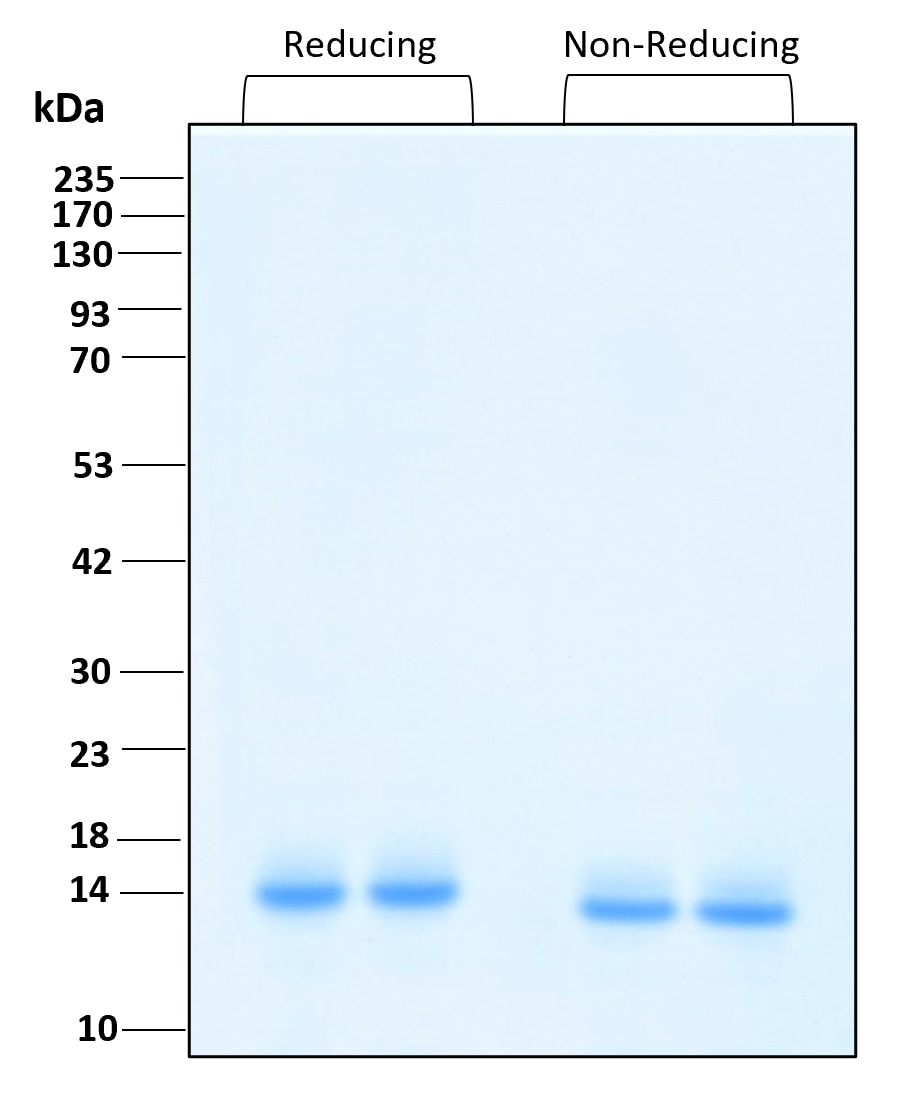
- HEK293 expressed
- Endotoxin-free
- Animal-component free
HumanKine® recombinant human Cystatin C protein
Cat no : HZ-1211
Synonyms
ARMD11, CST3, Cystatin 3, cystatin C, Gamma trace, Post gamma globulin
Validation Data Gallery
Technical Specifications
| GeneID | 1471 |
| Species | Human |
| Expression | HEK293 |
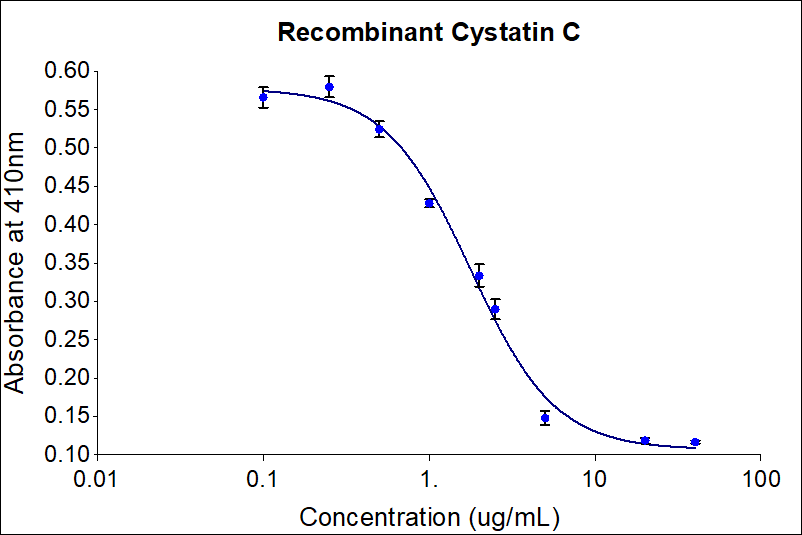
| Activity(Primary) | 0.5-2.6 µg/mL |
| Purity | >95% |
| Endotoxin | <1 EU/μg |
| Accession Number | P01034 |
| Molecular Mass | 15 to 18 kDa reduced, 14 to 17 kDa non-reduced, monomer, non-glycosylated |
| Formulation | 1x PBS, See Certificate of Analysis for details |
| Species Reactivity | human |
Stability and Reconstitution
| Stability and Storage | Product Form | Temperature Conditions | Storage Time (From Date of Receipt) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lyophilized | -20°C to -80°C | Until Expiry Date | |
| Lyophilized | Room Temperature | 2 weeks | |
| Reconstituted as per CofA | -20°C to -80°C | 6 months | |
| Reconstituted as per CofA | 4°C | 1 week | |
| Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. | |||
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the vial before opening. It is recommended to reconstitute the protein to 0.2 mg/mL in sterile 1x PBS pH 7.4. Gently swirl or tap vial to mix. |
Background
Cystatin C is a 13-kDa protein that is expressed globally in the body. In healthy individuals, glomerular filtration in the kidney maintains it at a safe level. When kidney function is impaired, Cystatin C levels rise quickly. This makes it an early and sensitive biomarker of renal dysfunction (PMID 24848523). A mutation in Cystatin C has been associated with amyloid angiopathy (PMID 11409420). Expression of this protein in vascular wall smooth muscle cells is severely reduced in both atherosclerotic and aneurysmal aortic lesions, establishing its role in vascular disease. In addition, this protein has been shown to have an antimicrobial function, inhibiting the replication of herpes simplex virus.
Synonyms
ARMD11, CST3, Cystatin 3, cystatin C, Gamma trace, Post gamma globulin