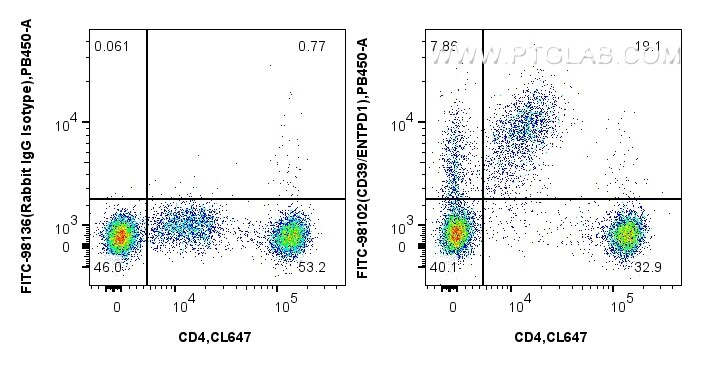
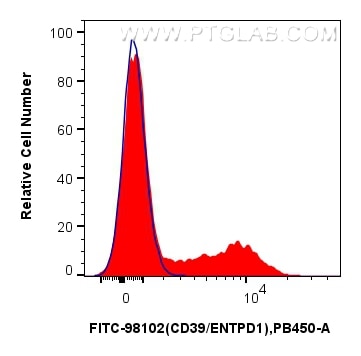
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | human PBMCs |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is N/A per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or N/A per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
FITC-98102 targets CD39/ENTPD1 in FC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Recombinant Protein Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 58 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC047664 |
| Gene Symbol | CD39 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 953 |
| Conjugate | FITC Plus Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 495 nm / 524 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P49961 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide and 0.5% BSA. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
ENTPD1 (Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1) is also named CD39, NTPDase 1, and Ecto-ATPDase 1 and belongs to the GDA1/CD39 NTPase family. In the nervous system, it can hydrolyze ATP and other nucleotides to regulate purinergic neurotransmission. It is a noncovalent tetrameric protein and detergent inhibition of enzymatic activity is caused by dissociation of ectoapyrase tetramers into monomers (PMID: 9733785 ).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for FITC Plus CD39/ENTPD1 antibody FITC-98102 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |