Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-Kir6.2
Kir6.2 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 16920-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
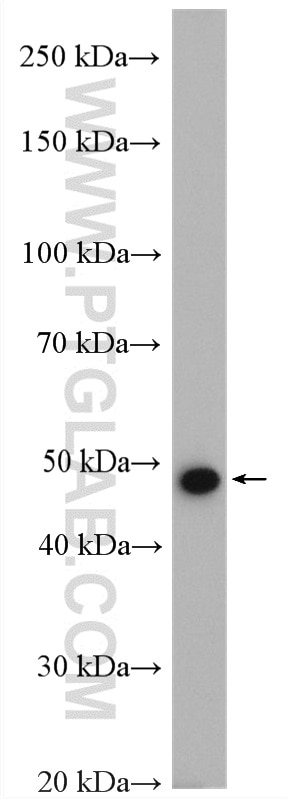
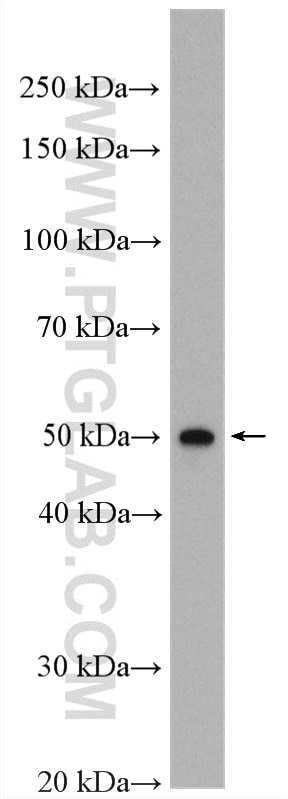
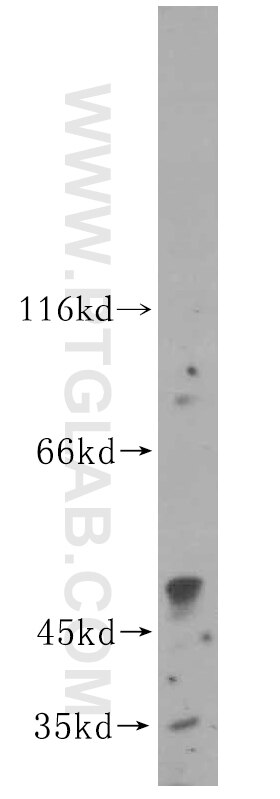
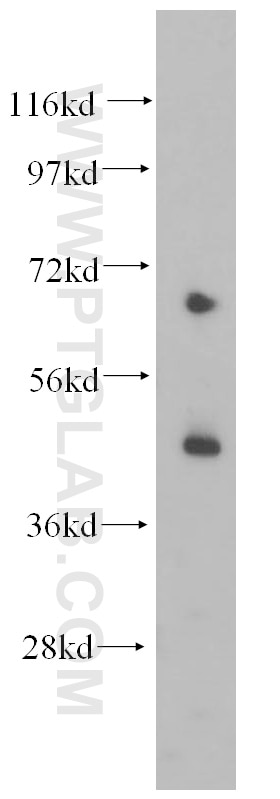
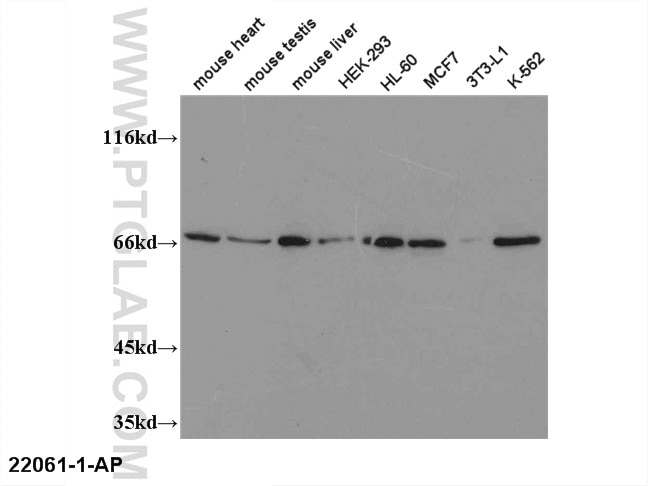
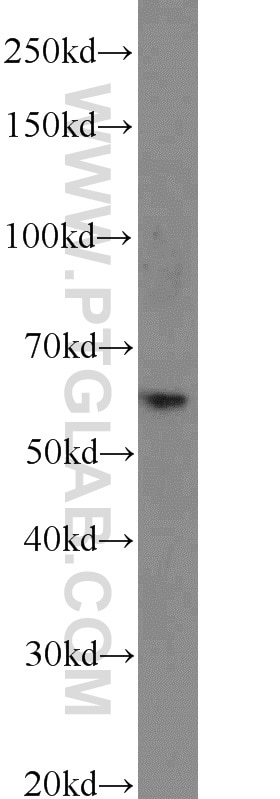
Applications testées
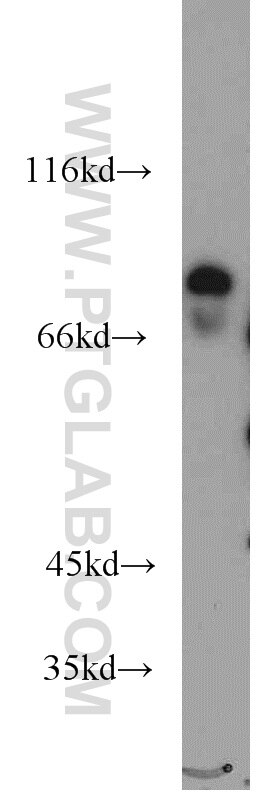
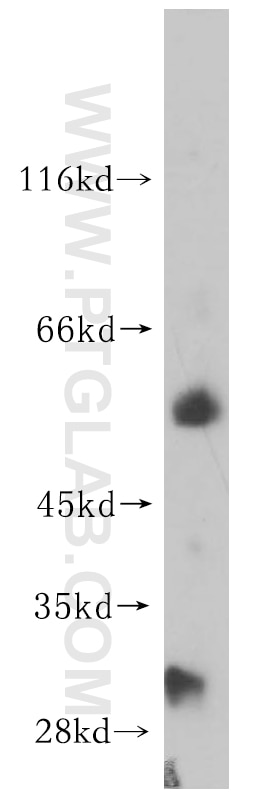
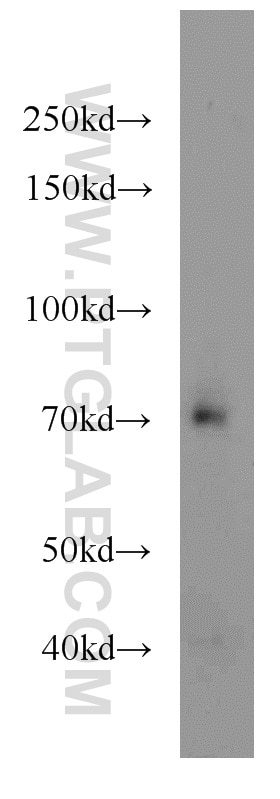
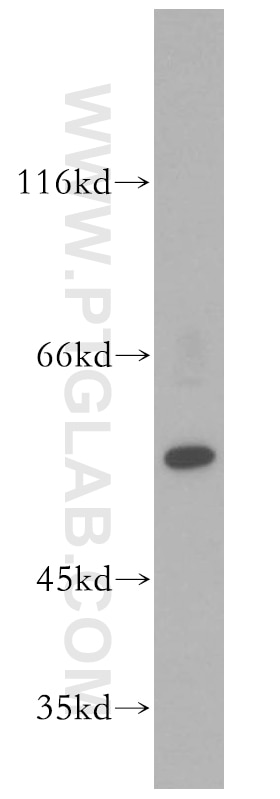
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu cardiaque de rat, cellules HepG2, tissu cardiaque humain, tissu de muscle squelettique de rat |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:200-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
16920-1-AP cible Kir6.2 dans les applications de WB, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Kir6.2 Protéine recombinante Ag10262 |
| Nom complet | potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 390 aa, 44 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 48 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC064497 |
| Symbole du gène | Kir6.2 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 3767 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Kir6.2 (also known as BIR or IKATP), encoded by the KCNJ11 gene, is the pore-forming unit of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel, an inward-rectifier potassium ion channel. Kir6.2 is controlled by G-proteins and is found associated with the sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) to constitute the ATP-sensitive K+ channel. The KCNJ11 gene is located at 11p15.1 and has no intron. Mutations in KCNJ11 are a cause of familial PHHI, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by unregulated ins secretion. Defects in KCNJ11 may also contribute to autosomal dominant non-ins-dependent diabetes mellitus type II (NIDDM), transient neonatal diabetes mellitus type 3 (TNDM3), and permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Kir6.2 antibody 16920-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Life Sci KATP channels as ROS-dependent modulator of neurotransmitter release at the neuromuscular junctions | ||
Sci Rep Glucocorticoid receptor-NECAB1 axis can negatively regulate insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells |