Tested Applications
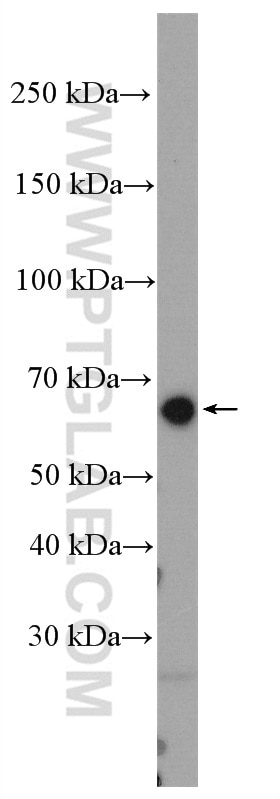
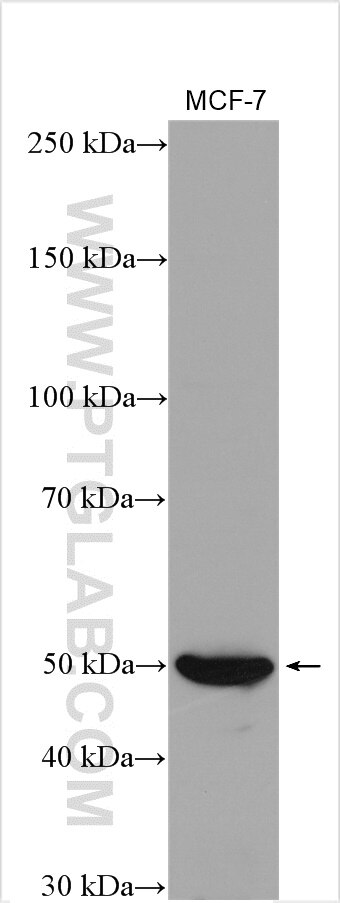
| Positive WB detected in | ROS1728 cells, MCF-7 cells |
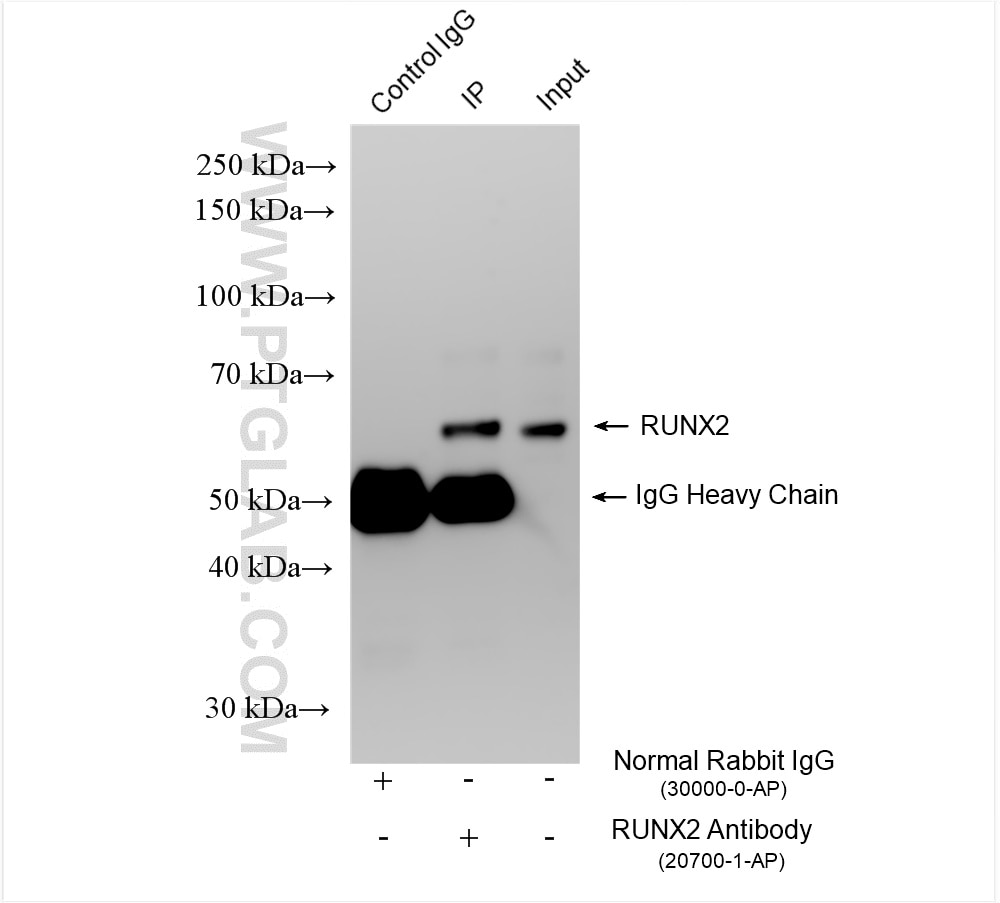
