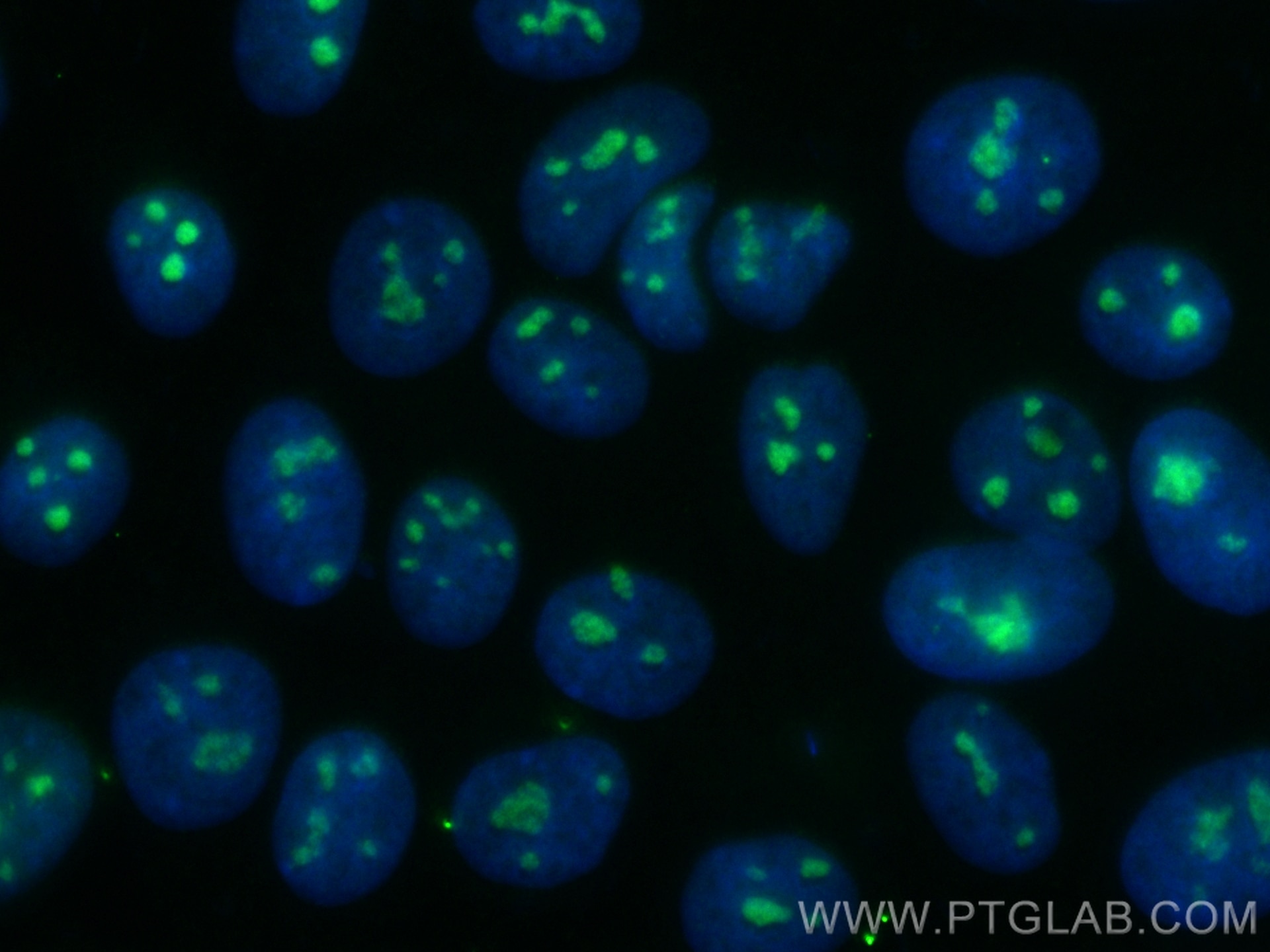
Tested Applications
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | MCF-7 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL488-84636 targets TERT in IF/ICC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 127 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_198255 |
| Gene Symbol | TERT |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7015 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O14746 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) is a catalytic subunit of telomerase. TERT plays a key role in cancer formation, ensuring chromosomal stability by maintaining telomere length, and allowing cells to avert senescence. It constitutes a limiting factor for formation of the telomerase complex in cancer cells. TERT is one of two major components of the larger telomerase complex, which extends telomeres by adding specific short repetitive DNA sequences. Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme essential for the replication of chromosome termini in most eukaryotes. Active in progenitor and cancer cells. Inactive, or very low activity, in normal somatic cells.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 TERT antibody CL488-84636 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |