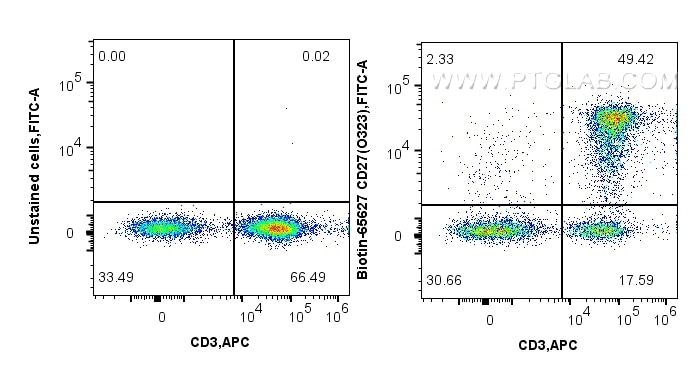
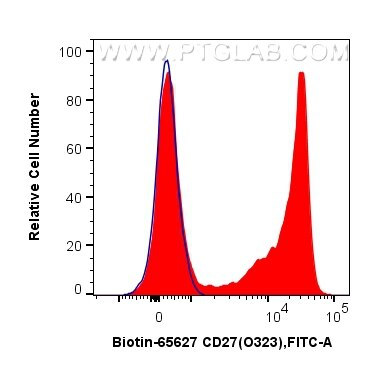
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | human PBMCs |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
Biotin-65627 targets CD27 in FC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | N/A Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | CD27 molecule |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 29 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC012160 |
| Gene Symbol | CD27 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 939 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000139193 |
| Conjugate | Biotin |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
CD27 (also known as TNFRSF7) is a type I glycoprotein expressed on some B cells and the majority of T cells, and is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family. CD27 is required for generation and long-term maintenance of T cell immunity (PMID: 11062504). It is a receptor for CD70 (CD27L). Ligation of CD27 by CD70 induces strong ubiquitination of TRAF and the activation of both canonical and non-canonical NF-kappaB pathways, as well as the JNK pathway (PMID: 19426224). CD27 may also play a role in apoptosis through association with SIVA1.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for Biotin CD27 antibody Biotin-65627 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |