Tested Applications
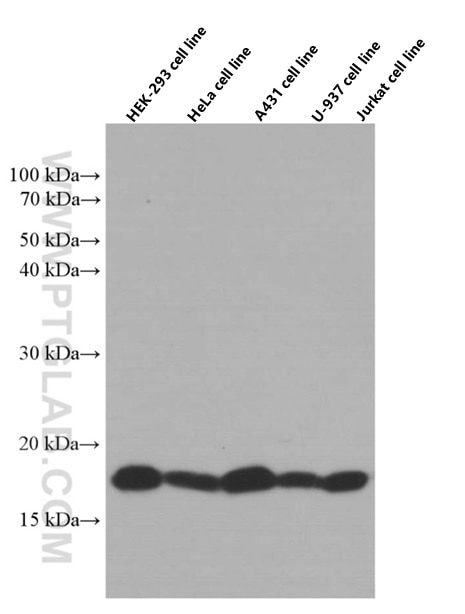
| Positive WB detected in | HEK-293 cells, Raji cells, K-562 cells, HeLa cells, A431 cells, U-937 cells, Jurkat cells |
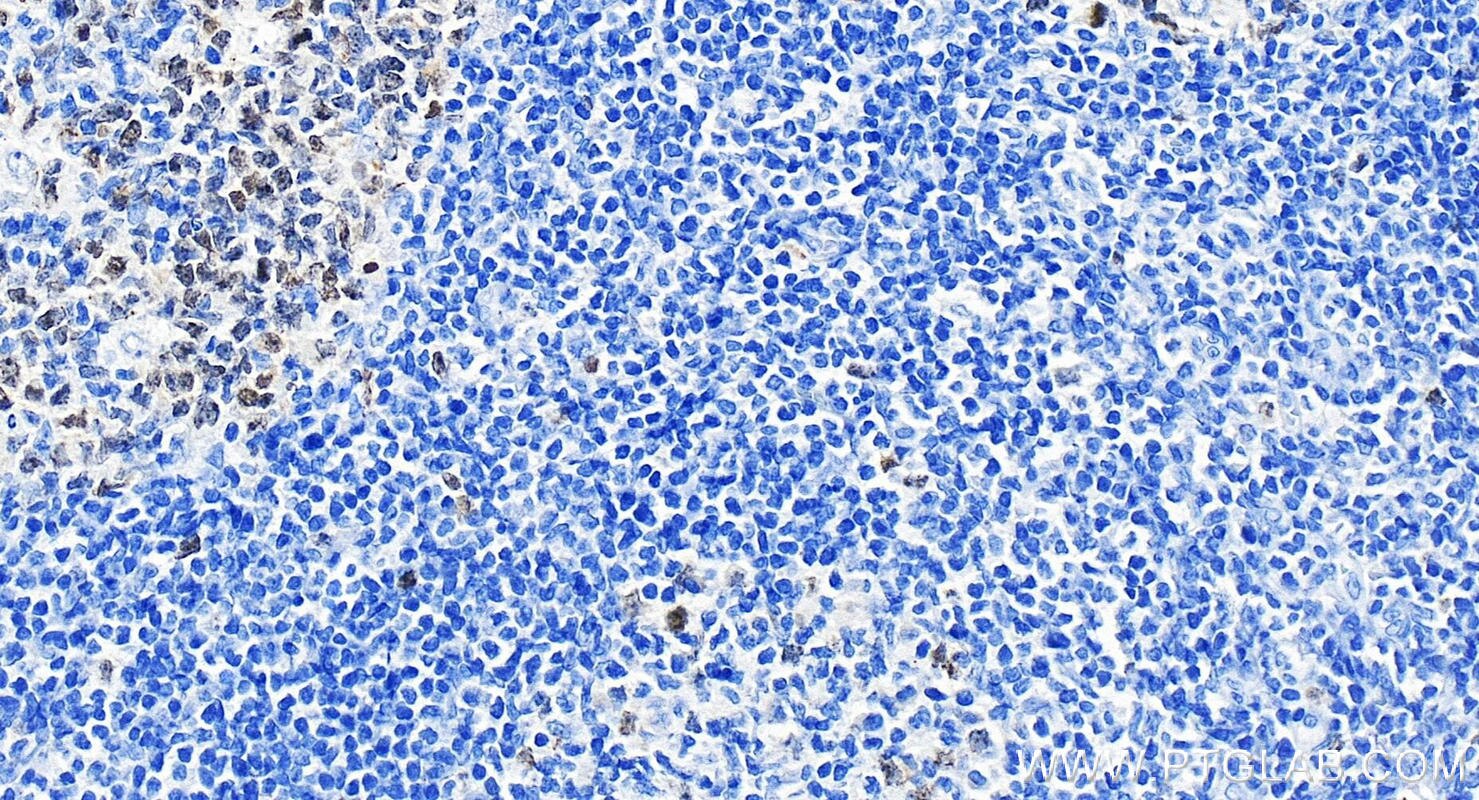
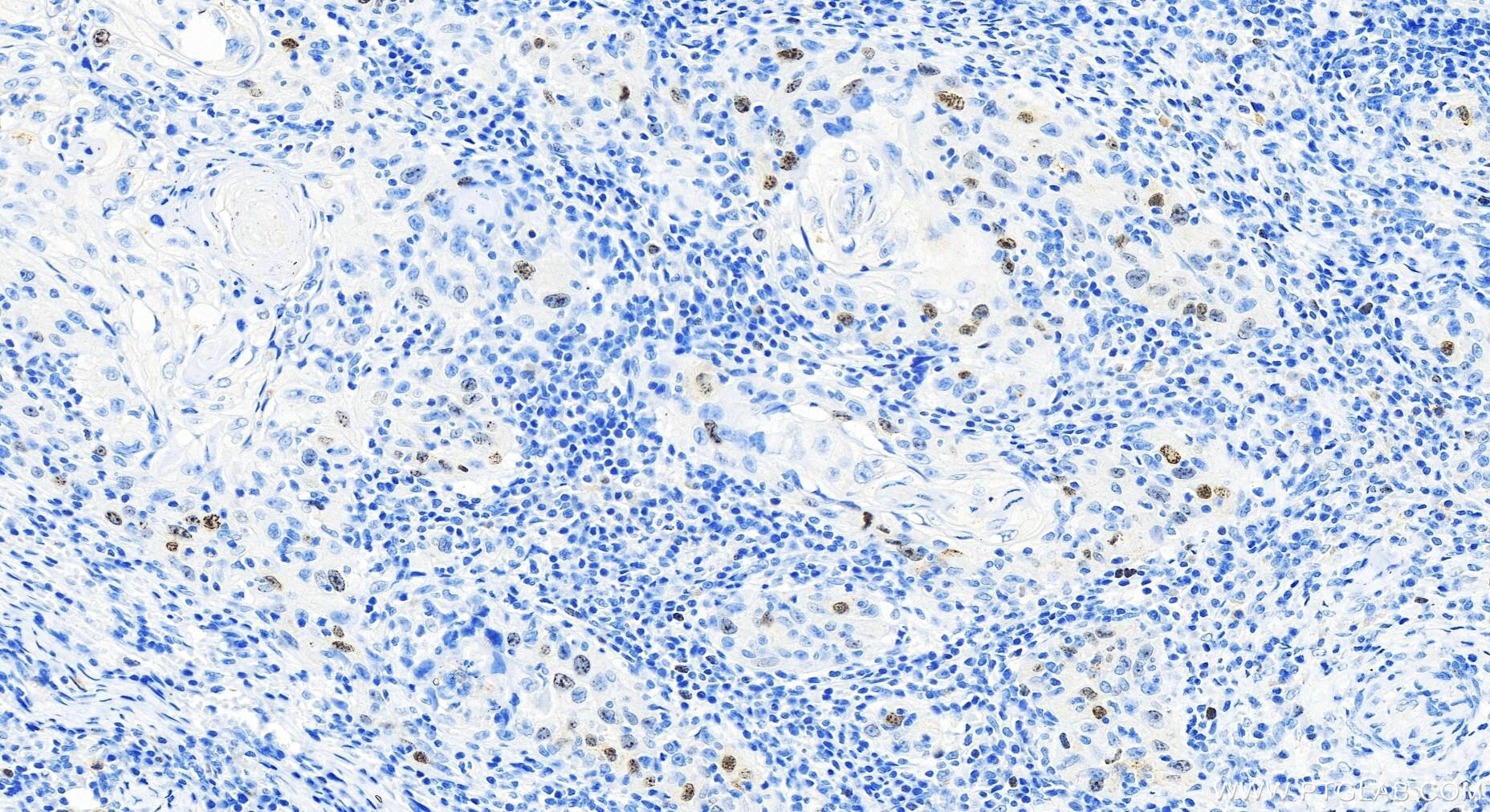
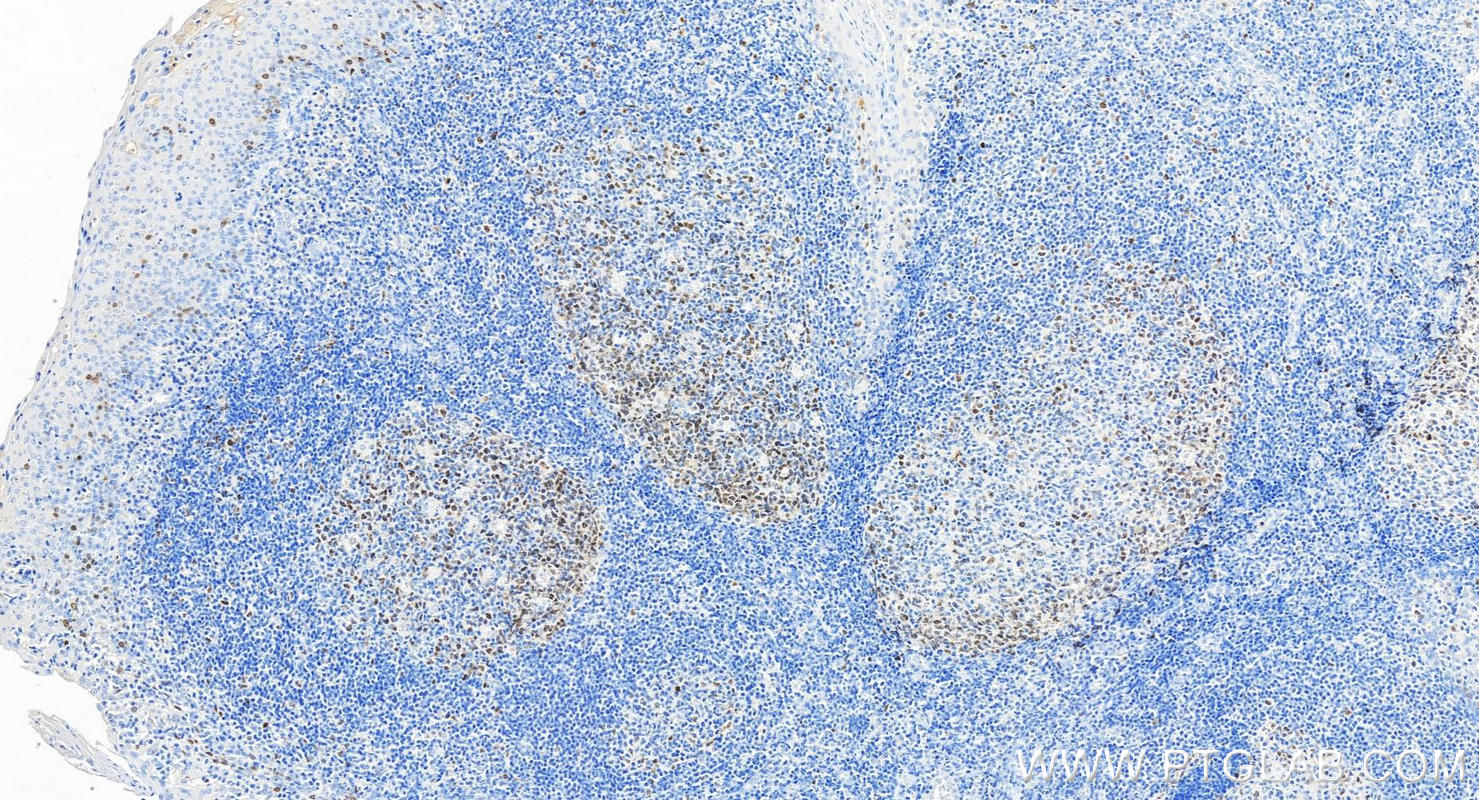
| Positive IHC detected in | human tonsillitis tissue, human skin cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 10 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
66495-1-Ig targets SURVIVIN in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | SURVIVIN fusion protein Ag20958 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 16 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 18 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC008718 |
| Gene Symbol | Survivin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 332 |
| RRID | AB_2881860 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O15392 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Survivin, also called BIRC5, is a unique member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein family. Survivin is a 16 kDa anti-apoptotic protein highly expressed during fetal development and cancer cell malignancy, but is completely absent in terminally differentiated cells. The differential expression of survivin in cancer versus normal tissues makes it a useful tool in cancer diagnosis and a promising therapeutic target. Survivin expression is also highly regulated by the cell cycle and is only expressed in the G2-M phase. It is known that survivin localizes to the mitotic spindle by interaction with tubulin during mitosis and may play a contributing role in regulating mitosis. Disruption of survivin-microtubule interactions results in loss of survivin's anti-apoptosis function and increased caspase-3 activity, a mechanism involved in cell death, during mitosis. It also is a direct target gene of the Wnt pathway and is upregulated by beta-catenin.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SURVIVIN antibody 66495-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for SURVIVIN antibody 66495-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Phytomedicine Astragaloside Ⅳ negatively regulates Gpr97-TPL2 signaling to protect against hyperhomocysteine-exacerbated sepsis associated acute kidney injury | ||
Bioeng Transl Med Multistage targeting and dual inhibiting strategies based on bioengineered tumor matrix microenvironment-mediated protein nanocages for enhancing cancer biotherapy. | ||
Exp Mol Med m 6 A-mediated upregulation of AC008 promotes osteoarthritis progression through the miR-328-3p‒AQP1/ANKH axis | ||
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) Proliferation inhibition and apoptosis promotion by dual silencing of VEGF and Survivin in human osteosarcoma.
| ||
Front Oncol Synergistic effects of nab-PTX and anti-PD-1 antibody combination against lung cancer by regulating the Pi3K/AKT pathway through the Serpinc1 gene | ||
Front Pharmacol Analysis of regulating activities of 5'-epiequisetin on proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo |