- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-ACAT1
ACAT1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, CoIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 16215-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
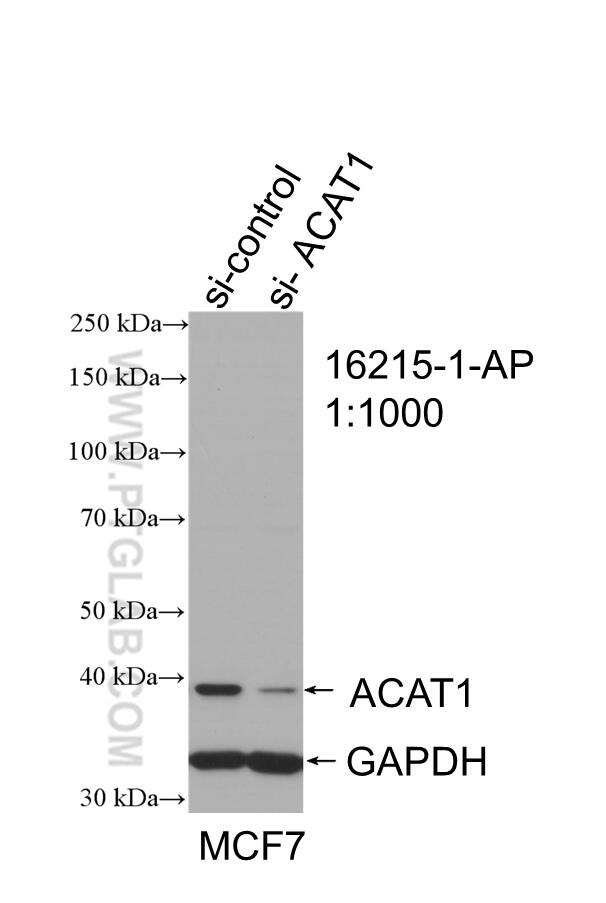
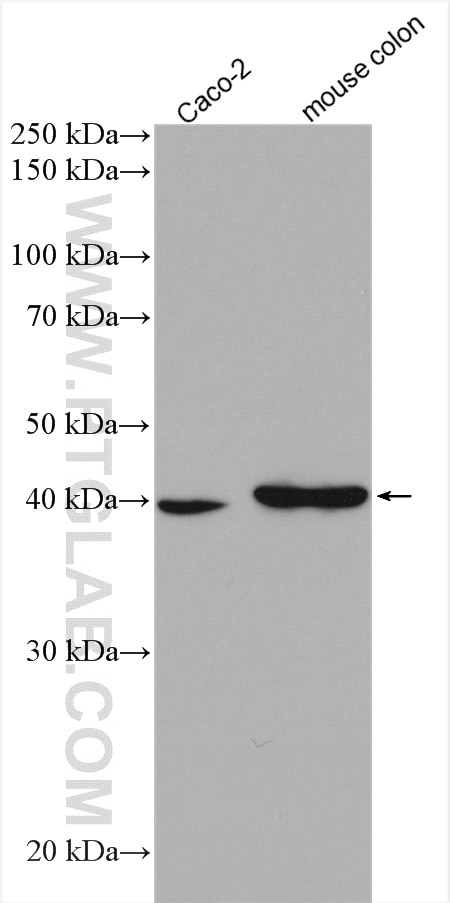
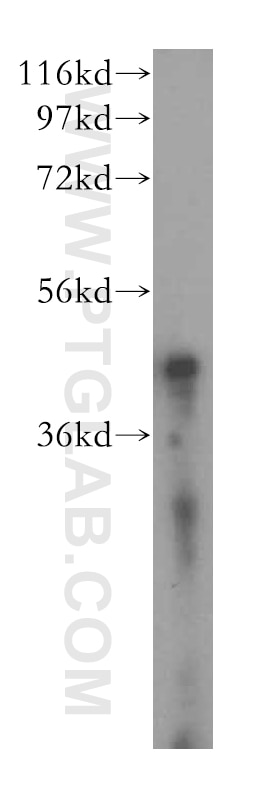
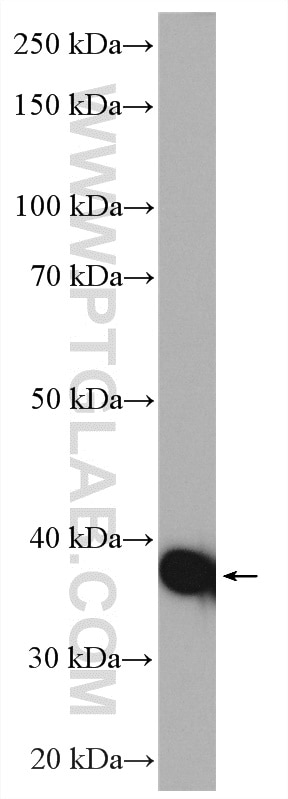
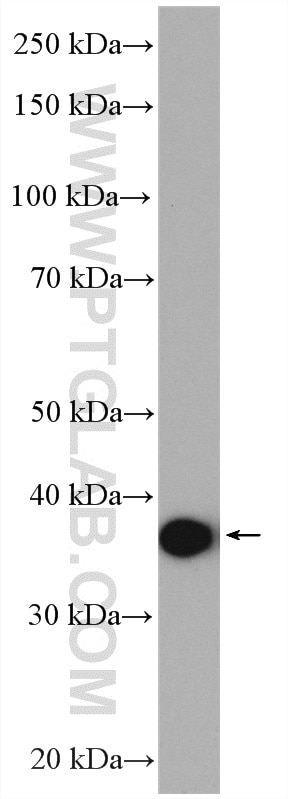
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu cardiaque de souris, cellules Caco-2, cellules MCF-7, tissu de côlon de souris, tissu de muscle squelettique de rat, tissu de muscle squelettique humain |
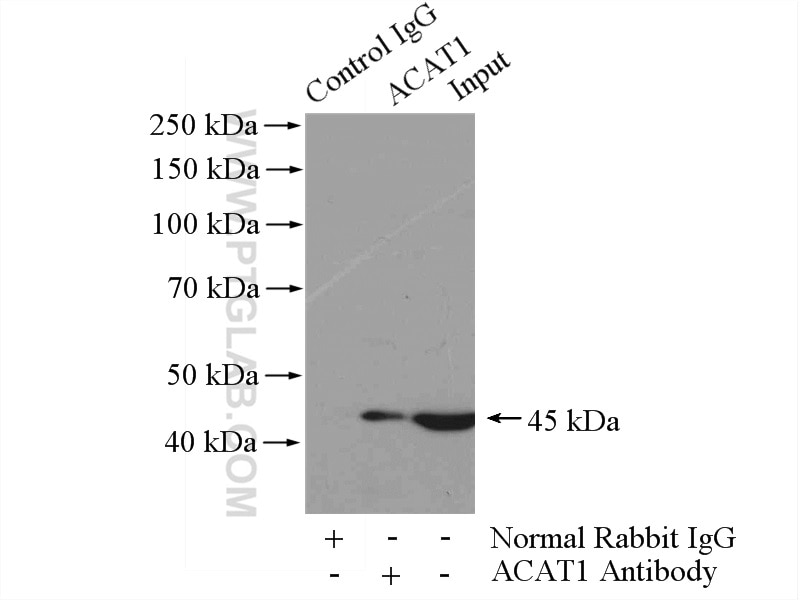
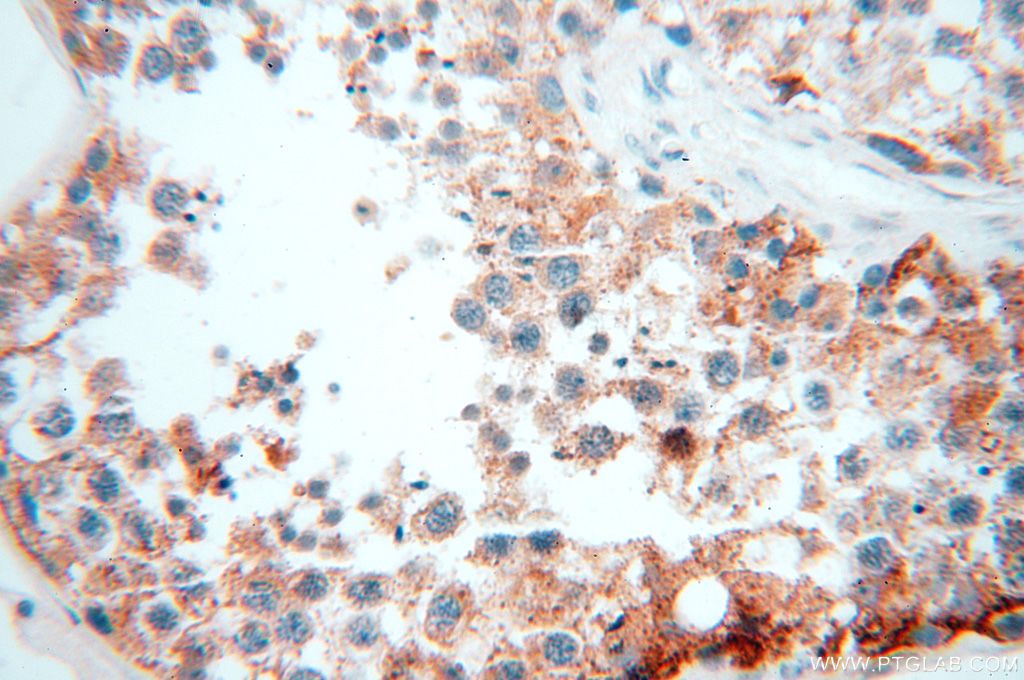
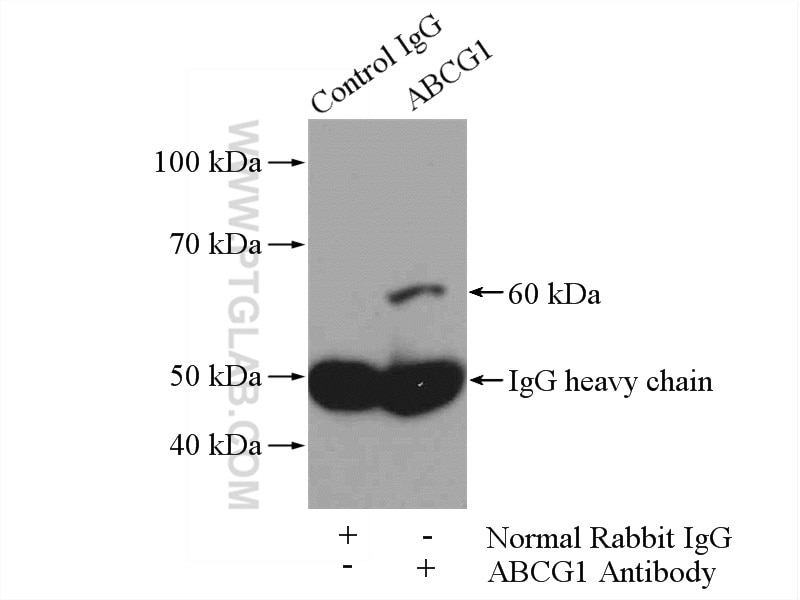
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu cardiaque de souris |
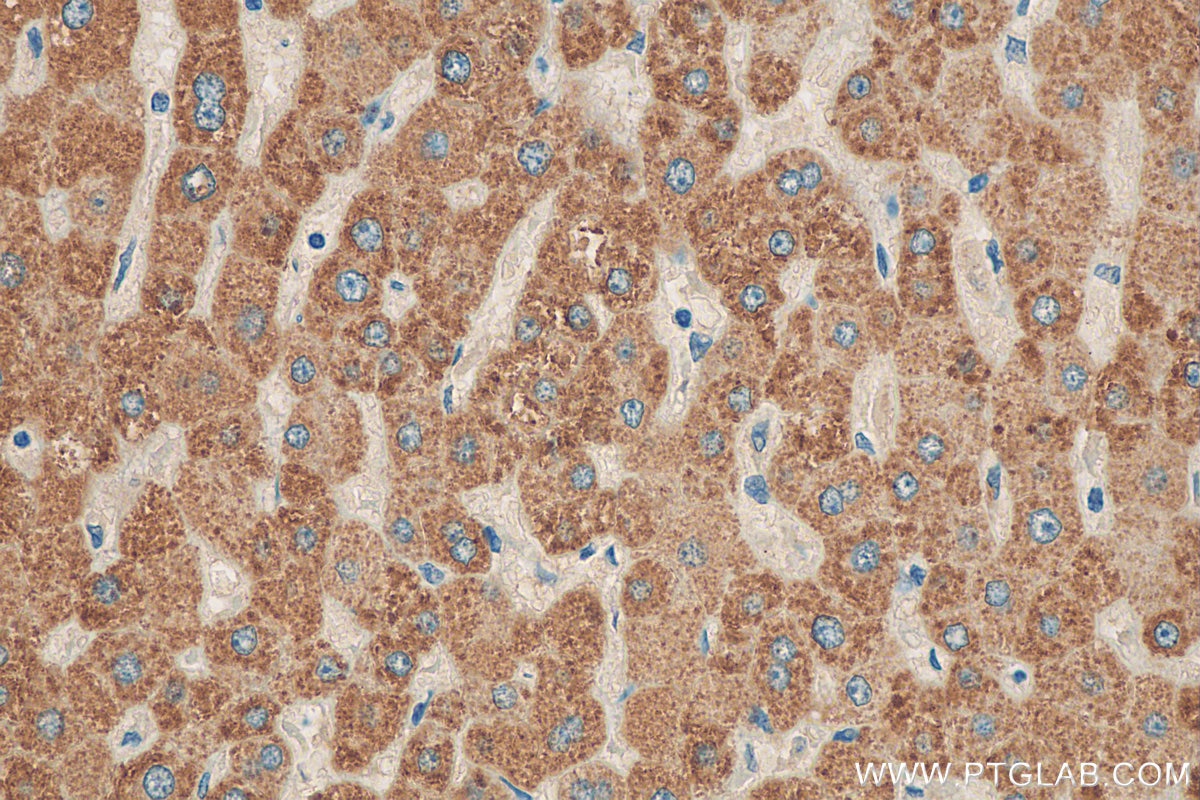
