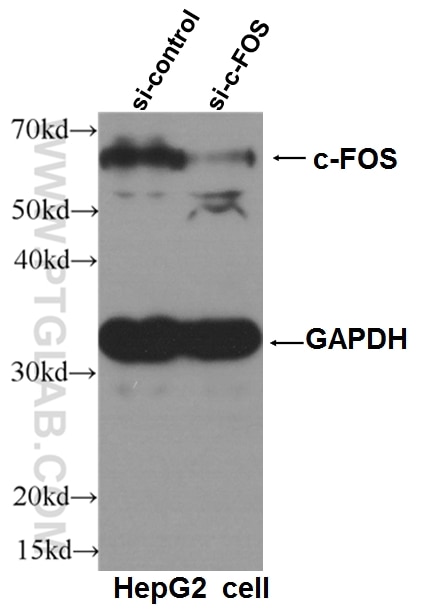
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 31 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
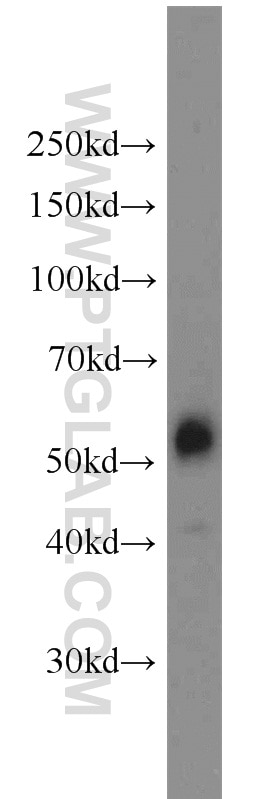
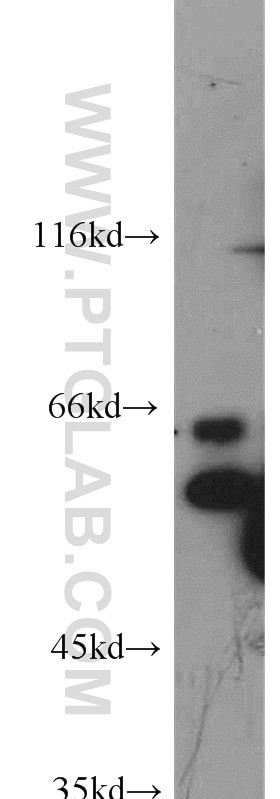
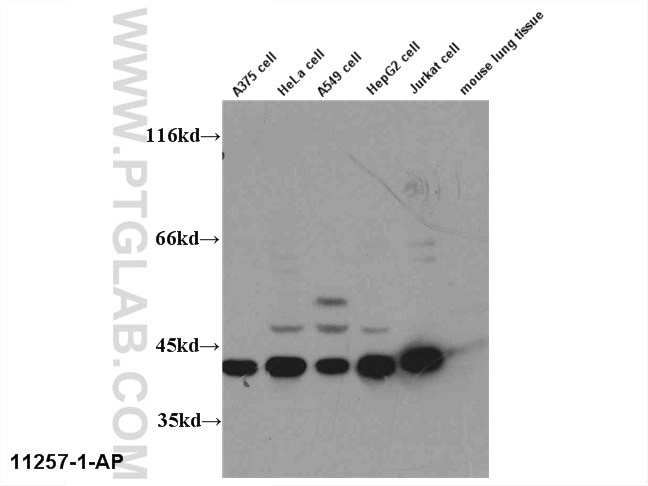
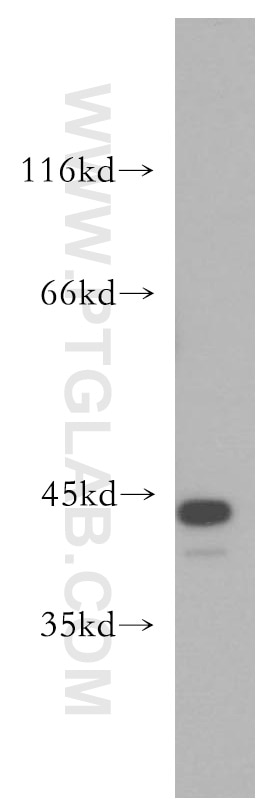
10024-2-AP bindet in WB, IHC, ELISA AP1,JUN,P39 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Rekombinantes Protein |
| Vollständiger Name | jun oncogene |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 331 aa, 36 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 36 kDa, 40-45 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC002646 |
| Gene symbol | JUN |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3725 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
JUN is also named as c-Jun and AP1, belongs to the bZIP family and Jun subfamily. JUN, the most extensively studied protein of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) complex, is involved in numerous cell activities, such as proliferation, apoptosis, survival, tumorigenesis and tissue morphogenesis (PMID: 22180088). JUN is a transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. It promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. JUN is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that acts as homo- or heterodimer, binding to DNA and regulating gene transcription (PMID: 9732876). In additon, extracellular signals can induce post-translational modifications of JUN, resulting in altered transcriptional activity and target gene expression (PMID:8464713). More over, it has uncovered multiple layers of a complex regulatory scheme in which JUN is able to crosstalk, amplify and integrate different signals for tissue development and disease. Jun is predominantly nuclear, ubiquitinated Jun colocalizes with lysosomal proteins (PMID: 15469925). This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against a region of human JUN. Both phosphorylated (p-c-Jun) and unphosphorylated forms of c-Jun, with sizes of 42-45 kDa and 36-39 kDa, respectively are obtain in some experiments (PMID:17210646).
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Death Dis Induction of COX-2-PGE2 synthesis by activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway contributes to neuronal death triggered by TDP-43-depleted microglia. | ||
Cell Death Dis PKCζ phosphorylates TRAF2 to protect against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury. | ||
FASEB J Sepsis reveals compartment-specific responses in intestinal proliferation and apoptosis in transgenic mice whose enterocytes re-enter the cell cycle. | ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res Loss of Nrf1 rather than Nrf2 leads to inflammatory accumulation of lipids and reactive oxygen species in human hepatoma cells, which is alleviated by 2-bromopalmitate | ||
J Exp Clin Cancer Res Matrix stiffness-upregulated LOXL2 promotes fibronectin production, MMP9 and CXCL12 expression and BMDCs recruitment to assist pre-metastatic niche formation. |