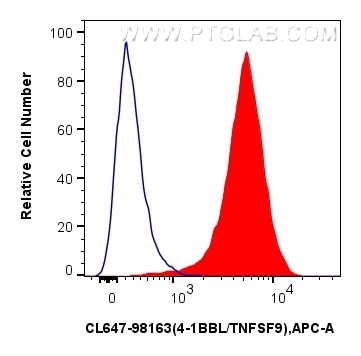
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | Raji cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is 5 ul per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or 5 ul per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL647-98163 targets 4-1BBL/TNFSF9 in FC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | 4-1BBL/TNFSF9 fusion protein Eg0010 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 9 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 254 aa, 27 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC104805 |
| Gene Symbol | TNFSF9 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8744 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 647 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 654 nm / 674 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P41273 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide and 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
TNFSF9, also named as 4-1BBL, belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family. It is a cytokine that binds to TNFRSF9. TNSF9 induces the proliferation of activated peripheral blood T-cells. It may have a role in activation-induced cell death (AICD) and may play a role in cognate interactions between T-cells and B-cells/macrophages.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for CL Plus 647 4-1BBL/TNFSF9 antibody CL647-98163 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |