- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
CEBPA Polyklonaler Antikörper
CEBPA Polyklonal Antikörper für IP, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte und mehr (3)
Anwendung
WB, IP, IHC, IF, ChIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 18311-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
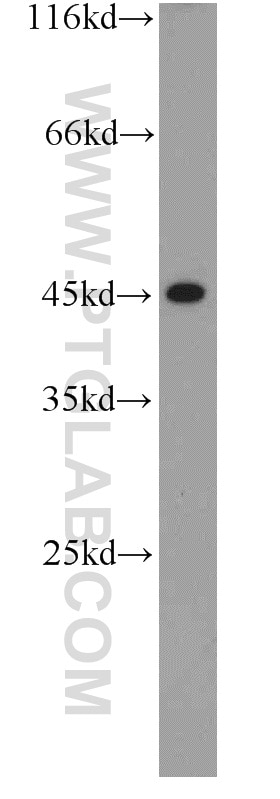
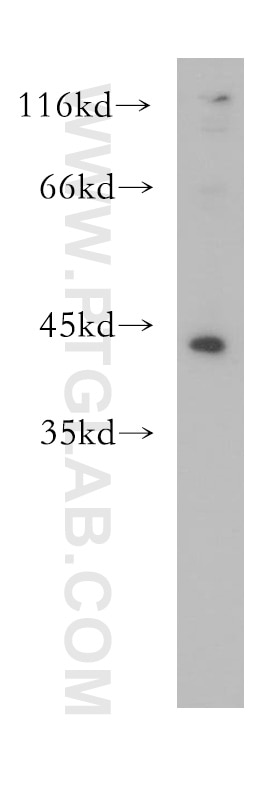
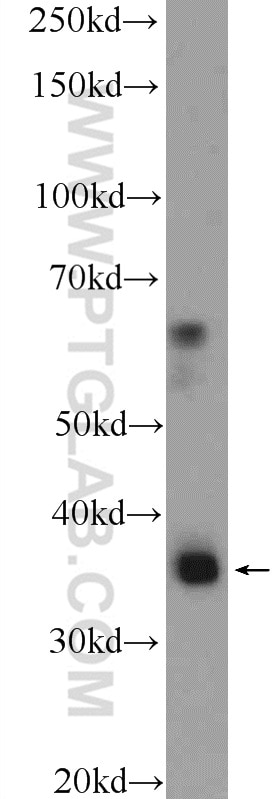
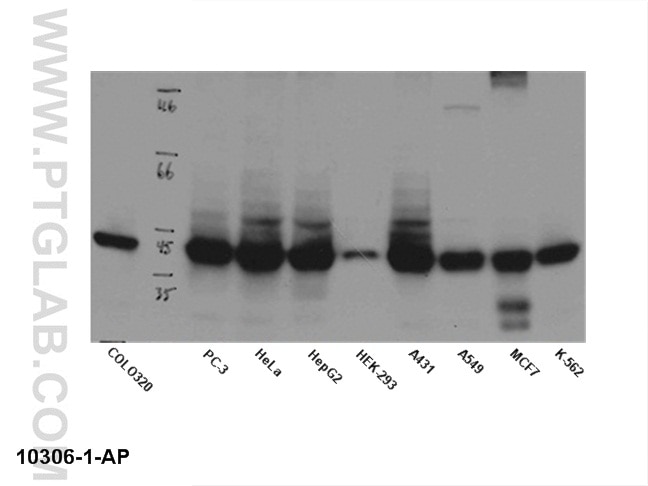
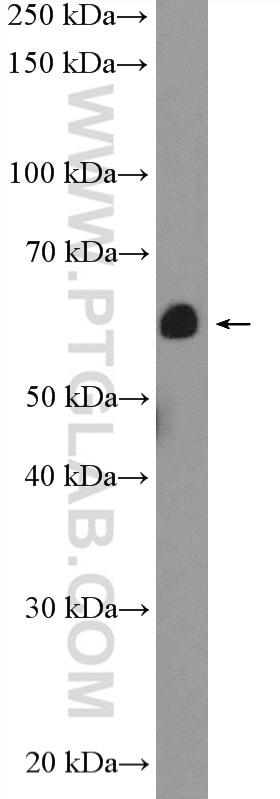
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | L02-Zellen, humanes Lebergewebe |
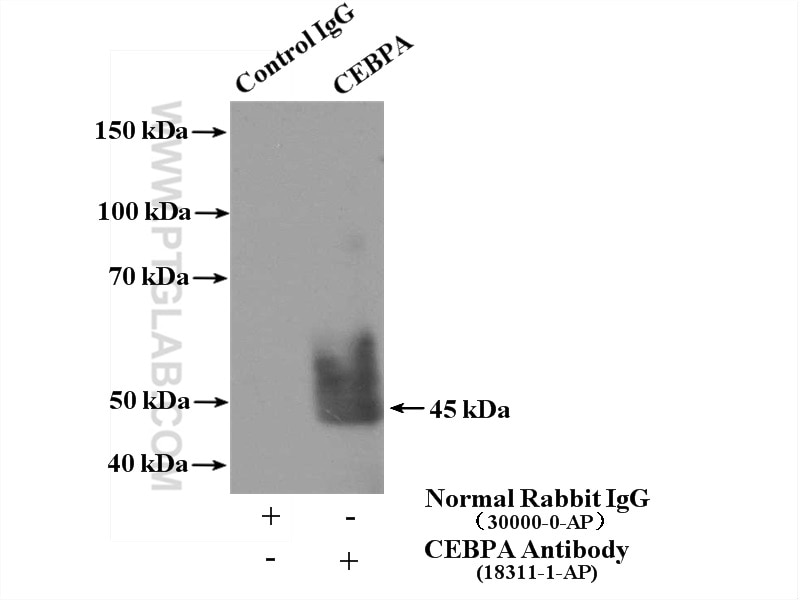
| Erfolgreiche IP | L02-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 48 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 7 publications below |
Produktinformation
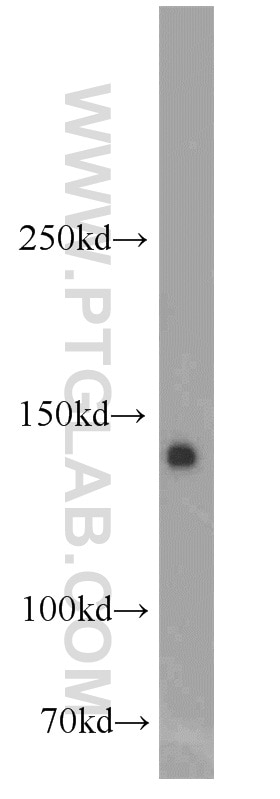
18311-1-AP bindet in WB, IP, IHC, IF, ChIP, ELISA CEBPA und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, hamster, Hausschwein, Maus, Ratte, Ziege |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), alpha |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 38 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 40-45 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC160133 |
| Gene symbol | CEBPA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1050 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
CEBPA and its isoforms play important roles in lineage determination and gene activation in a variety of cell types by activating transcription from lineage-specific promoters. CEBPA is a DNA-binding protein that recognizes two different motifs: the CCAAT homology common to many promoters and the enhanced core homology common to many enhancers. In hematopoiesis, C/EBPa is a key factor in driving the development of myeloid cells interacting with a variety of factors, including c-Myc, PU.1, and microRNAs. