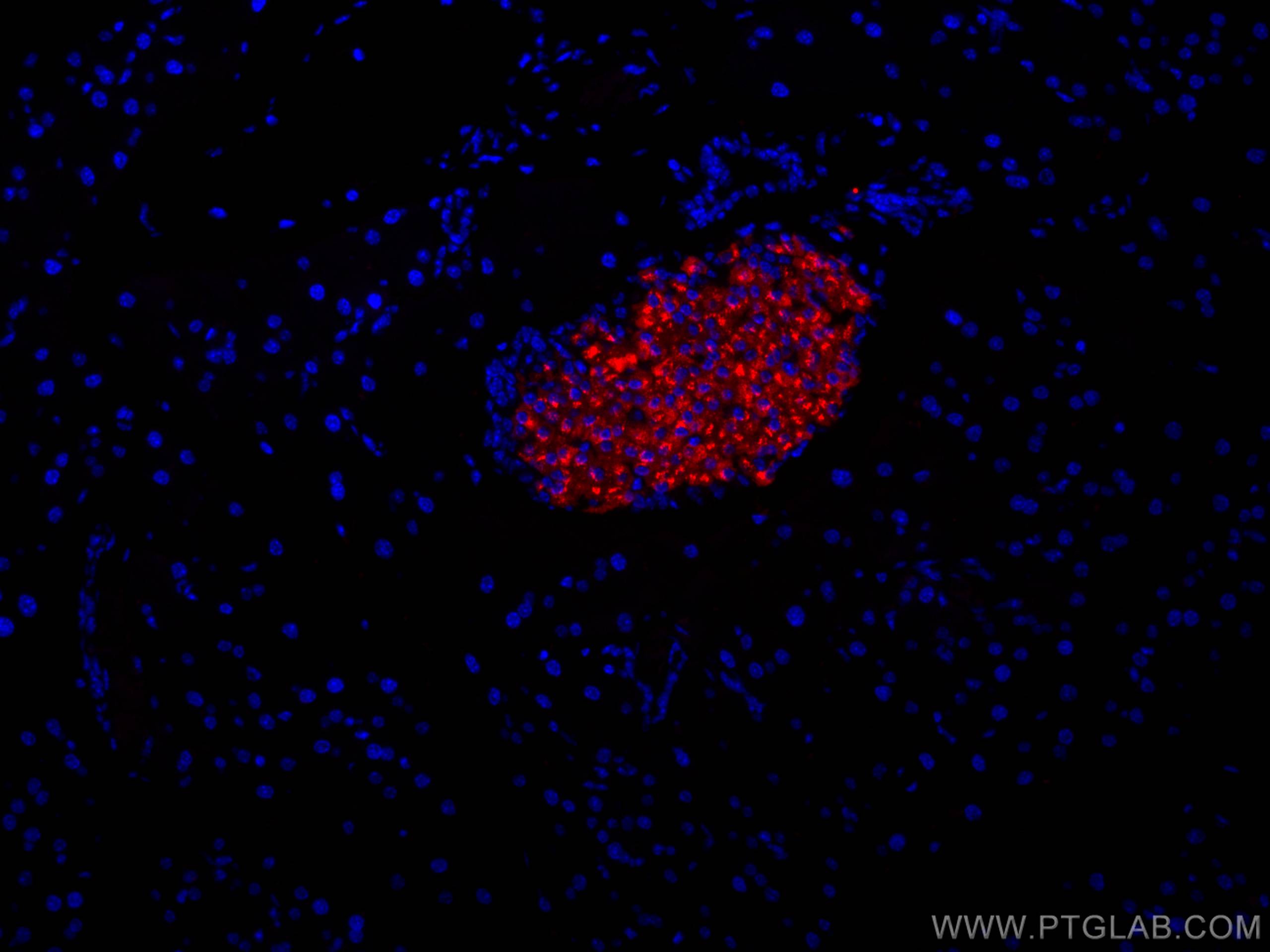
Tested Applications
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse pancreas tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:150-1:600 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL594-67668 targets Ins1 in IF-P applications and shows reactivity with mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Ins1 fusion protein Ag29988 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | insulin I |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 12 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_008386 |
| Gene Symbol | Ins1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 16333 |
| RRID | AB_2920169 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01325 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
insulin I is a peptide hormone that plays a vital role in the regulation of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. The encoded precursor protein undergoes proteolytic cleavage to produce a disulfide-linked heterodimeric functional protein that is stored in secretory granules. An increase in blood glucose levels, among others, induces the release of insulin from the secretory granules. Mice deficient in the functional hormone encoded by this gene develop diabetes mellitus.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL594 Ins1 antibody CL594-67668 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |