- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
RB1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
RB1 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 17218-1-AP
Synonyme
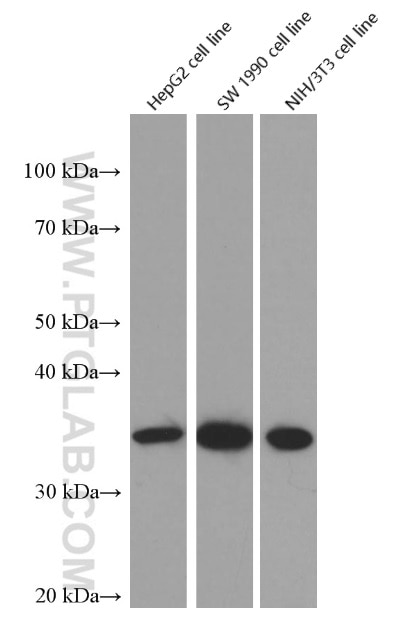
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
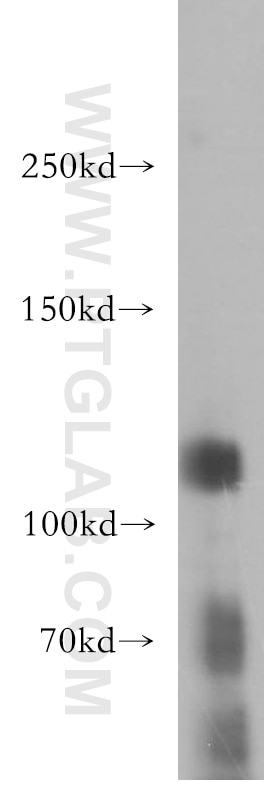
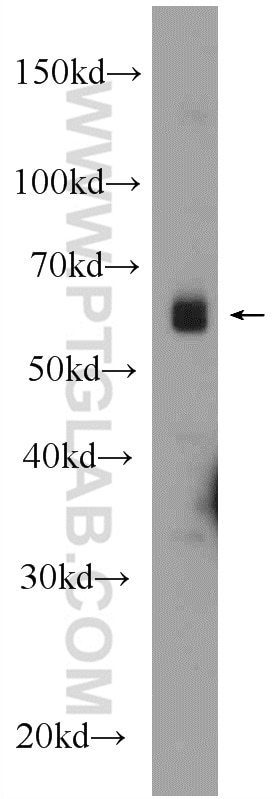
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HT-1080.Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 22 publications below |
Produktinformation
17218-1-AP bindet in WB, ELISA RB1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Zebrafisch |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | RB1 fusion protein Ag11035 |
| Vollständiger Name | retinoblastoma 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 928 aa, 106 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 110 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC039060 |
| Gene symbol | RB1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5925 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
RB1, also named as pp110, pRb and p105 Rb, belongs to the retinoblastoma protein (RB) family. It is a key regulator of entry into cell division that acts as a tumor suppressor. RB1 acts as a transcription repressor of E2F1 target genes. The underphosphorylated, active form of RB1 interacts with E2F1 and represses its transcription activity, leading to cell cycle arrest. It is directly involved in heterochromatin formation by maintaining overall chromatin structure and, in particular, that of constitutive heterochromatin by stabilizing histone methylation. It recruits and targets histone methyltransferases SUV39H1, SUV420H1 and SUV420H2, leading to epigenetic transcriptional repression. RB1 controls histone H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation and inhibits the intrinsic kinase activity of TAF1. It mediates transcriptional repression by SMARCA4/BRG1 by recruiting a histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex to the c-FOS promoter. In resting neurons, transcription of the c-FOS promoter is inhibited by BRG1-dependent recruitment of a phospho-RB1-HDAC1 repressor complex. Upon calcium influx, RB1 is dephosphorylated by calcineurin, which leads to release of the repressor complex. In case of viral infections, interactions with SV40 large T antigen, HPV E7 protein or adenovirus E1A protein induce the disassembly of RB1-E2F1 complex thereby disrupting RB1's activity. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against residues near the C terminus of human RB1.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RB1 antibody 17218-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun Whole-exome sequencing of alpha-fetoprotein producing gastric carcinoma reveals genomic profile and therapeutic targets. | ||
J Hazard Mater Neurotoxicity of aluminum oxide nanoparticles and their mechanistic role in dopaminergic neuron injury involving p53-related pathways. | ||
Aging Cell Berberine ameliorates cellular senescence and extends the lifespan of mice via regulating p16 and cyclin protein expression. | ||
Development Retinoblastoma 1 protects T cell maturation from premature apoptosis by inhibiting E2F1.
| ||
Oncotarget High expression of N-myc (and STAT) interactor predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor growth in human glioblastoma. | ||
Oncotarget Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission promotes cell proliferation through crosstalk of p53 and NF-κB pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. |