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-beta and CEBP-gamma. The encoded protein has been shown to bind to the promoter and modulate the expression of the gene encoding leptin which plays an important role in body weight homeostasis. CEBPA can interact with CDK2 and CDK4, thereby inhibiting these kinases and causing growth arrest in cultured cells. Several pathways have been implicated as the means by which CEBPA mediates cell cycle arrest and proliferation, including p21, cyclin-dependent kinases and the E2F complex via c-Myc. The calcualted molecular weight of CEBPA is 38 kDa, but modified CEBPA is about 42 kDa (PMID: 19623175).
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CEBPA antibody 18311-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for CEBPA antibody 18311-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab CircACC1 Regulates Assembly and Activation of AMPK Complex under Metabolic Stress.
| ||
Exp Mol Med Protective effect of hepatocyte-enriched lncRNA-Mir122hg by promoting hepatocyte proliferation in acute liver injury | ||
J Clin Invest Dysregulation of PI3K and hippo signaling pathways synergistically induces chronic pancreatitis via Ctgf upregulation. | ||
Bone Res mTORC1 induces plasma membrane depolarization and promotes preosteoblast senescence by regulating the sodium channel Scn1a. | ||
Theranostics PIWIL3/OIP5-AS1/miR-367-3p/CEBPA feedback loop regulates the biological behavior of glioma cells.
| ||
Leukemia Circulating cytokines present in multiple myeloma patients inhibit the osteoblastic differentiation of adipose stem cells. |