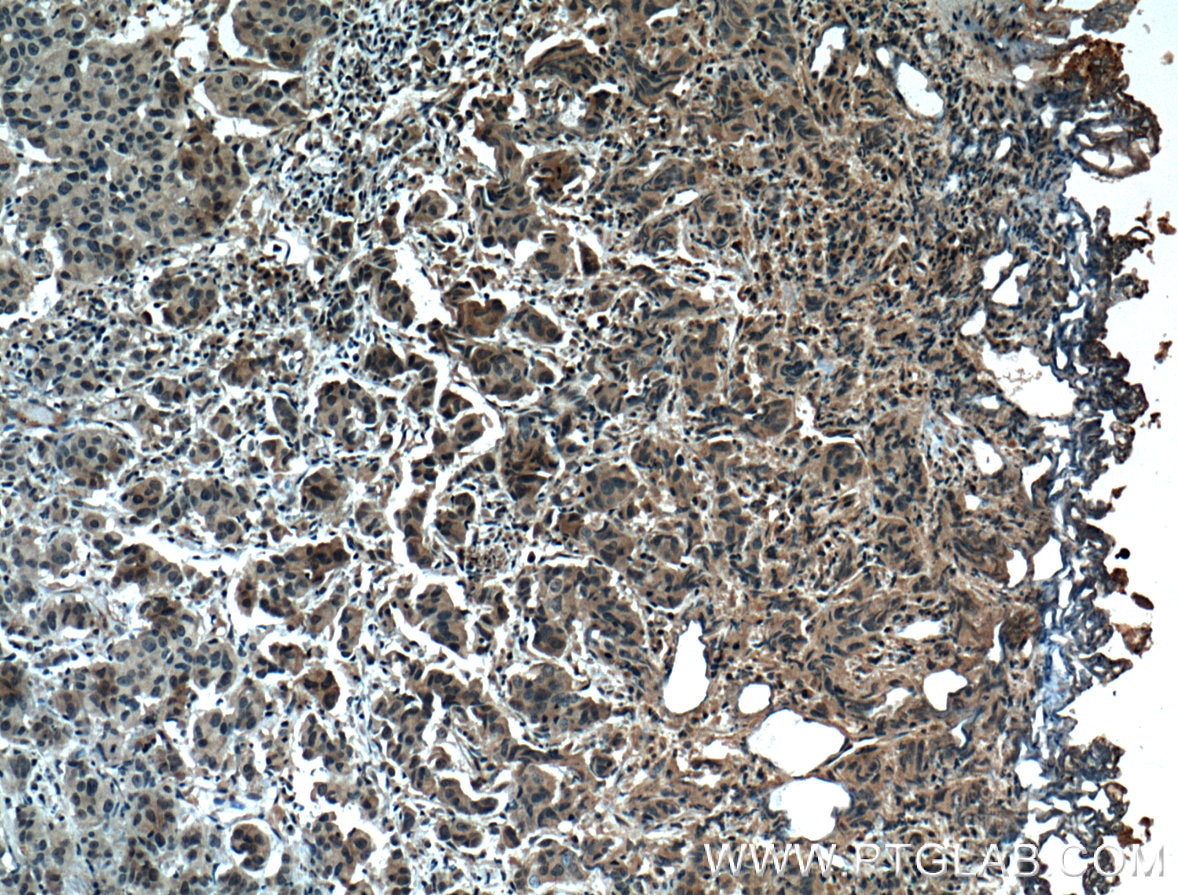
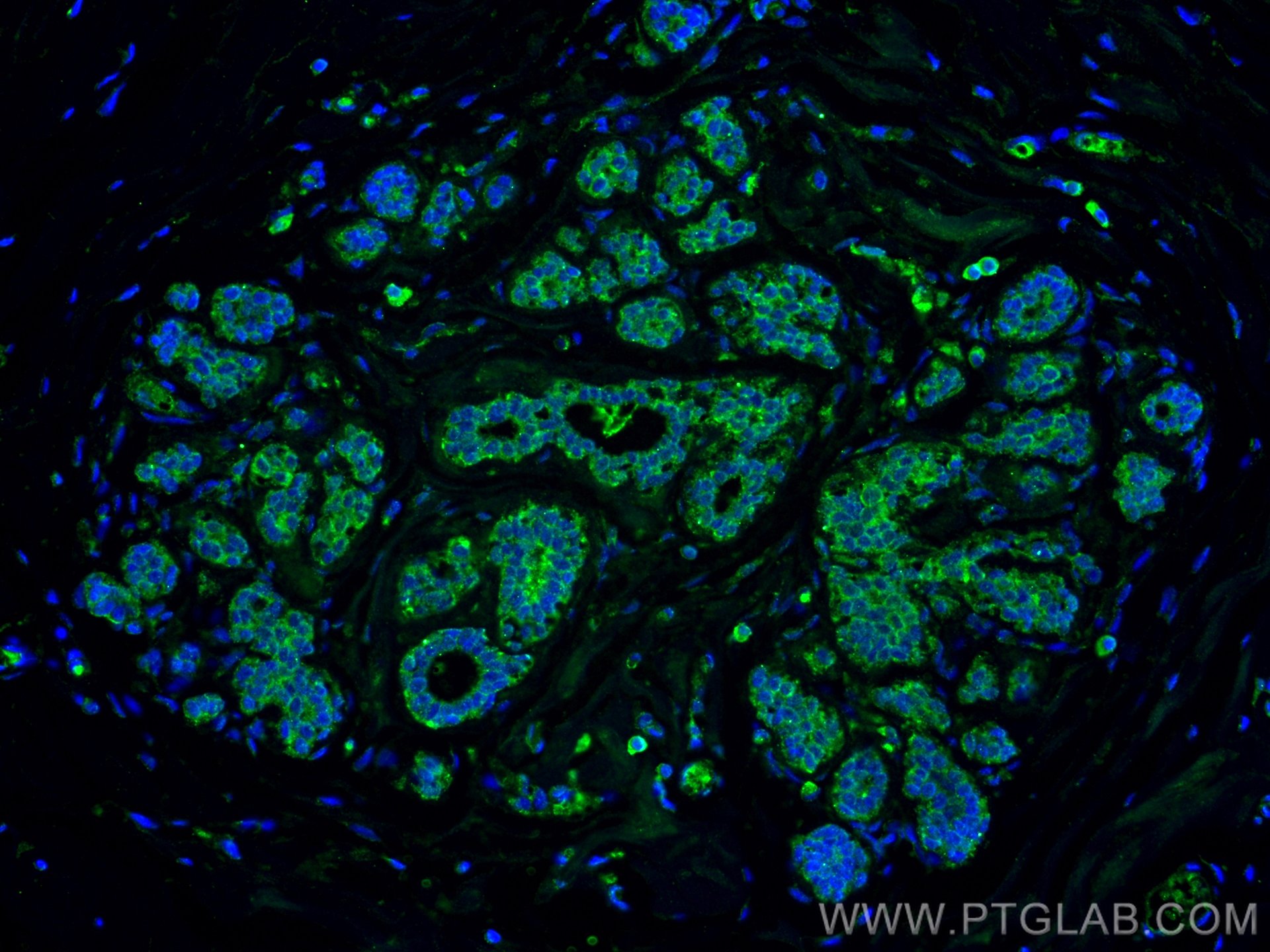
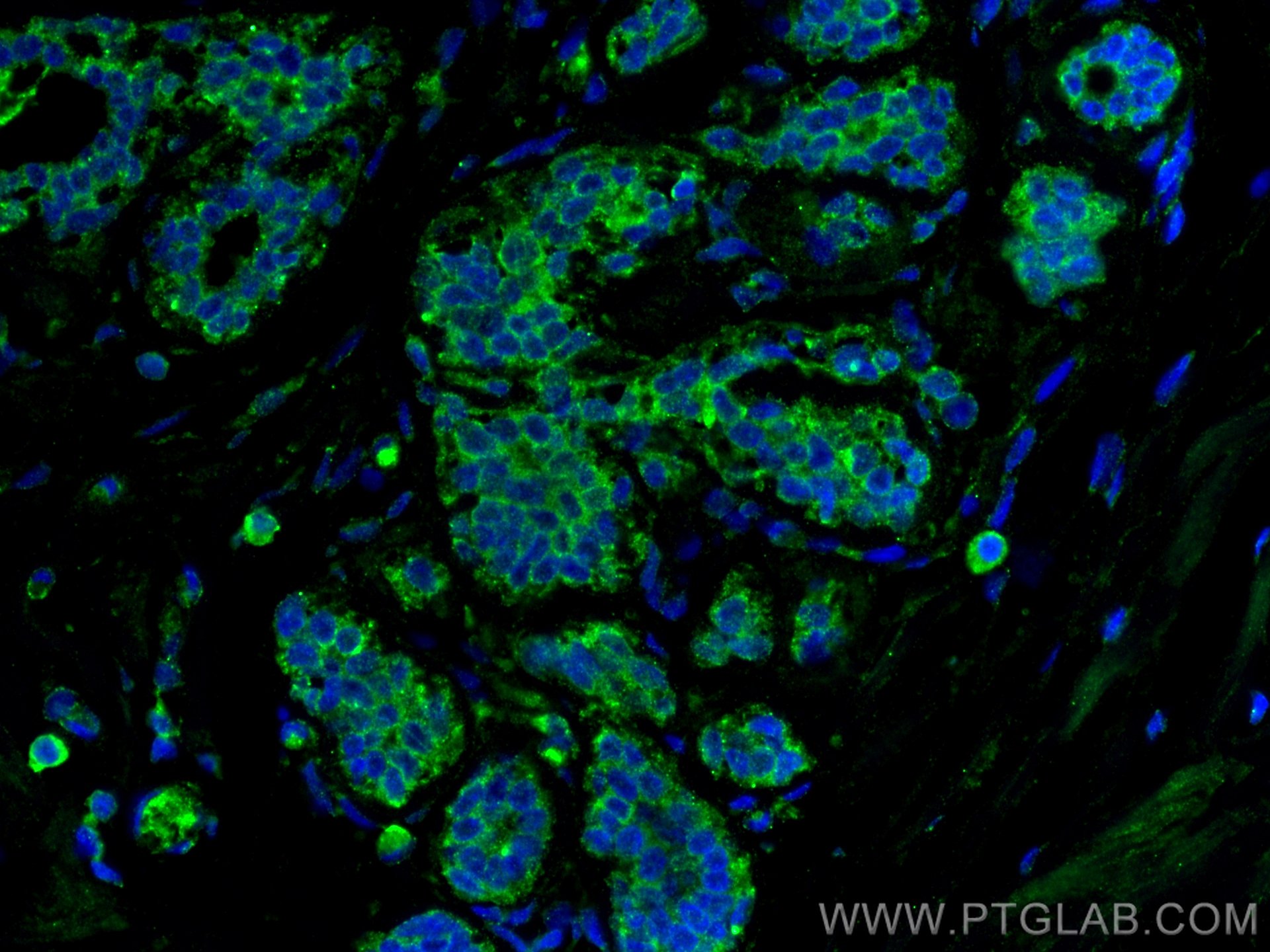
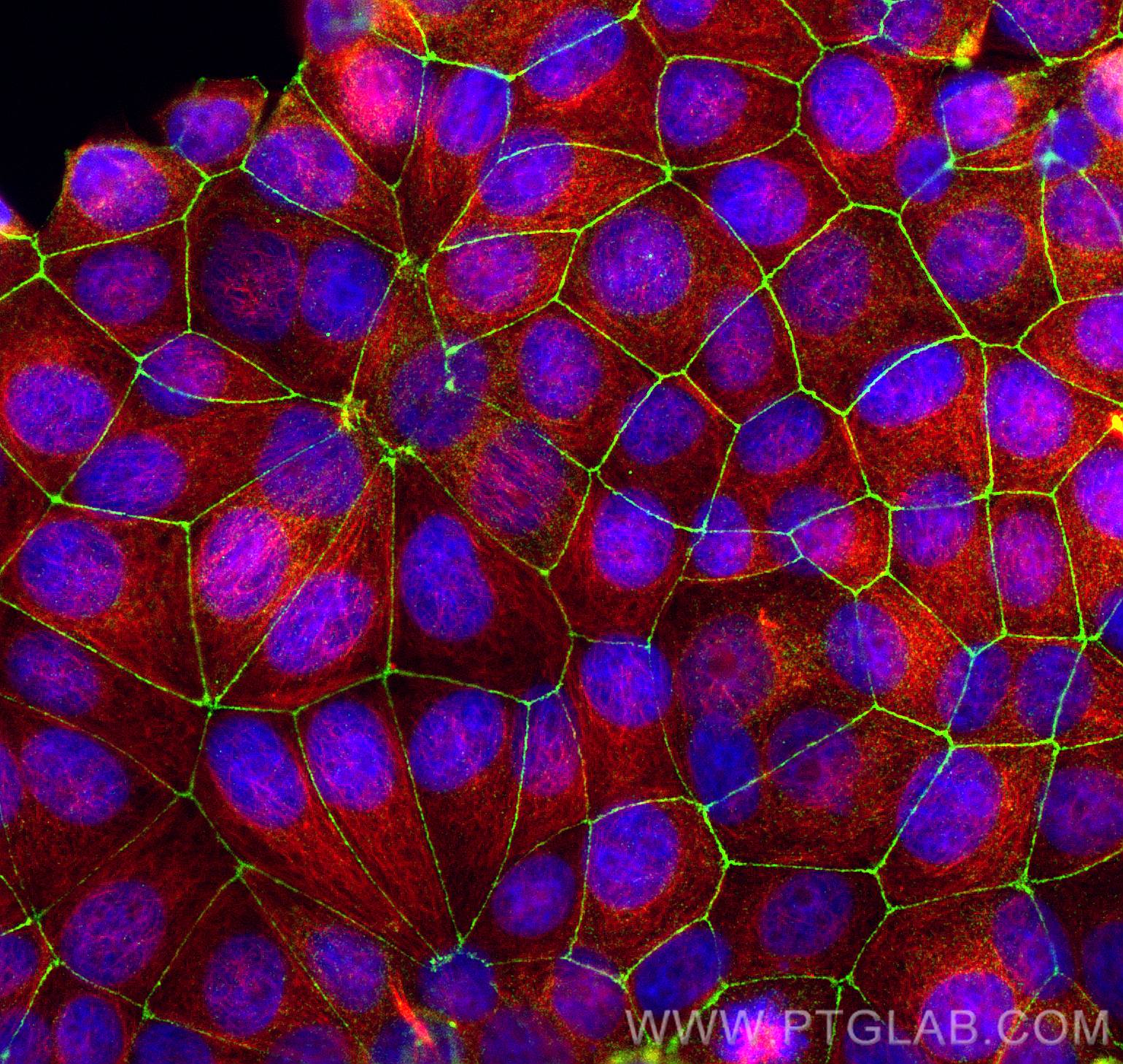
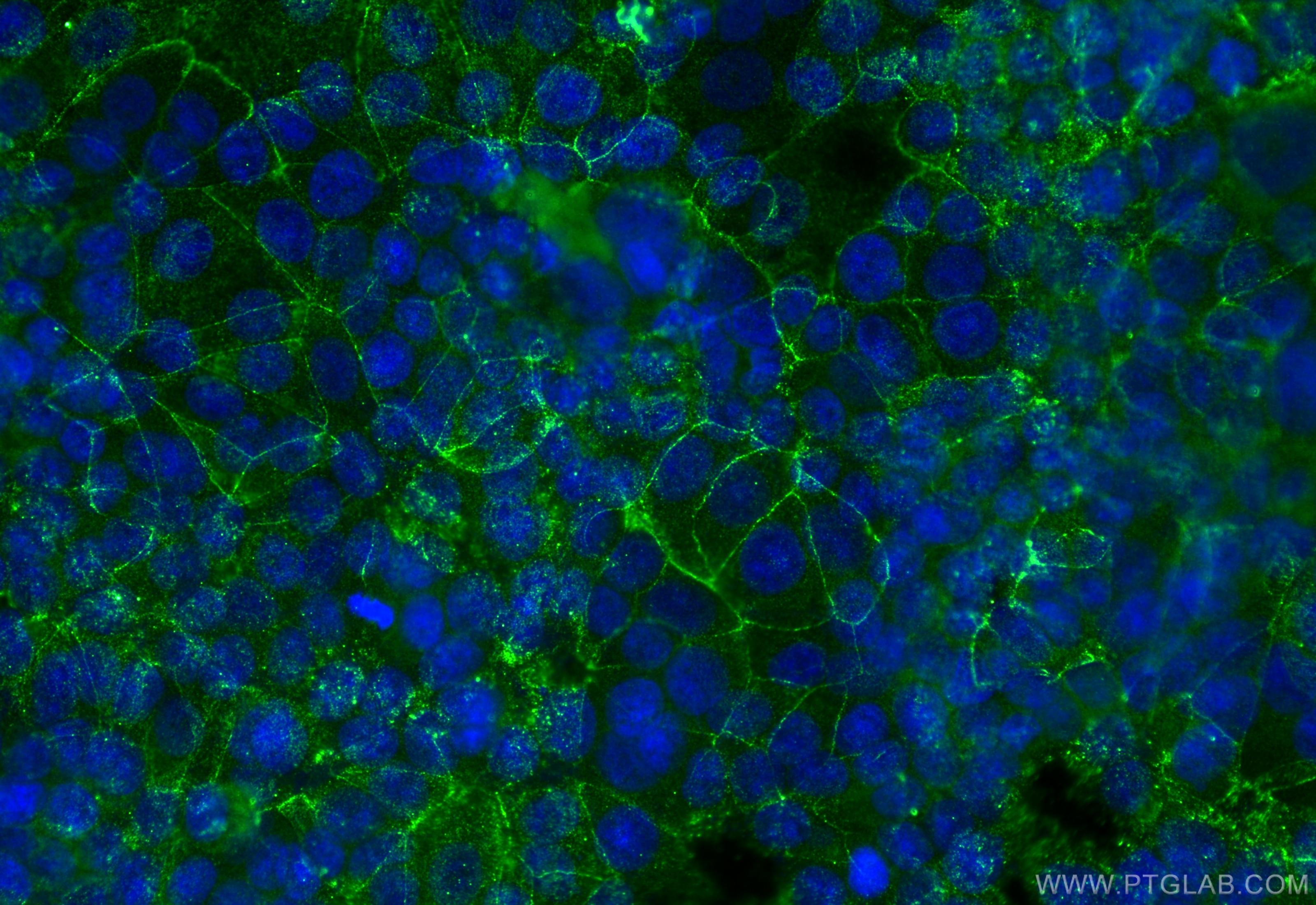
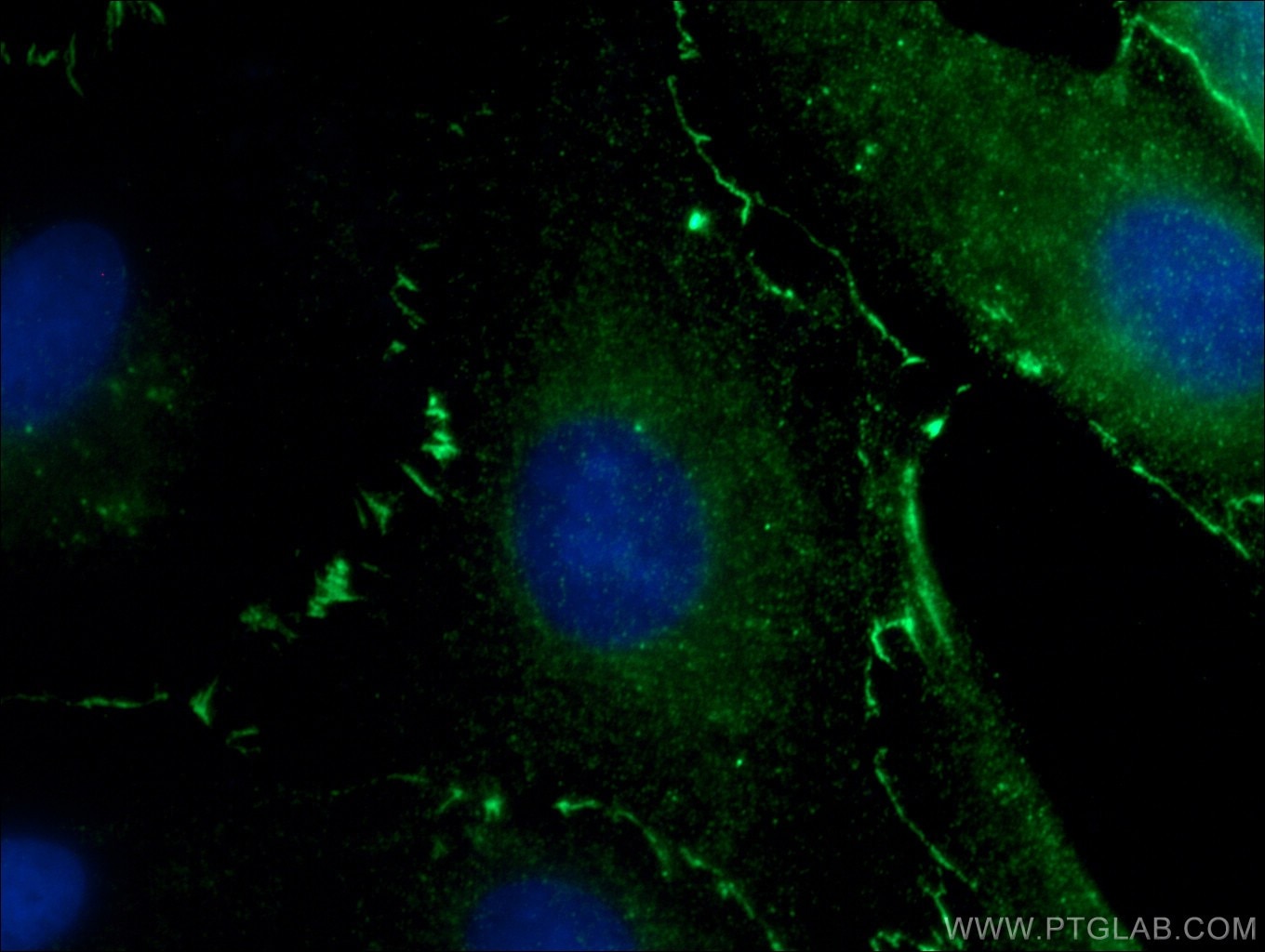
Product Information
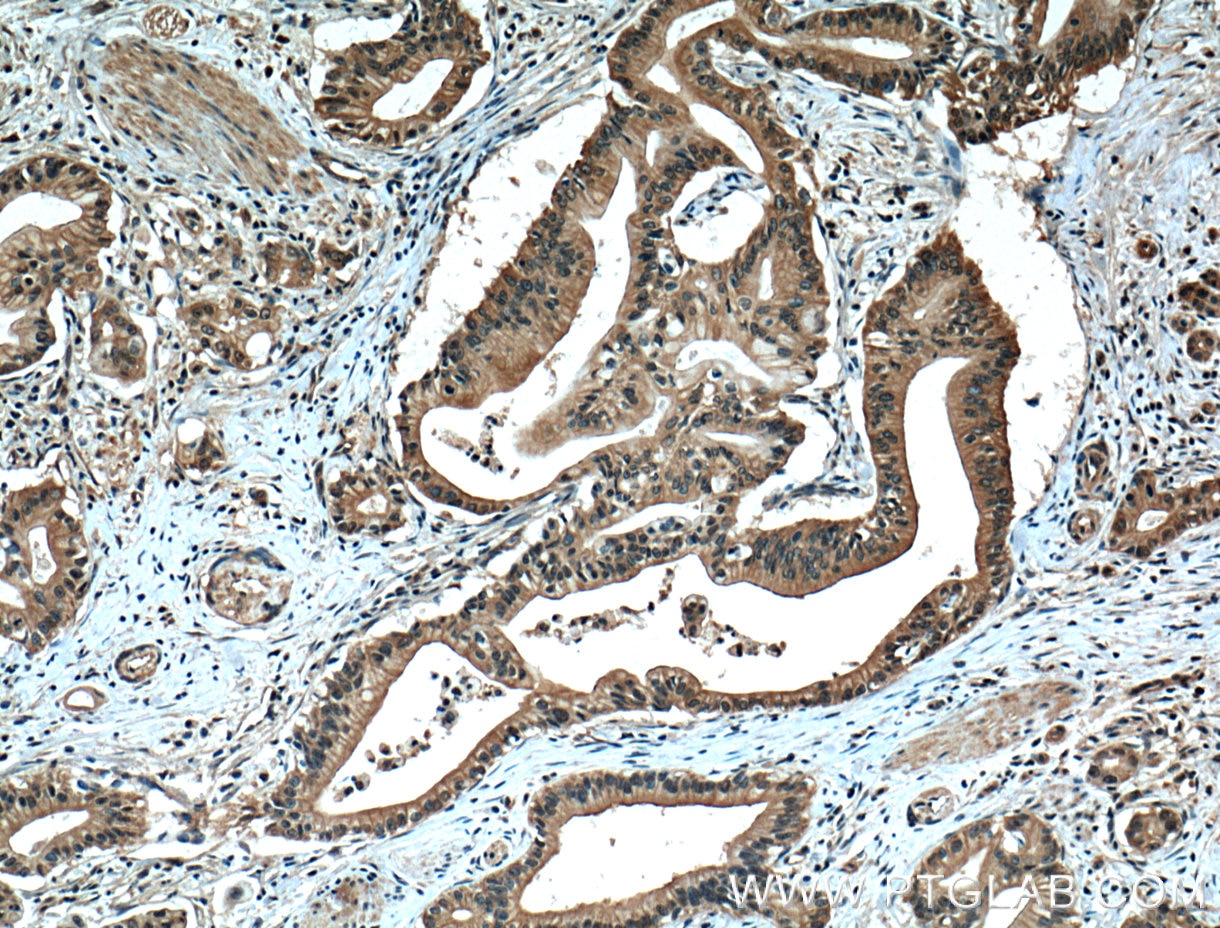
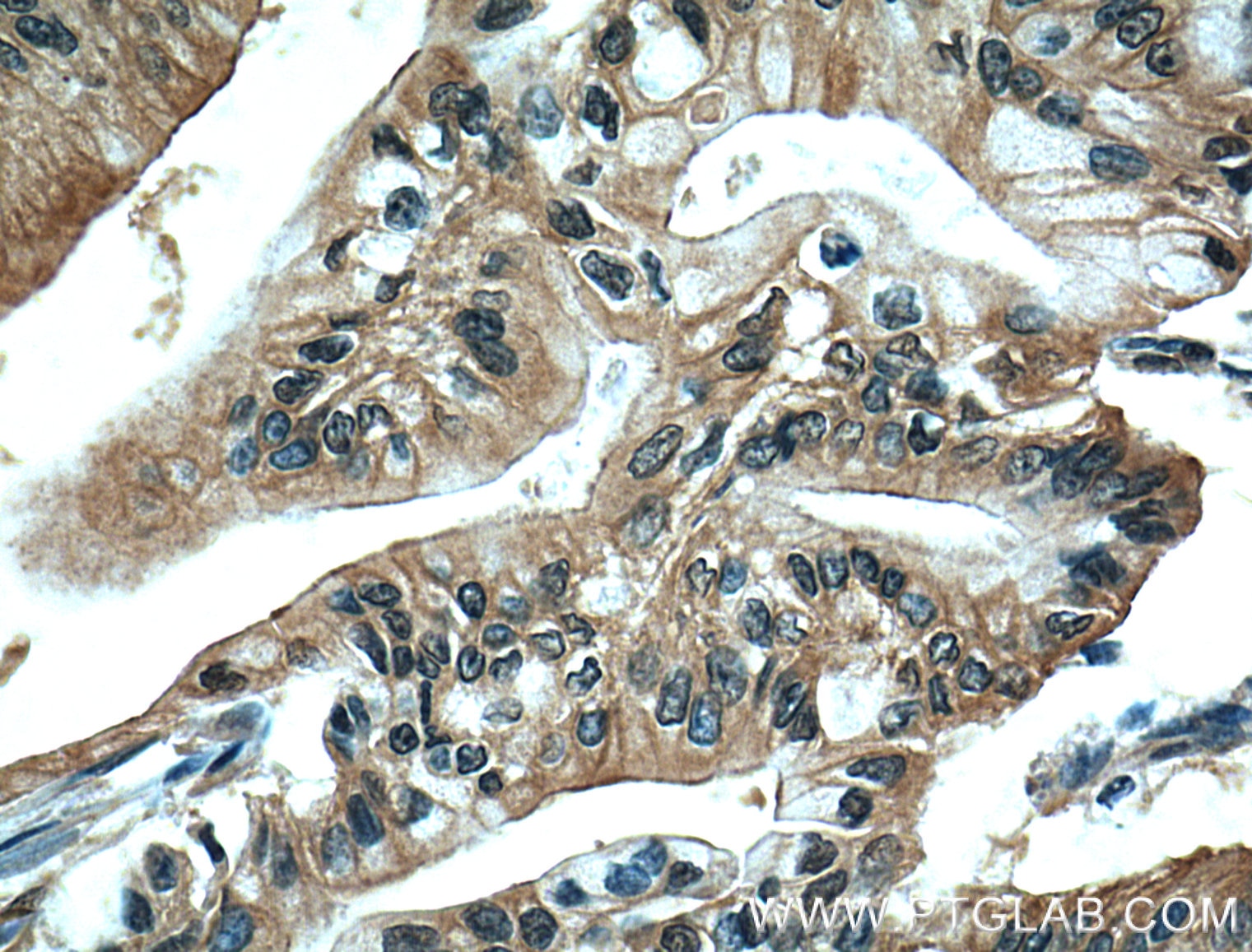
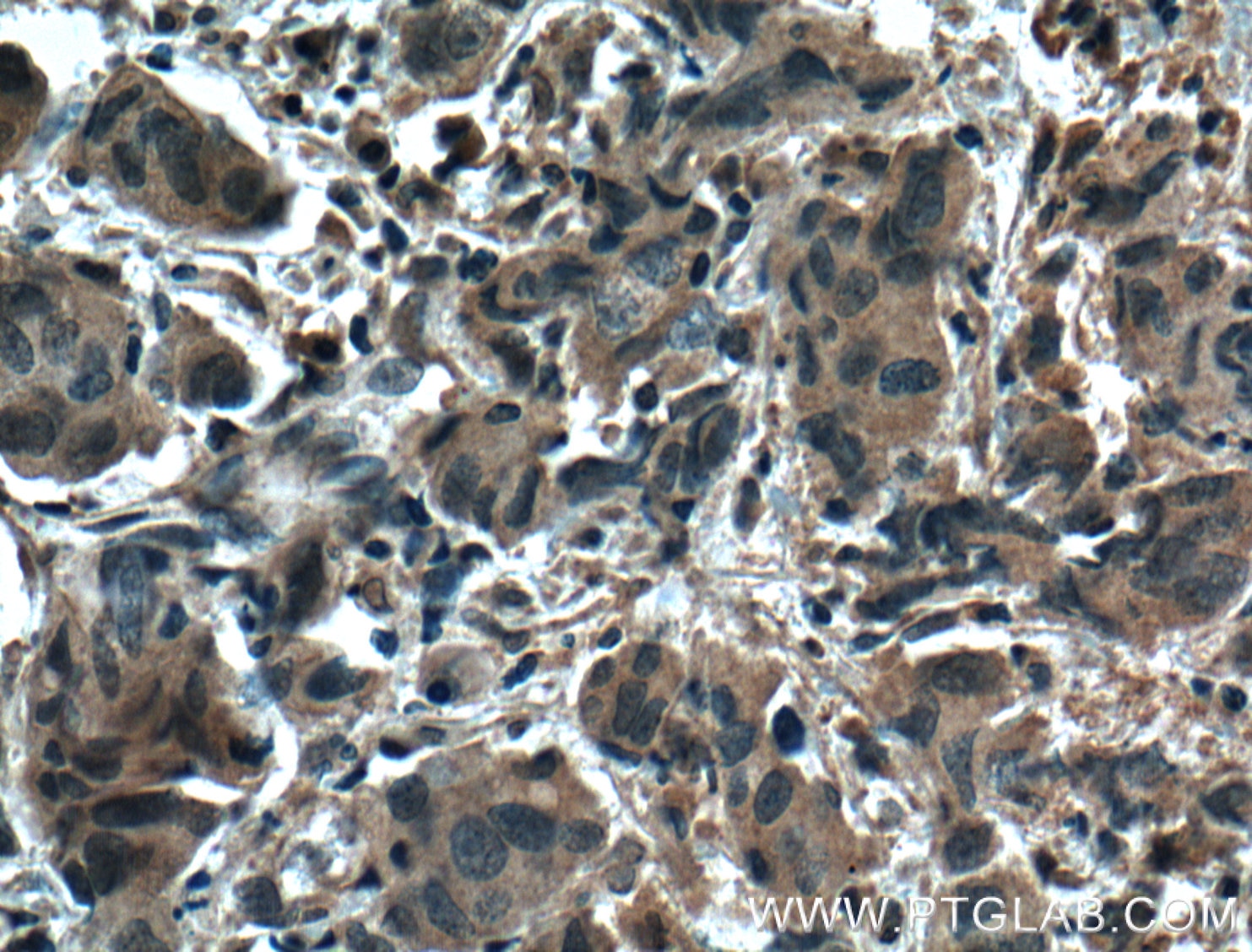
66452-1-PBS targets ZO-1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, canine samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, canine |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag16454 