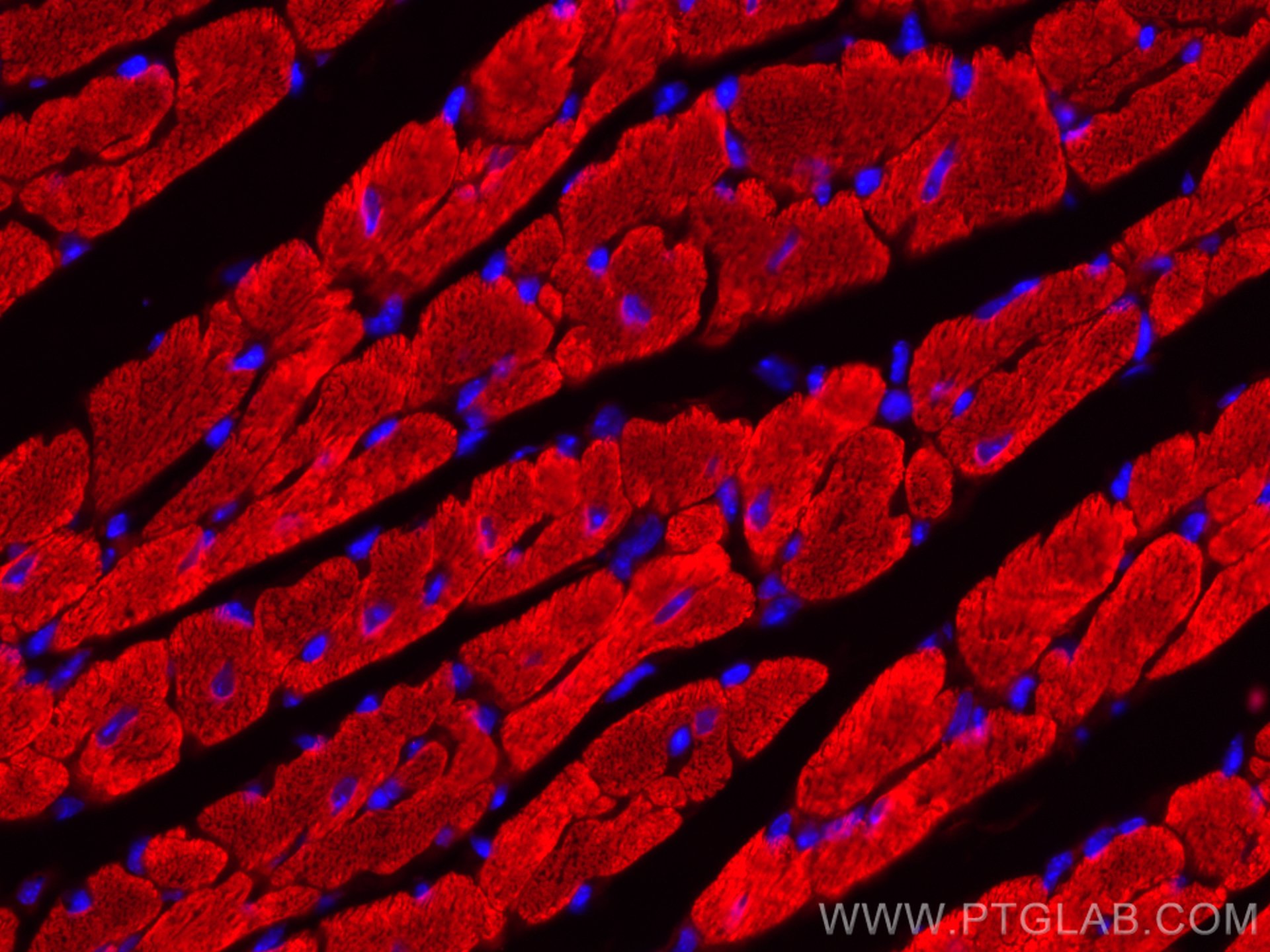
Tested Applications
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse heart tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL594-10906 targets Myosin Light Chain 2/MLC-2V in IF-P applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, zebrafish samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, zebrafish |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag1356 Product name: Recombinant human MYL2 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-166 aa of BC015821 Sequence: MAPKKAKKRAGGANSNVFSMFEQTQIQEFKEAFTIMDQNRDGFIDKNDLRDTFAALGRVNVKNEEIDEMIKEAPGPINFTVFLTMFGEKLKGADPEETILNAFKVFDPEGKGVLKADYVREMLTTQAERFSKEEVDQMFAAFPPDVTGNLDYKNLVHIITHGEEKD Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | myosin, light chain 2, regulatory, cardiac, slow |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 19 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 19 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC015821 |
| Gene Symbol | Myosin Light Chain 2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4633 |
| RRID | AB_2919753 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| Excitation Laser | Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm) |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P10916 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Background
MYL2 belongs to the myosin family of motor proteins. Their common features are ATP hydrolysis, actin binding, and potential for kinetic energy transduction. MYL2 stands for Myosin regulatory light chain 2, ventricular/cardiac muscle isoform (MLC-2), also known as the regulatory light chain of myosin (RLC). This isoform is distinct from those expressed in skeletal muscle (MYLPF), smooth muscle (MYL12B), and cardiac atrial muscle (MYL7) (PMID: 21345328). Due to its tissue specificity, MYL2 has been widely used as a marker of mature ventricular cardiomyocytes.
What is the molecular weight of MYL2?
There are two isoforms of this protein in humans that differ only slightly in length and produce proteins composed of 152 and 166 aa, which correspond to about 19 kDa (PMID: 16678204).
What is the subcellular localization of MYL2?
It is uniquely expressed in the cytoplasm of heart muscles. It colocalizes with actin cytoskeleton staining.
What is the tissue specificity of MYL2?
MYL2 is specifically expressed in ventricular cardiac tissue.
What is the function of MYL2 in cardiac tissue?
MYL2 is a contractile protein that plays a role in heart development and function. During cardiogenesis it plays an early role in cardiac contractility by promoting cardiac myofibril assembly and represents one of the earliest markers of ventricular specification (PMID 8506363).
In general, MYL2 interacts with the neck/tail region of the muscle thick filament protein myosin to regulate myosin motility and function (PMID 8316858). Its N-terminal domain is responsible for calcium and magnesium binding at their activating concentrations. This induces a functionally important conformational change (PMID: 18202317). However, the ion dissociation rate is not fast enough to modulate cardiac contractility on a beat-by-beat basis (PMIDs: 188447, 8804617). In addition, RLC function can be modulated by posttranslational modifications such as phosphorylation and deamidation in the N-terminal region. As a result, a significant change in the charge of the protein is introduced, which undoubtedly alters its interaction with the C-terminal myosin alpha-helical domain (PMID: 26074085).
What is MYL2's involvement in disease?
Diseases associated with MYL2 dysfunction include forms of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathies, congenital fiber-type disproportion, and heart failure (PMID: 26074085).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL594 Myosin Light Chain 2/MLC-2V antibody CL594-10906 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |