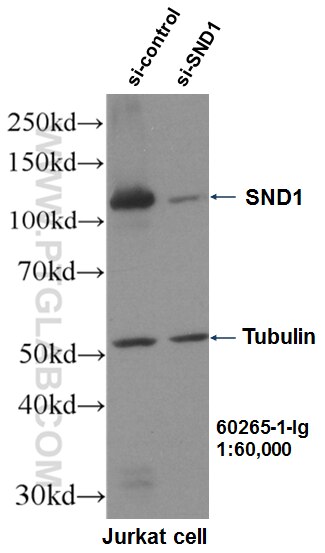
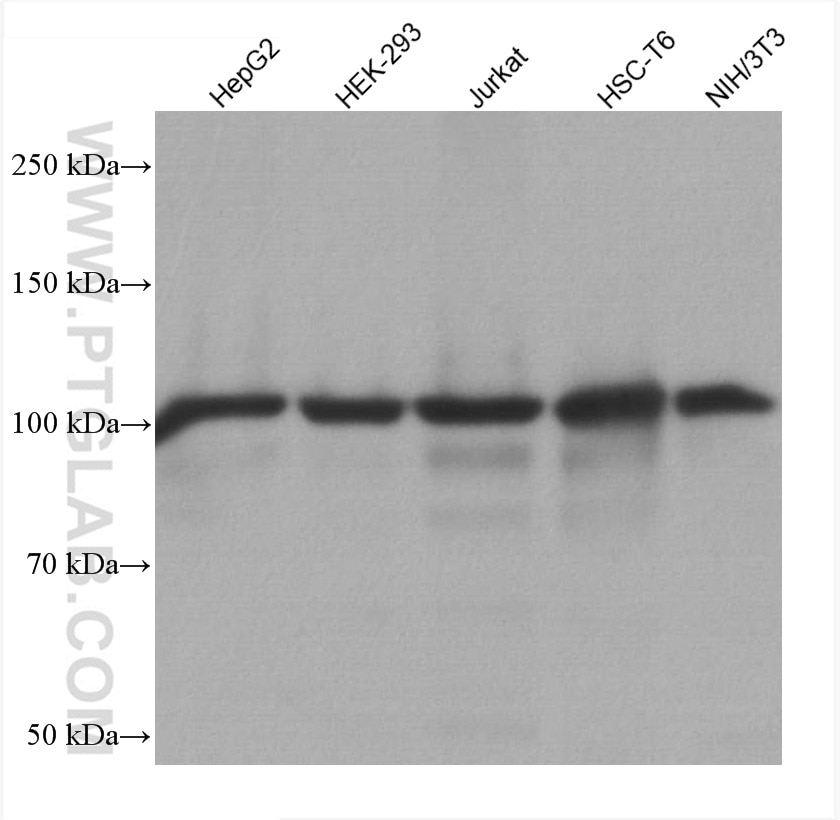
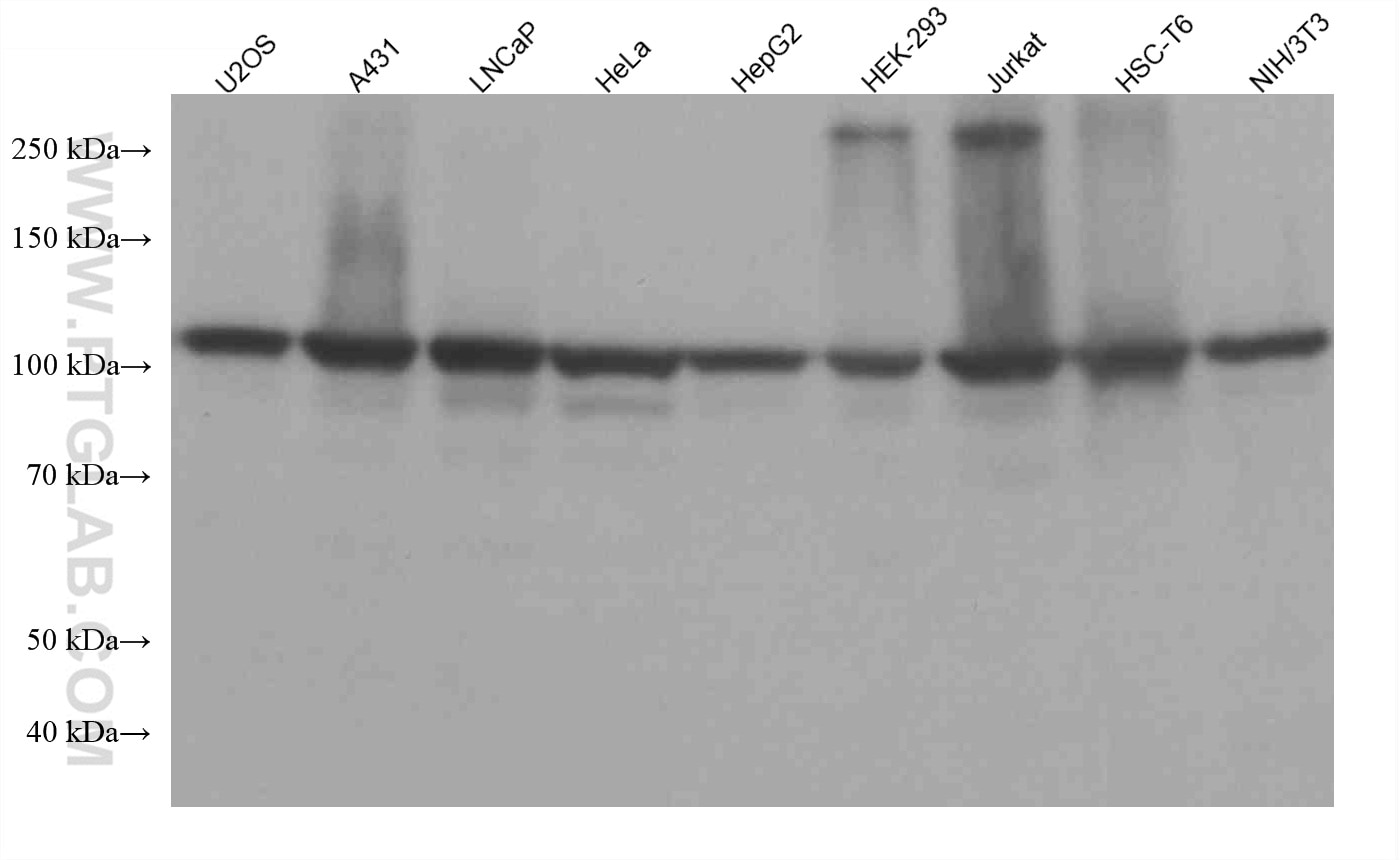
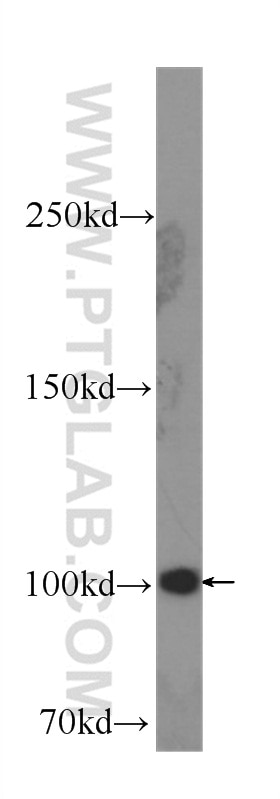
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | HepG2 cells, HeLa cells, Jurkat cells, U2OS cells, HEK-293 cells, HSC-T6 cells, NIH/3T3 cells, A431 cells, LNCaP cells |
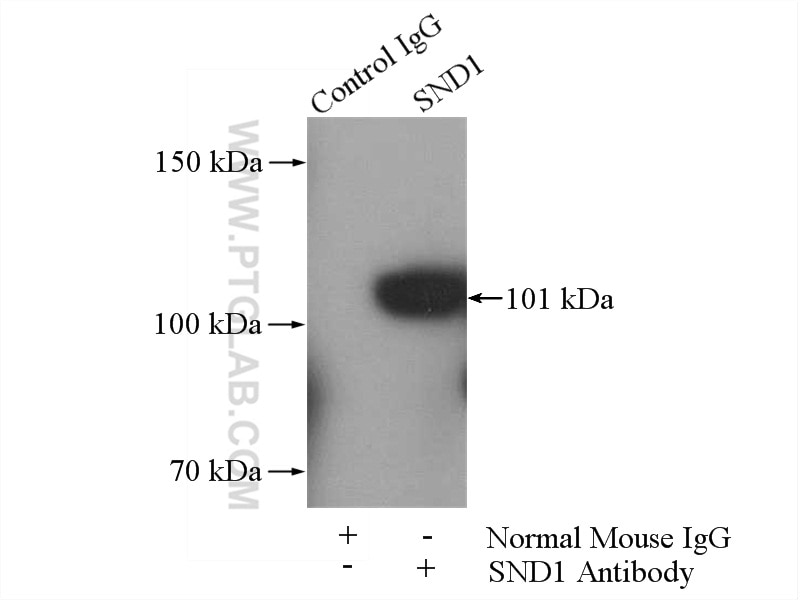
| Positive IP detected in | HeLa cells |
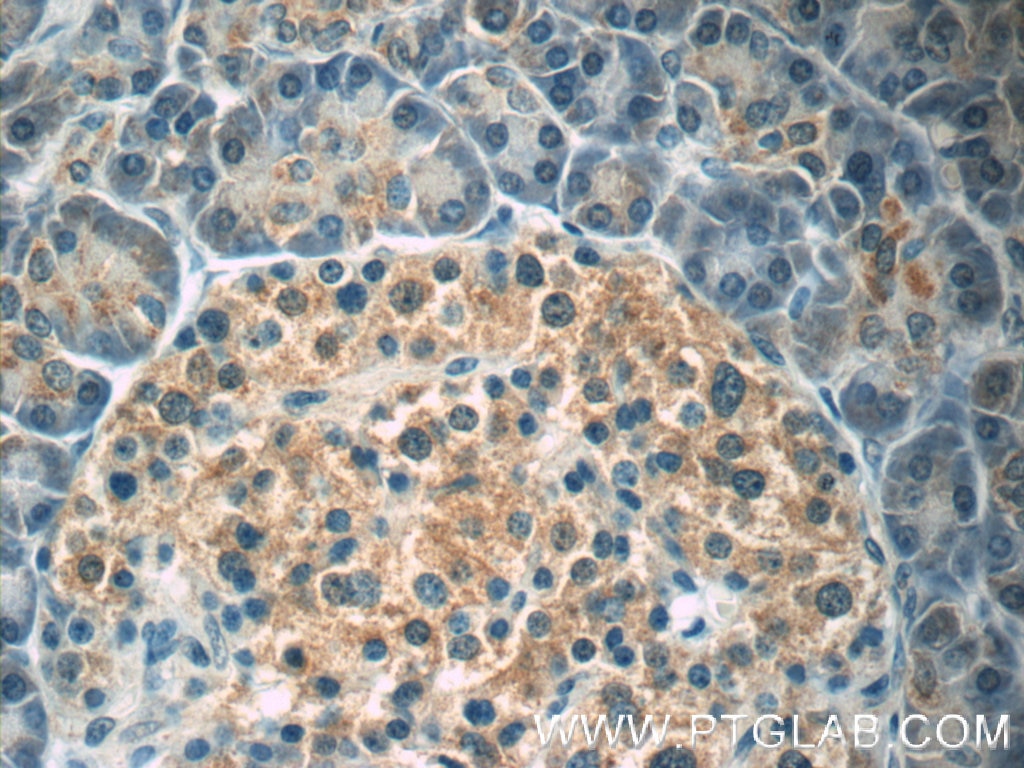
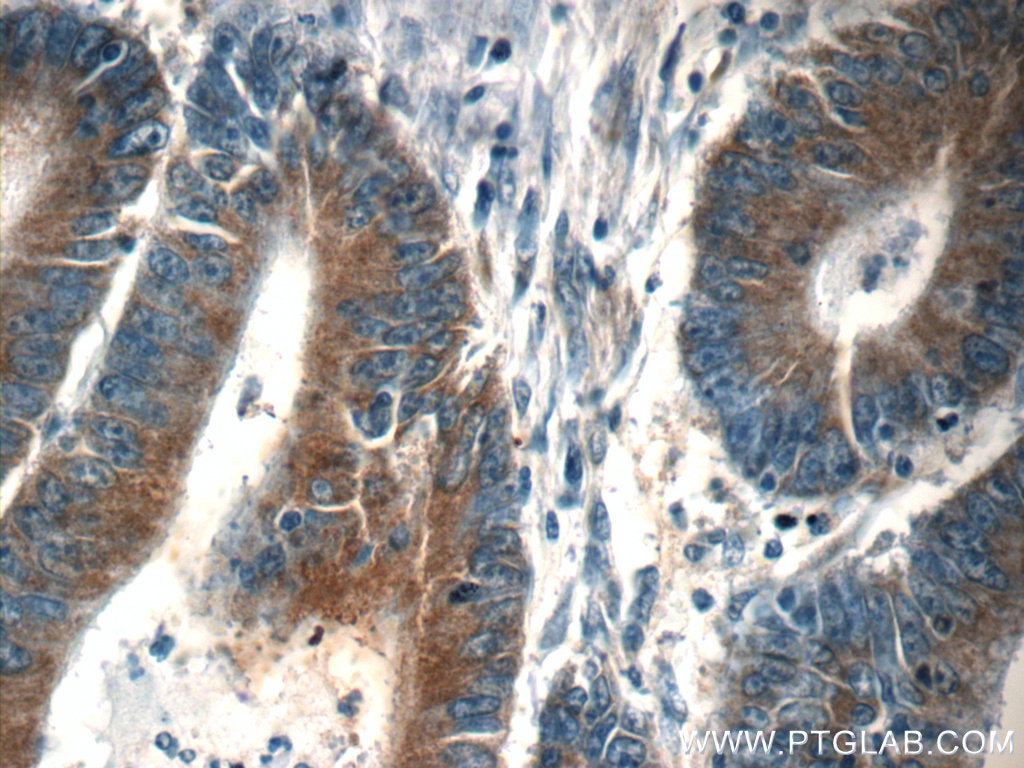
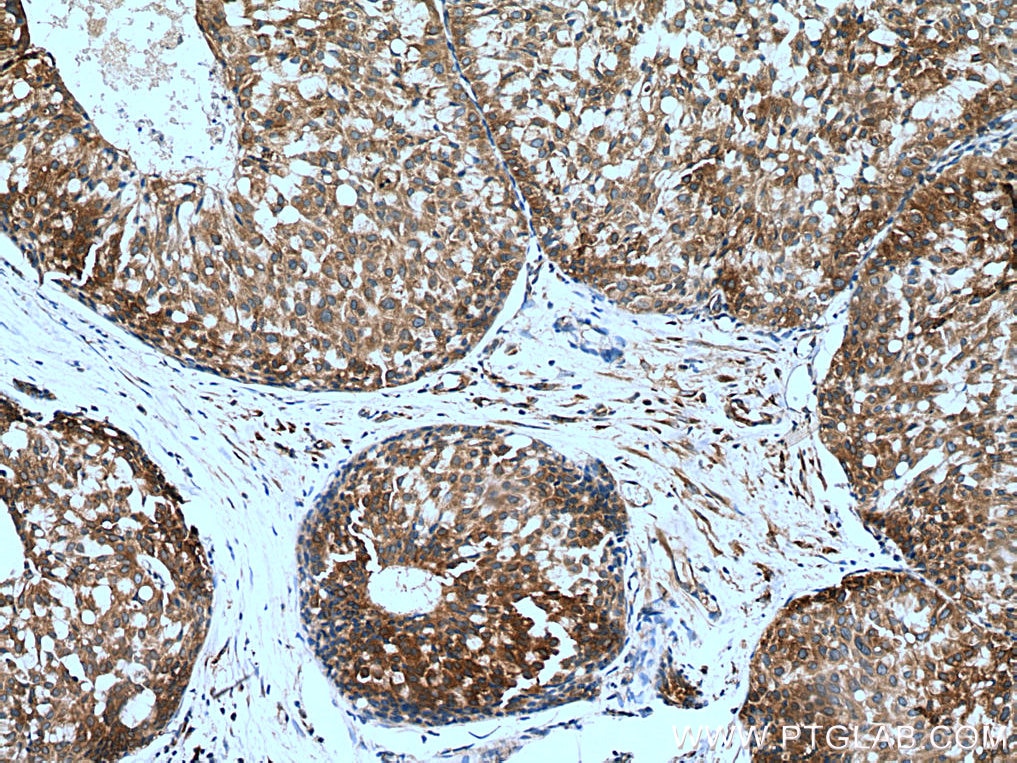
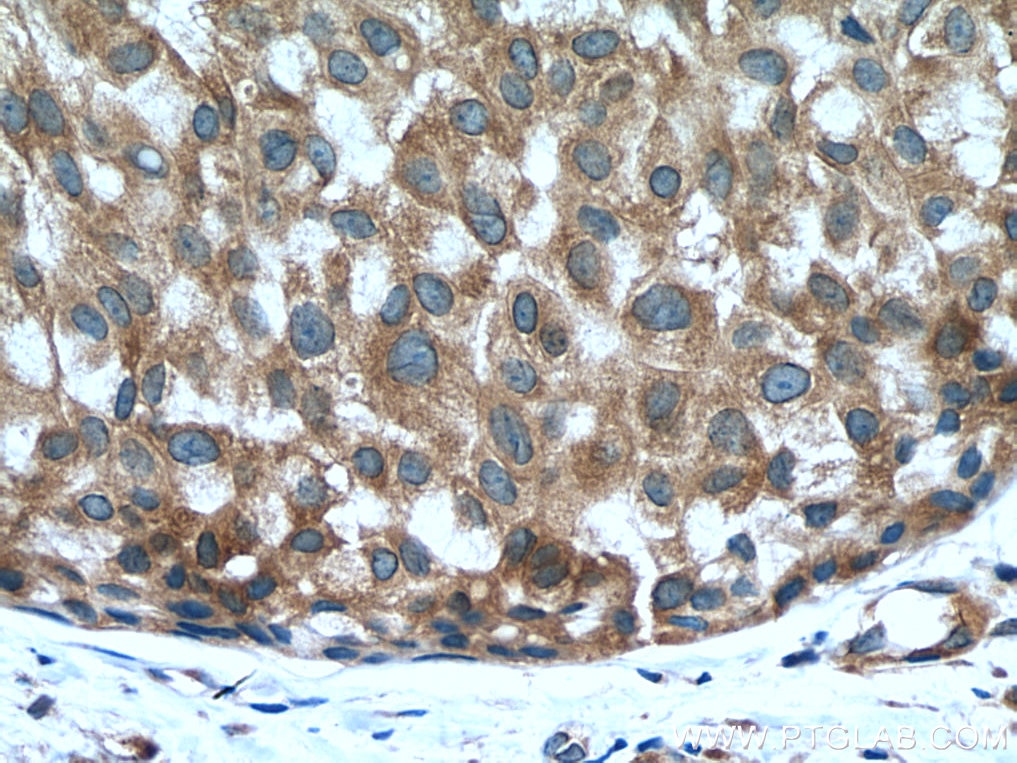
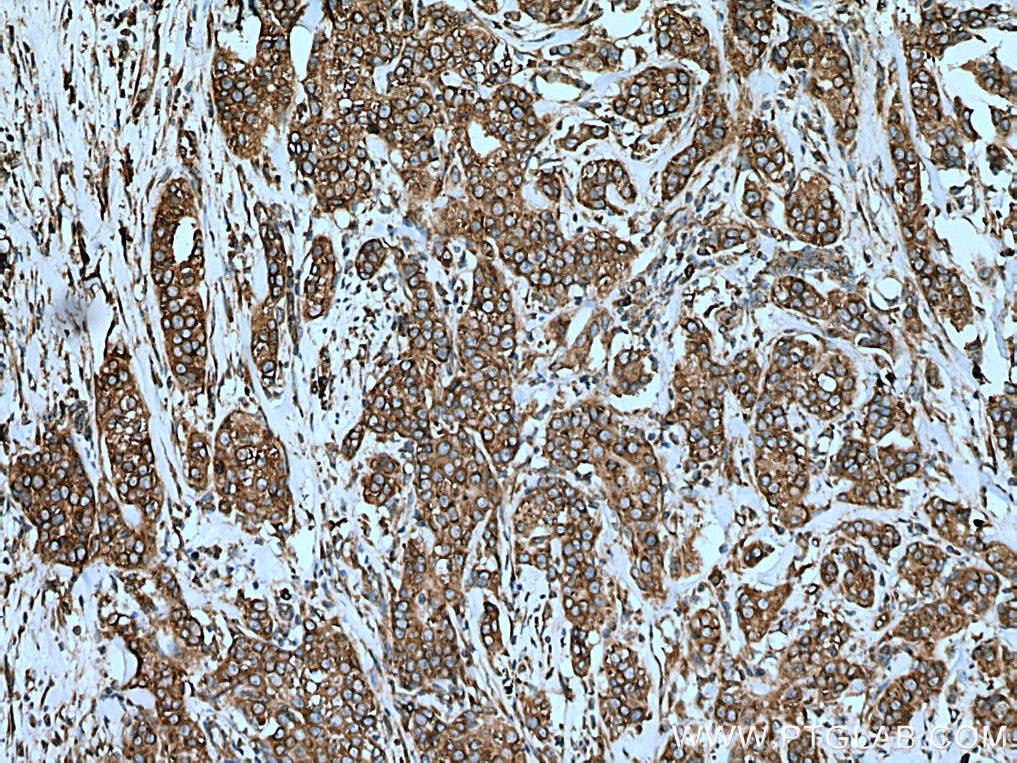
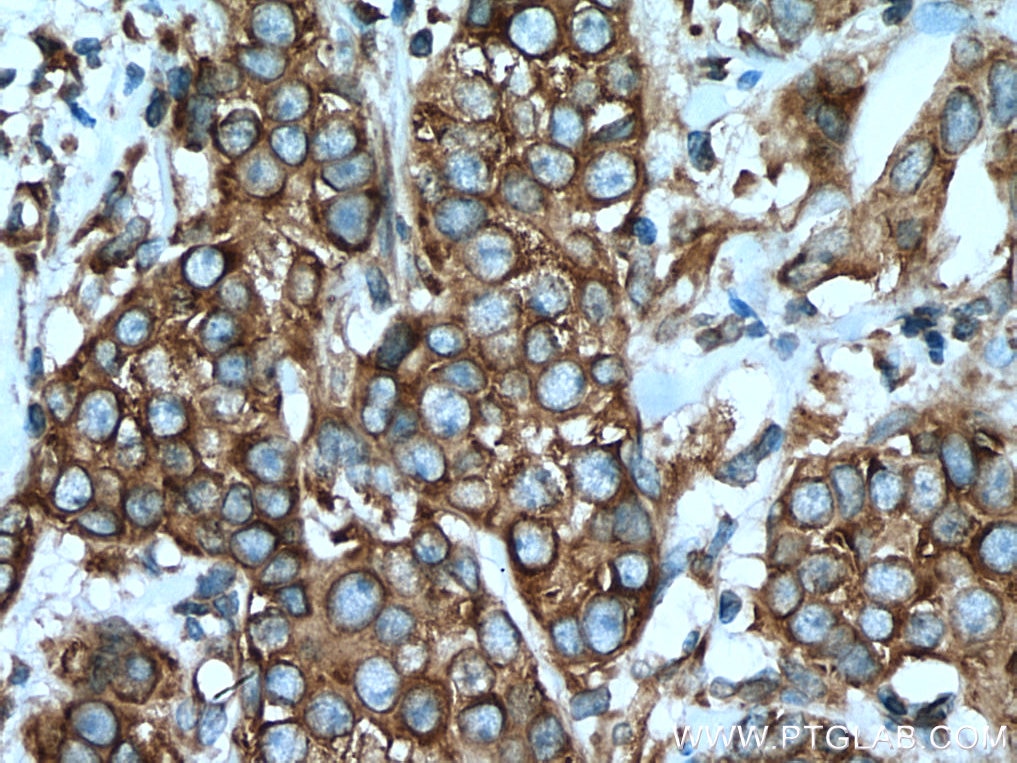
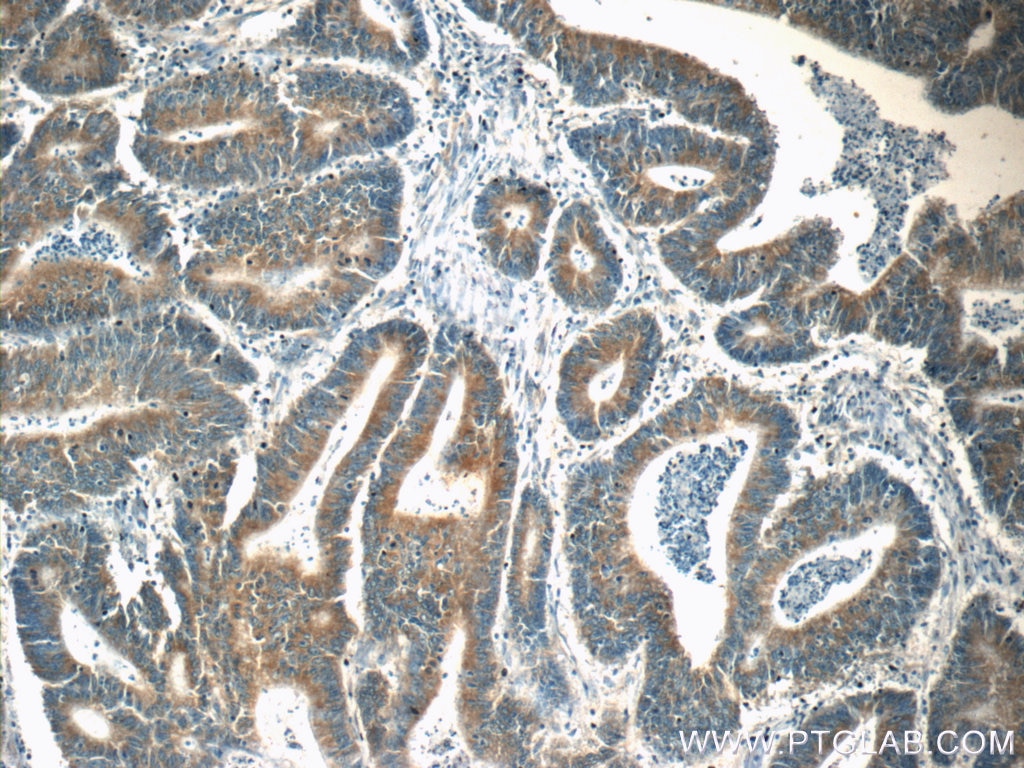
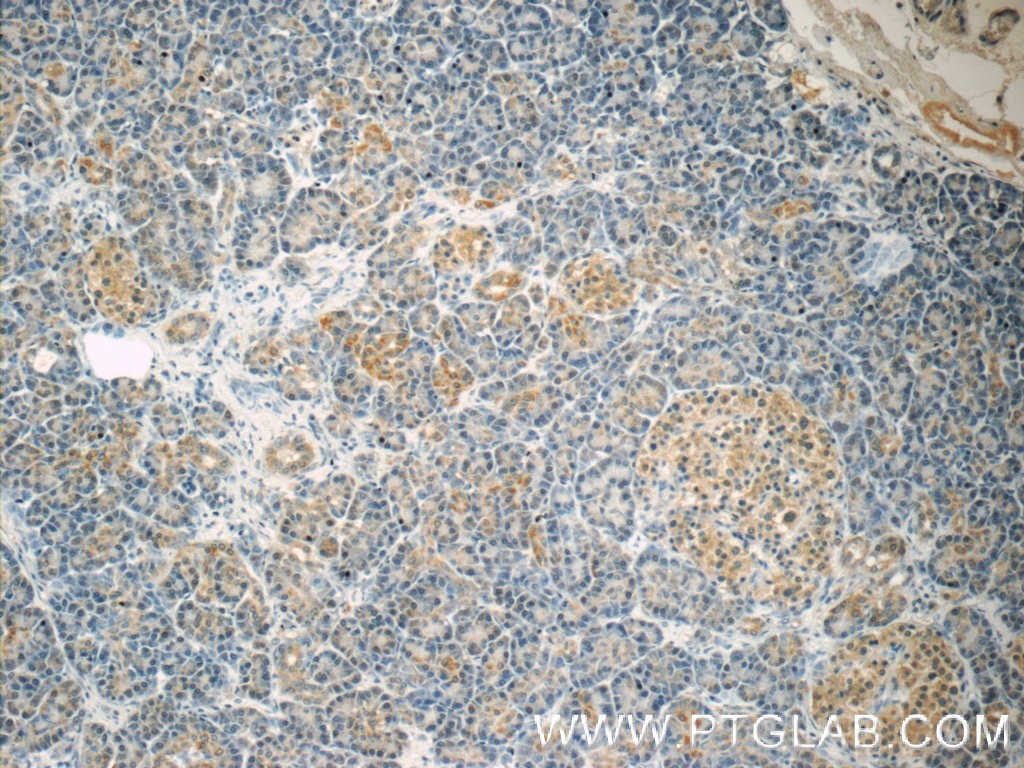
| Positive IHC detected in | human pancreas tissue, human breast hyperplasia tissue, human breast cancer tissue, human colon cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
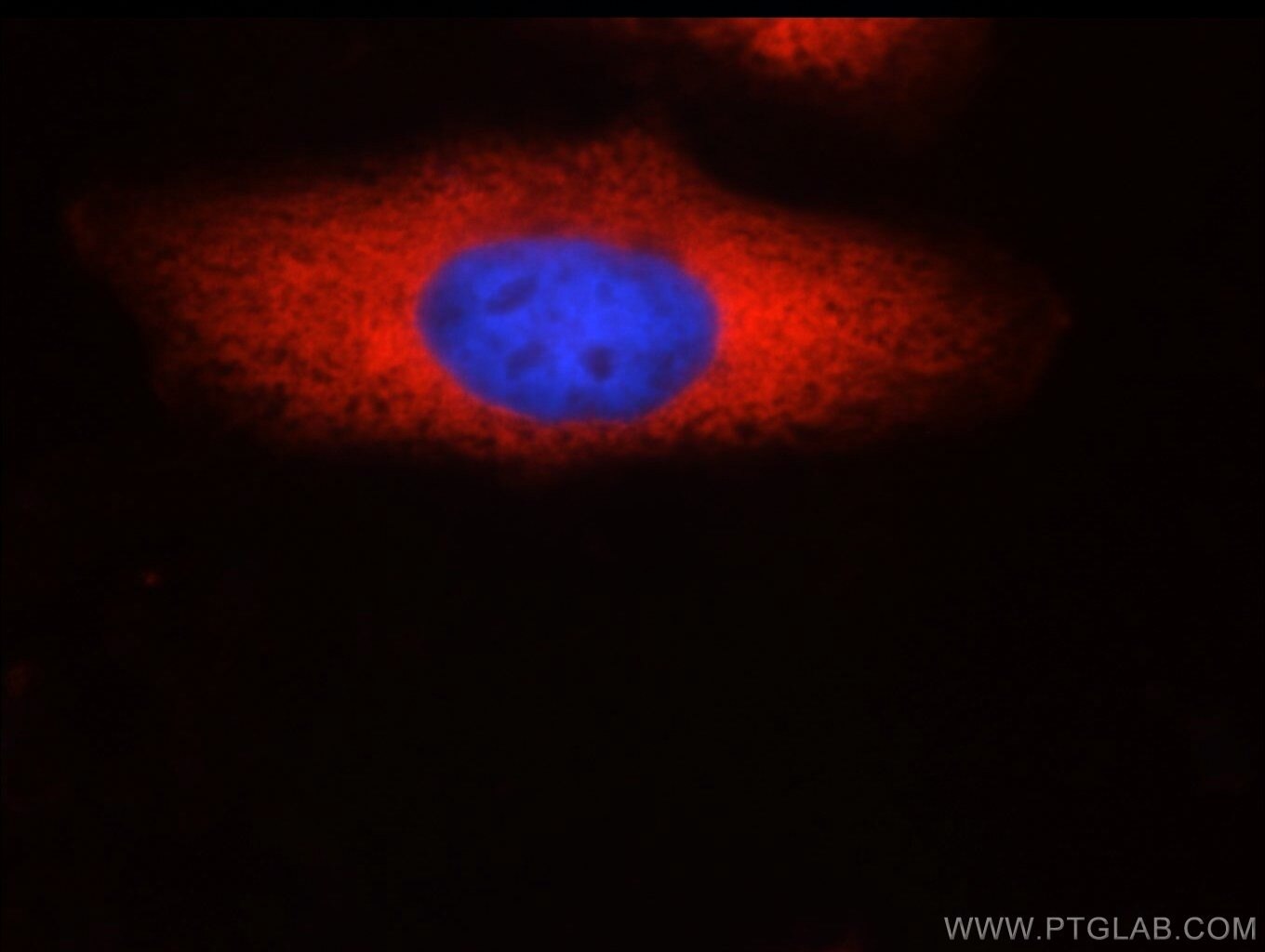
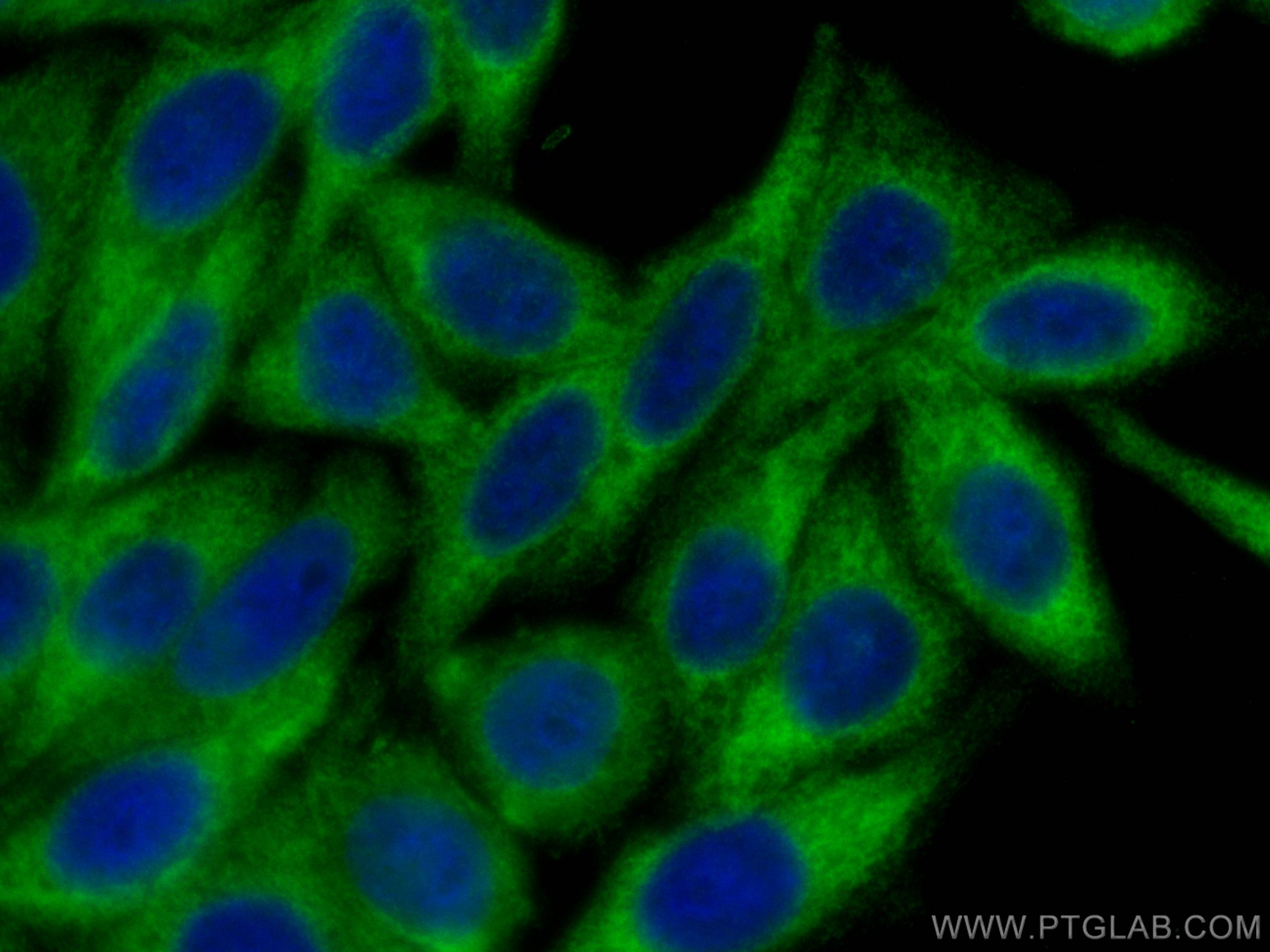
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 8 publications below |
| IF | See 5 publications below |
| ELISA | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
60265-1-Ig targets SND1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag1200 Product name: Recombinant human SND1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 548-911 aa of BC017180 Sequence: TCLITFLLAGIECPRGARNLPGLVQEGEPFSEEATLFTKELVLQREVEVEVESMDKAGNFIGWLHIDGANLSVLLVEHALSKVHFTAERSSYYKSLLSAEEAAKQKKEKVWAHYEEQPVEEVMPVLEEKERSASYKPVFVTEITDDLHFYVQDVETGTQLEKLMENMRNDIASHPPVEGSYAPRRGEFCIAKFVDGEWYRARVEKVESPAKIHVFYIDYGNREVLPSTRLGTLSPAFSTRVLPAQATEYAFAFIQVPQDDDARTDAVDSVVRDIQNTQCLLNVEHLSAGCPHVTLQFADSKGDVGLGLVKEGLVMVEVRKEKQFQKVITEYLNAQESAKSARLNLWRYGDFRADDADEFGYSR Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | staphylococcal nuclease and tudor domain containing 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 101 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 101 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC017180 |
| Gene Symbol | SND1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 27044 |
| RRID | AB_2881386 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q7KZF4 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing 1 (SND1), is a multifunctional nuclease that consists of four staphylococcal nuclease domains and a tudor domain. SND1 acts as a coactivator that facilitates transcriptional activity of STAT5, 6 and c-Myc. SND1 is a comprising part of the RNA-induced silencing complex(RISC), and takes part in the functions of miRNA, regulates transcription through transcriptional coactivation, RNA interference, RNA splicing, and RNA editing. Higher level of SND1 has been found in colon cancer and prostate cancer, can promote HCC angiogenesis in xenograft model through induction of angiogenic factors.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for SND1 antibody 60265-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for SND1 antibody 60265-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for SND1 antibody 60265-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for SND1 antibody 60265-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell SND1 binds SARS-CoV-2 negative-sense RNA and promotes viral RNA synthesis through NSP9 | ||
Sci Adv Oncoprotein SND1 hijacks nascent MHC-I heavy chain to ER-associated degradation, leading to impaired CD8+ T cell response in tumor. | ||
Sci Adv Oncoprotein SND1 hijacks nascent MHC-I heavy chain to ER-associated degradation, leading to impaired CD8+ T cell response in tumor. | ||
Elife The Tudor SND1 protein is an m6A RNA reader essential for replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.
| ||
J Cell Physiol The phosphorylation of Tudor-SN mediated by JNK is involved in the regulation of milk protein synthesis induced by prolactin in BMECs. |