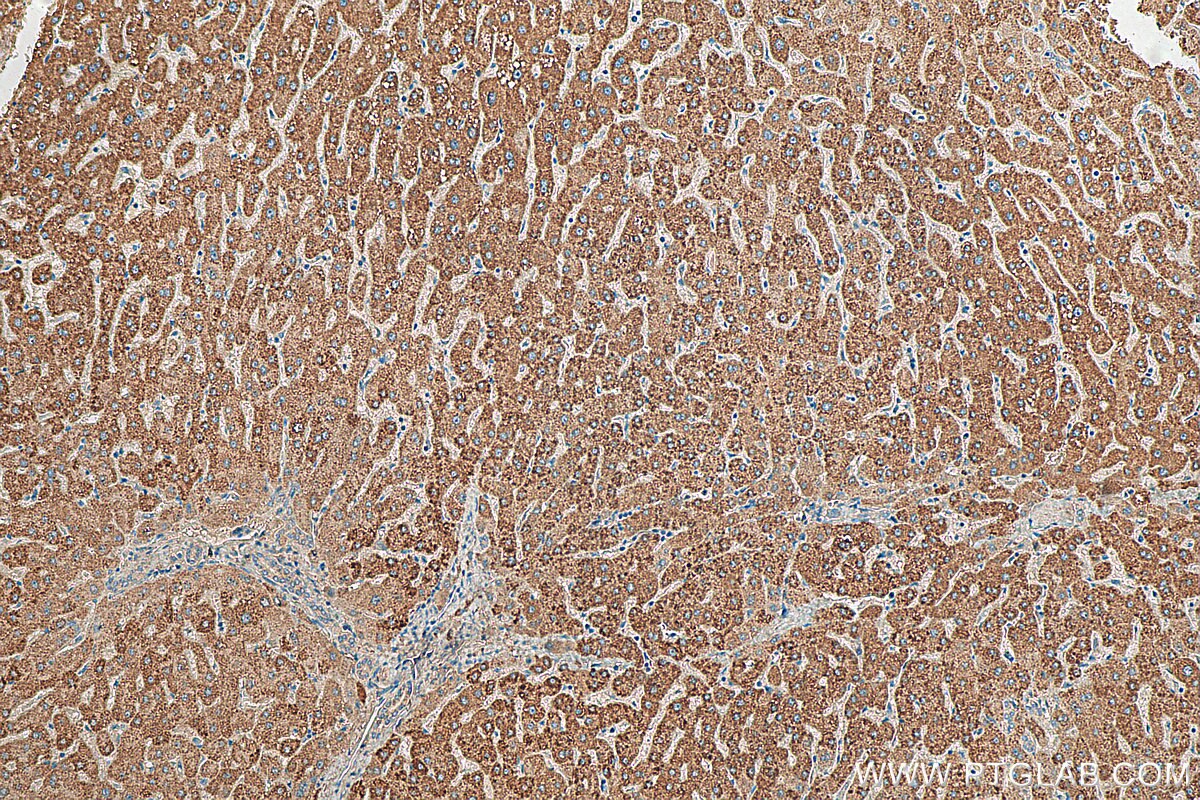
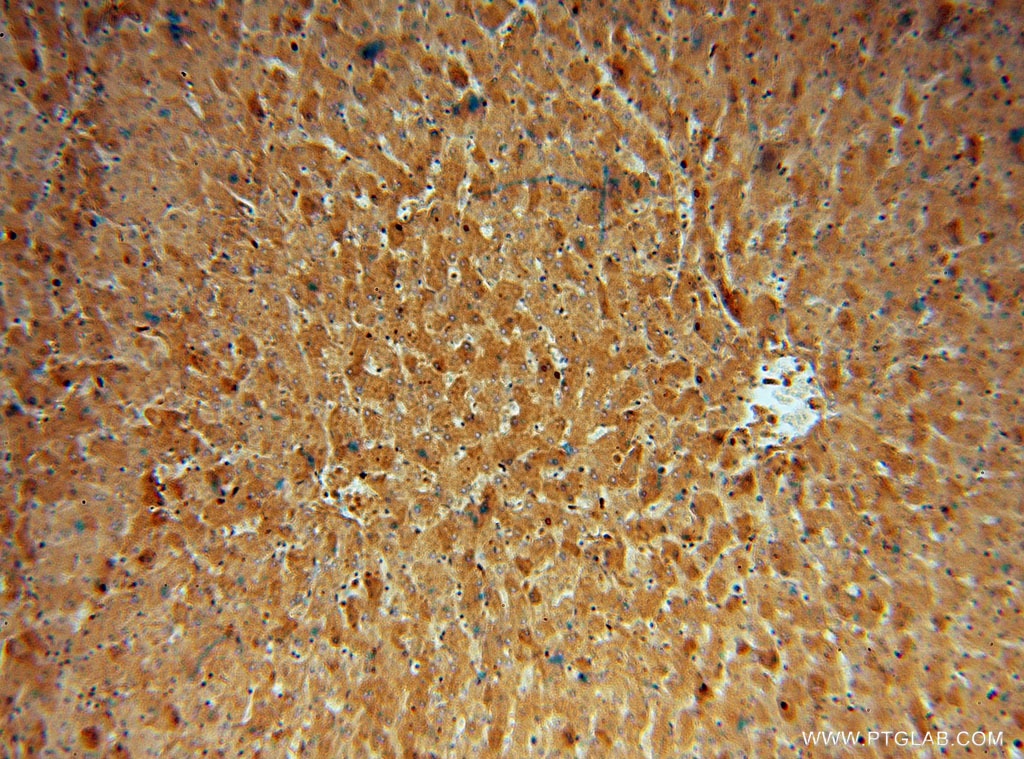
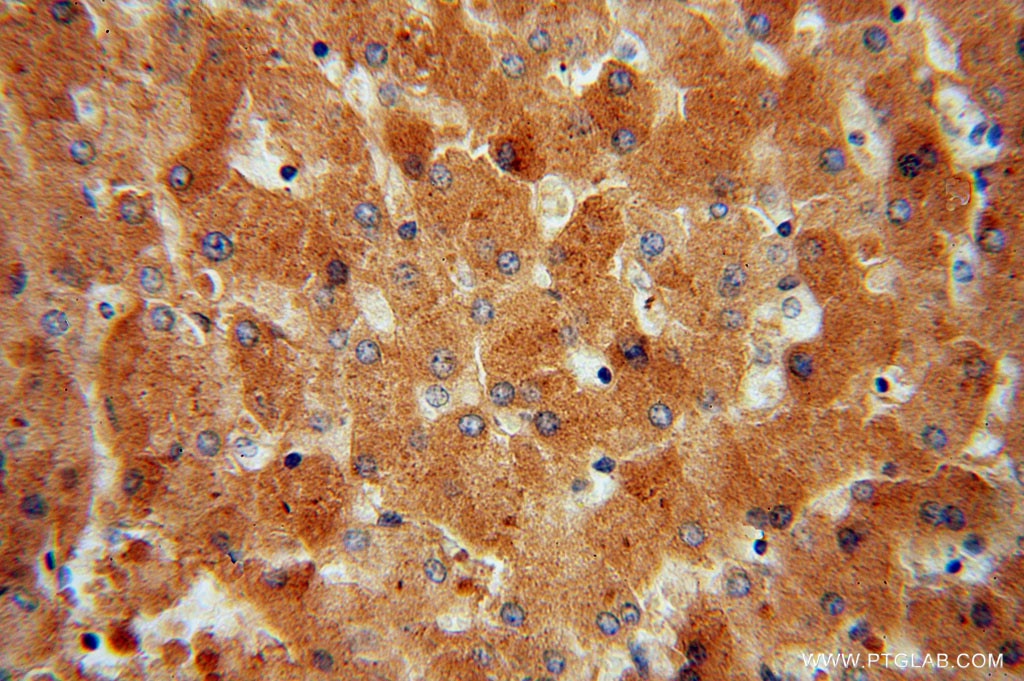
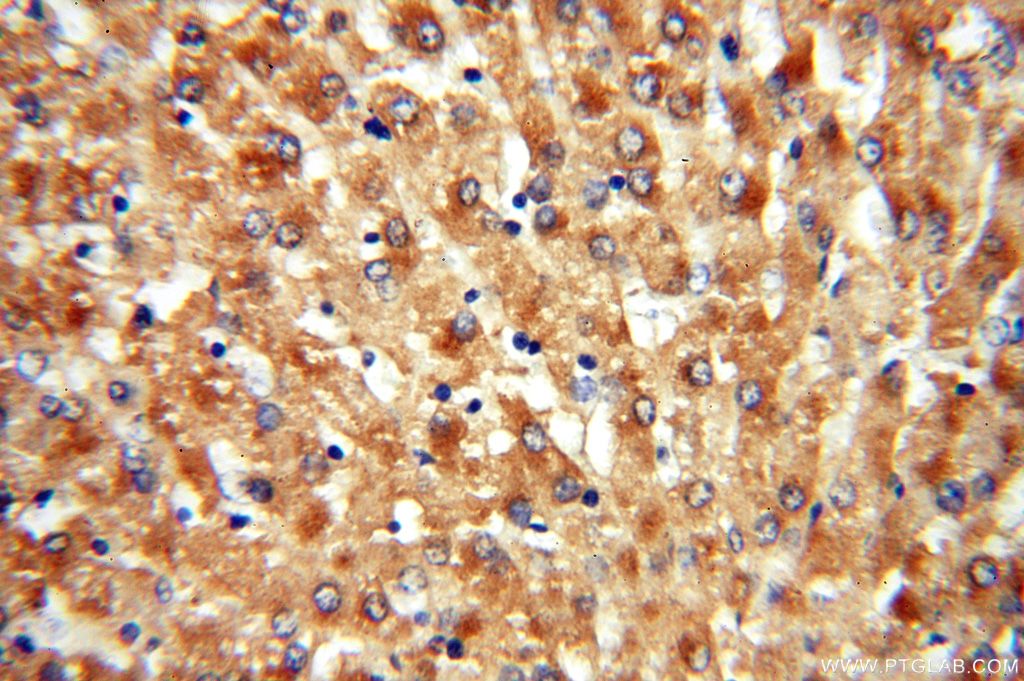
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu hépatique humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
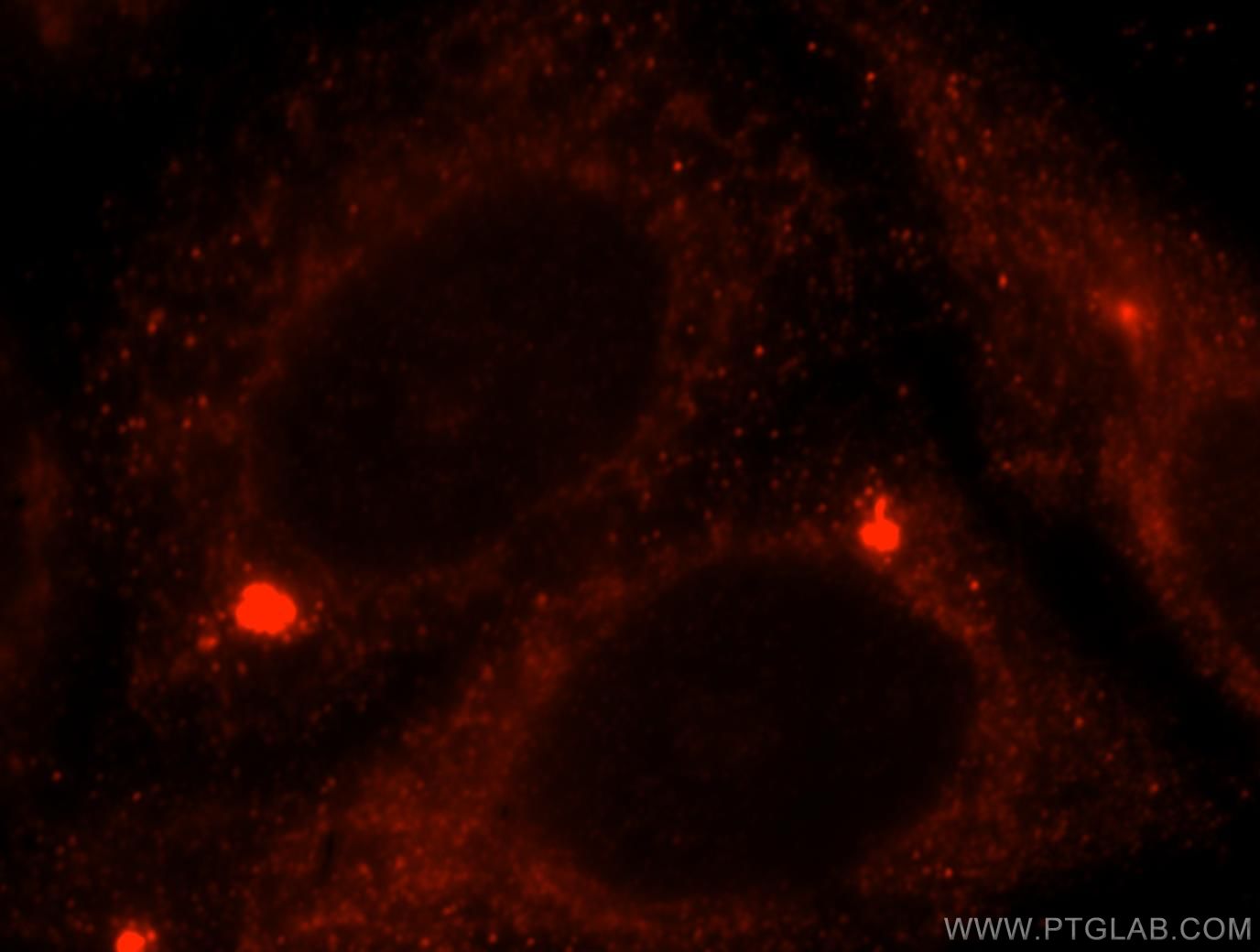
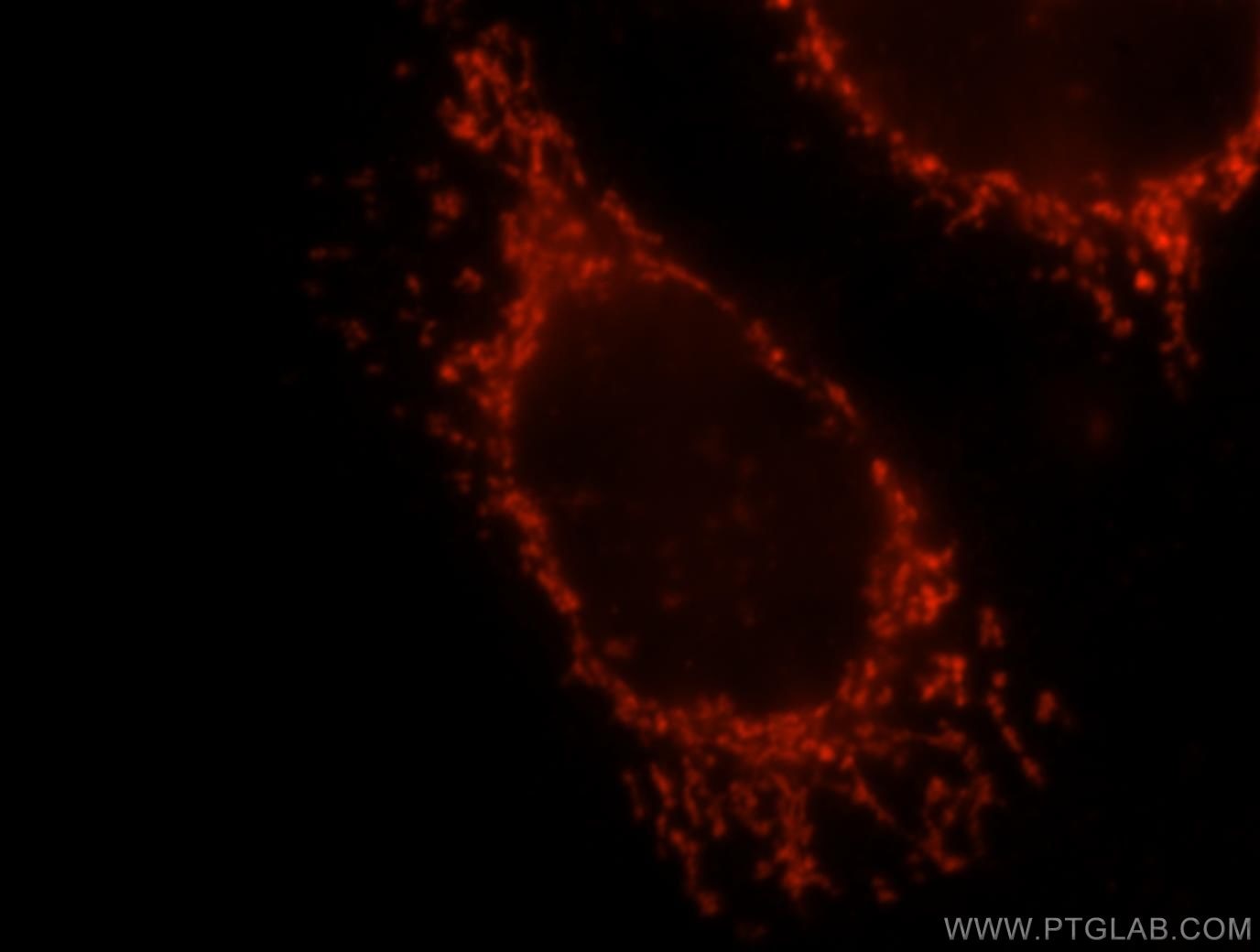
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HeLa |