Product name: Recombinant human ZO1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1446-1748 aa of BC111712 Sequence: SLHIHSKGAHGEGNSVSLDFQNSLVSKPDPPPSQNKPATFRPPNREDTAQAAFYPQKSFPDKAPVNGTEQTQKTVTPAYNRFTPKPYTSSARPFERKFESPKFNHNLLPSETAHKPDLSSKTPTSPKTLVKSHSLAQPPEFDSGVETFSIHAEKPKYQINNISTVPKAIPVSPSAVEEDEDEDGHTVVATARGIFNSNGGVLSSIETGVSIIIPQGAIPEGVEQEIYFKVCRDNSILPPLDKEKGETLLSPLVMCGPHGLKFLKPVELRLPHCDPKTWQNKCLPGDPNYLVGANCVSVLIDHF Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | tight junction protein 1 (zona occludens 1) |
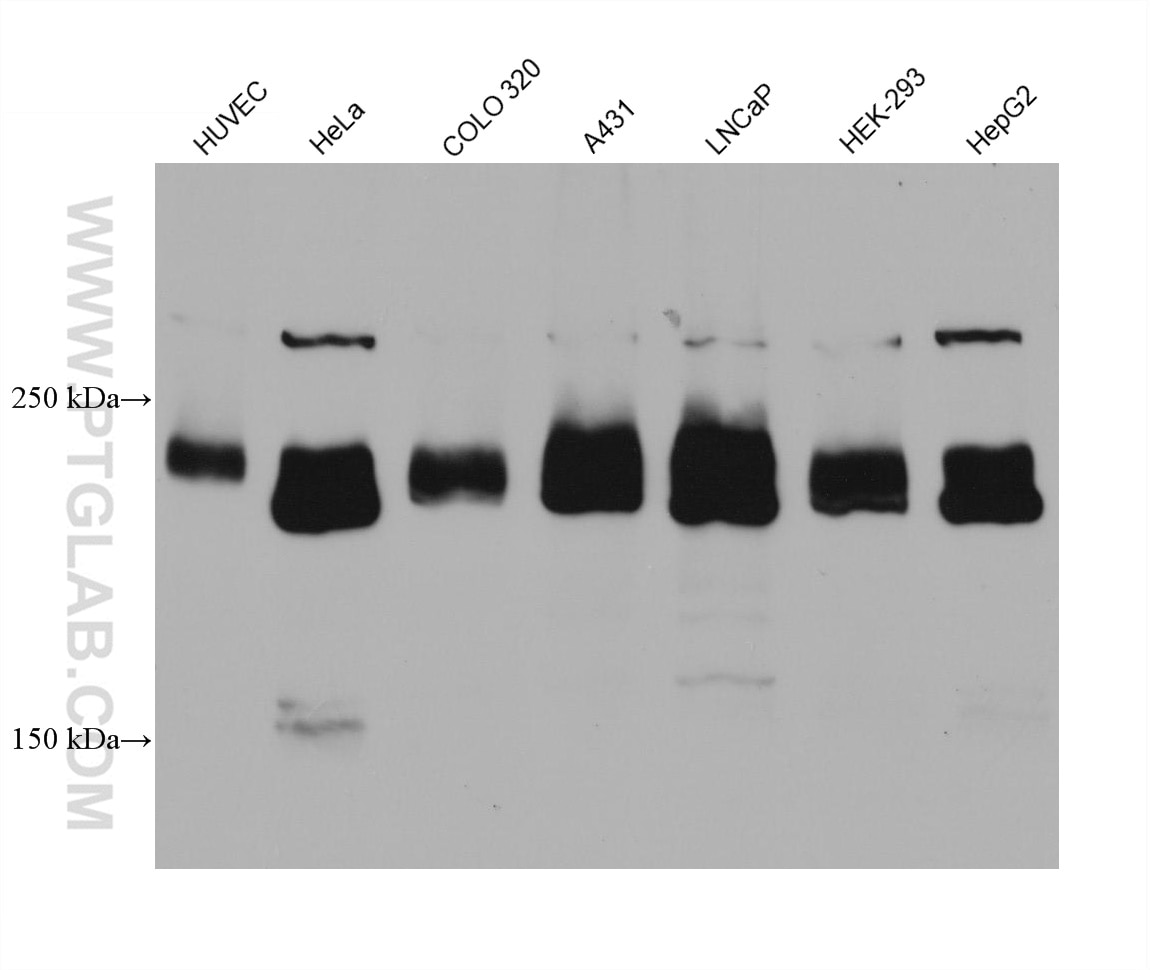
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 1748 aa, 195 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 230 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC111712 |
| Gene Symbol | ZO-1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7082 |
| RRID | AB_2881821 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q07157 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Tight junction (or zonula occludens) form the continuous intercellular barrier between epithelial and endothelial cells, which is required to separate tissue spaces and regulate selective movement of solutes across the epithelium and endothelium (PMID: 20066090). ZO-1 (also known as TJP1) is a peripheral membrane phosphoprotein located on the cytoplasmic face and is expressed in tight junctions of both epithelial and endothelial cells (PMID: 3528172). It binds the transmembrane proteins occludin and the claudins linking them to cytoskeletal actin (PMID: 17418867). ZO-1 belongs to a family of multidomain proteins known as the membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs (MAGUKs). It is a pivotal tight junction protein and may be involved in signalling mechanisms regulating cell proliferation and differentiation (PMID: 22782886).