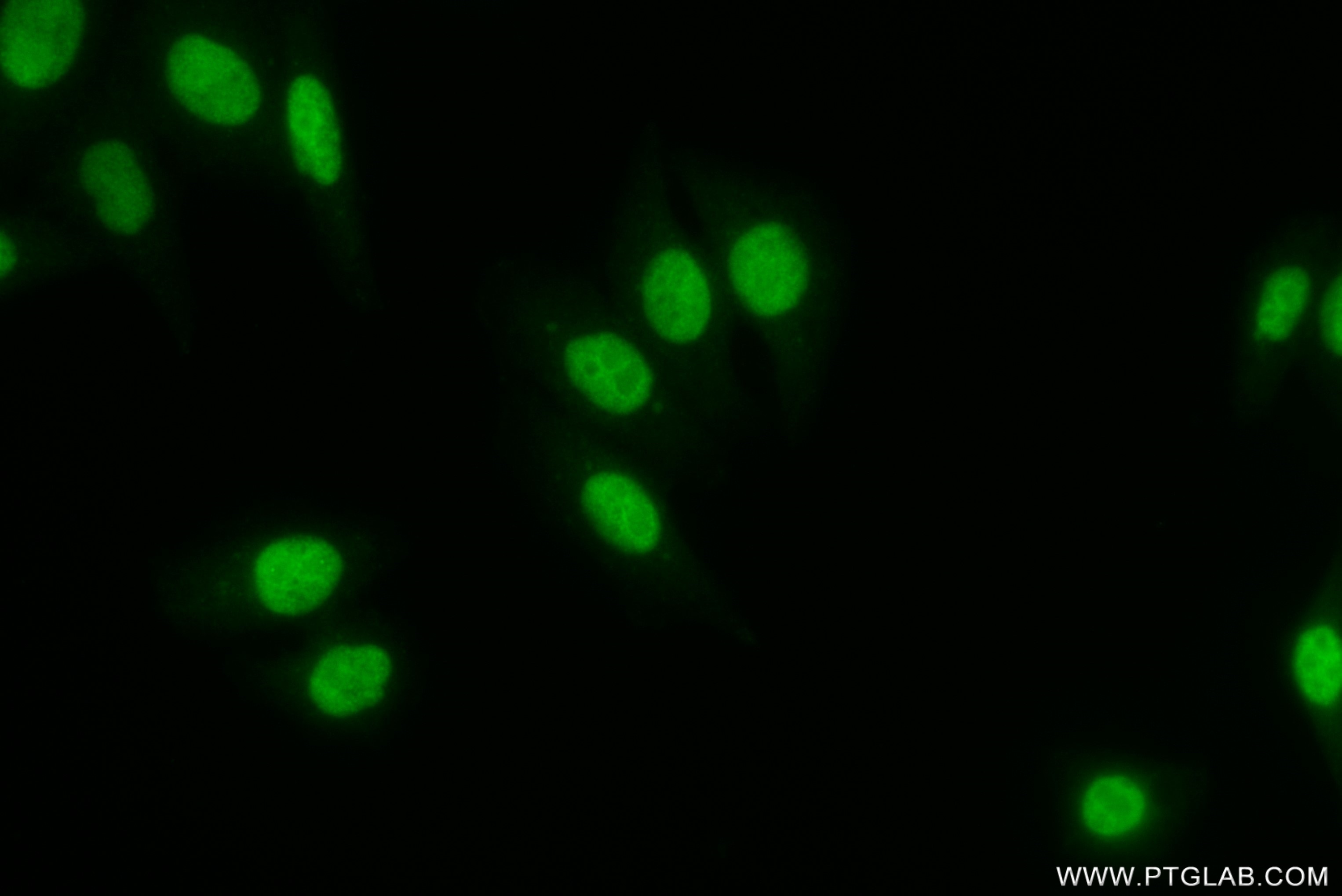
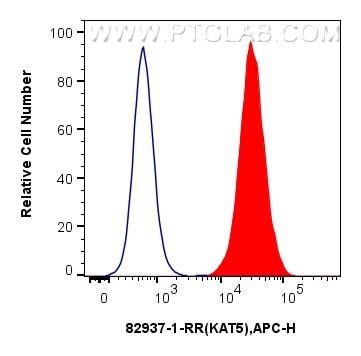
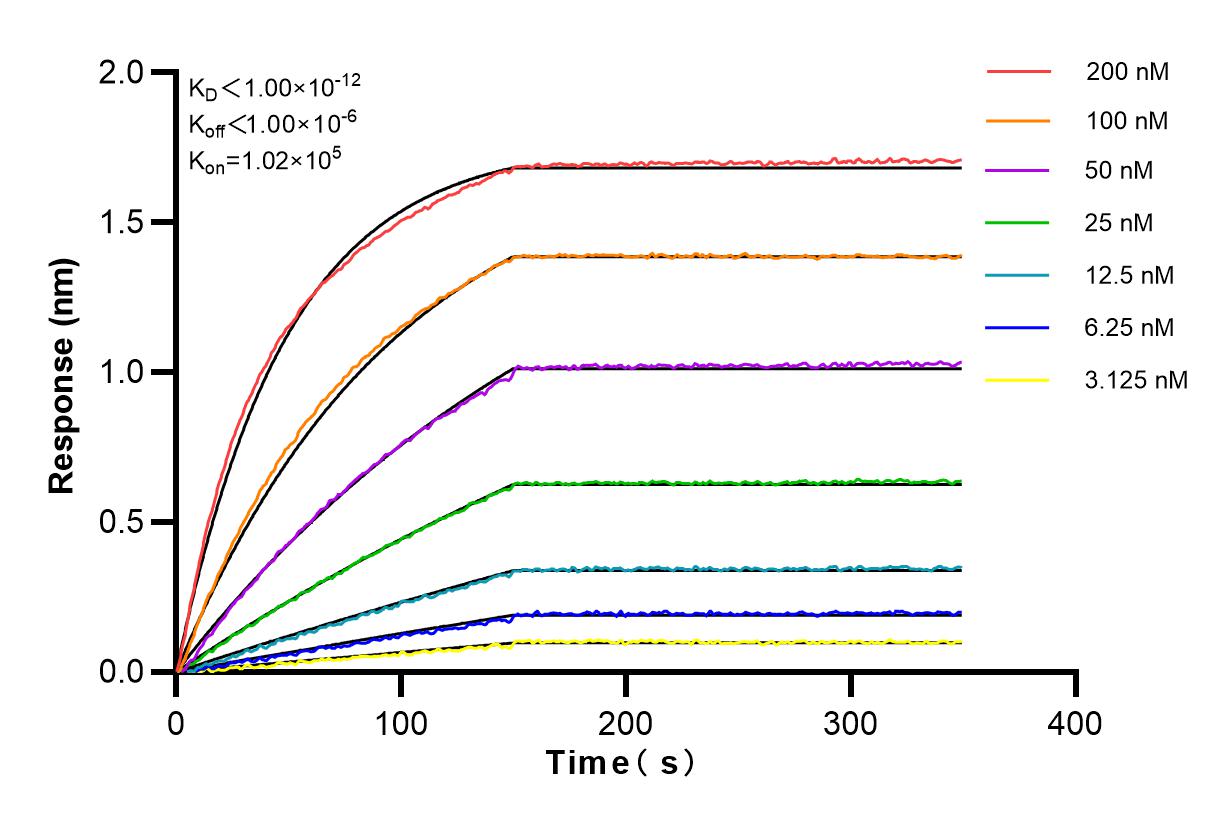
Product Information
82937-1-PBS targets TIP60/KAT5 in IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | TIP60/KAT5 fusion protein Ag1261 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | K(lysine) acetyltransferase 5 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 60 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC000166 |
| Gene Symbol | KAT5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10524 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q92993 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
KAT5, also named as The histone acetyltransferase (HAT) Tat interactive protein 60 kD belongs to the MYST protein family that contains atypical zinc finger and histone acetyltransferase domains. Also, KAT5 contains a chromodomain. KAT5 is a catalytic subunit of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex. The NuA4 HAT complex plays a role in transcriptional activation of select genes mainly by acetylation of nucleosomal histone H4 and H2A, which influence nucleosome-DNA interaction and promotes interaction of the modified histones with other proteins that could regulate transcription positively. This complex also involves in the activation of transcriptional programs associated with oncogene and proto-oncogene mediated growth induction, tumor suppressor mediated growth arrest and replicative senescence, DNA repair and apoptosis.