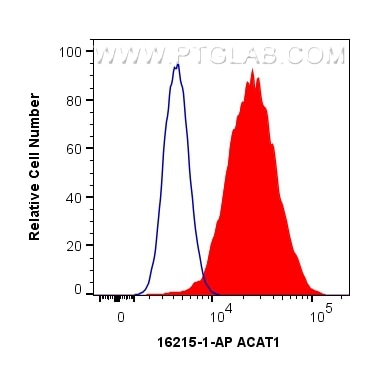
| Résultats positifs en FC (Intra) | cellules HeLa, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 25 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
16215-1-AP cible ACAT1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, CoIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | ACAT1 Protéine recombinante Ag9215 |
| Nom complet | acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 45 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 38-45 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC010942 |
| Symbole du gène | ACAT1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 38 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
ACAT1 (acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase), is a mitochondrial enzyme catalyzing the reversible formation or breakdown of acetoacetyl-CoA and plays important roles in ketogenesis and ketolysis. Deficiency of ACAT1 causes an inherited metabolic disorder. Recently ACAT1 has been reported to get involved in cancer progression.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for ACAT1 antibody 16215-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for ACAT1 antibody 16215-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for ACAT1 antibody 16215-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for ACAT1 antibody 16215-1-AP | Download protocol |
| FC protocol for ACAT1 antibody 16215-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Adv Mater Supramolecular Hydrogel with Ultra-Rapid Cell-Mediated Network Adaptation for Enhancing Cellular Metabolic Energetics and Tissue Regeneration | ||
Cell Metab TMEM41B acts as an ER scramblase required for lipoprotein biogenesis and lipid homeostasis. | ||
Cell Res Hepatocellular carcinoma redirects to ketolysis for progression under nutrition deprivation stress. | ||
Hum Mol Genet Partial Complex I deficiency due to the CNS conditional ablation of Ndufa5 results in a mild chronic encephalopathy but no increase in oxidative damage. | ||
Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol S100A11 Promotes Liver Steatosis via FOXO1-Mediated Autophagy and Lipogenesis. |