| Positive IP detected in | ROS1728 cells |
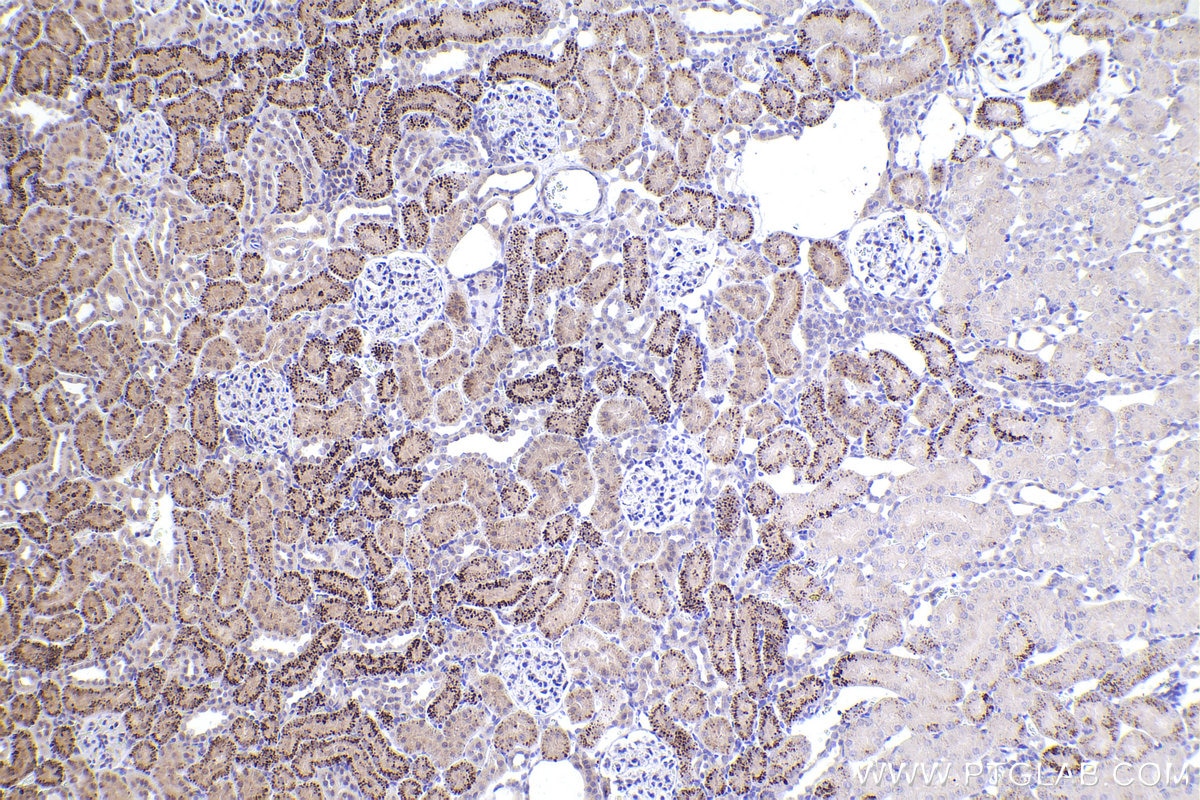
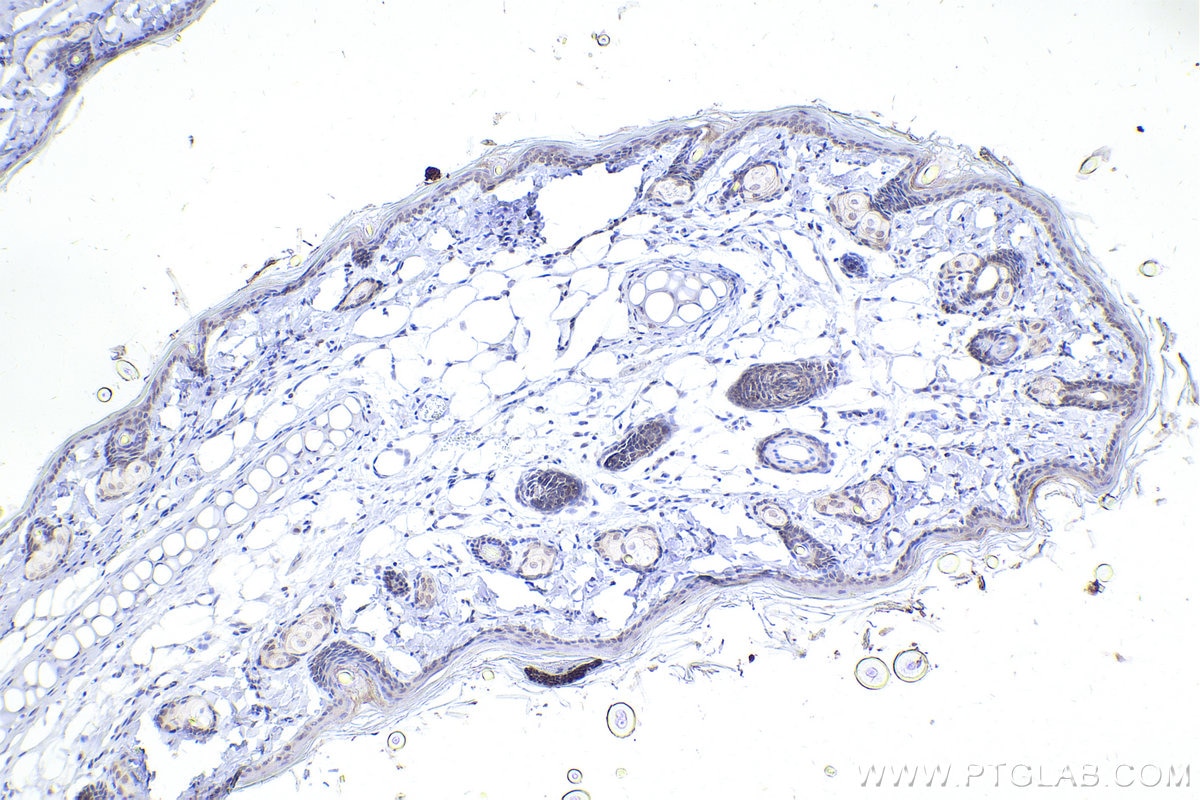
| Positive IHC detected in | rat skin tissue, rat kidney tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
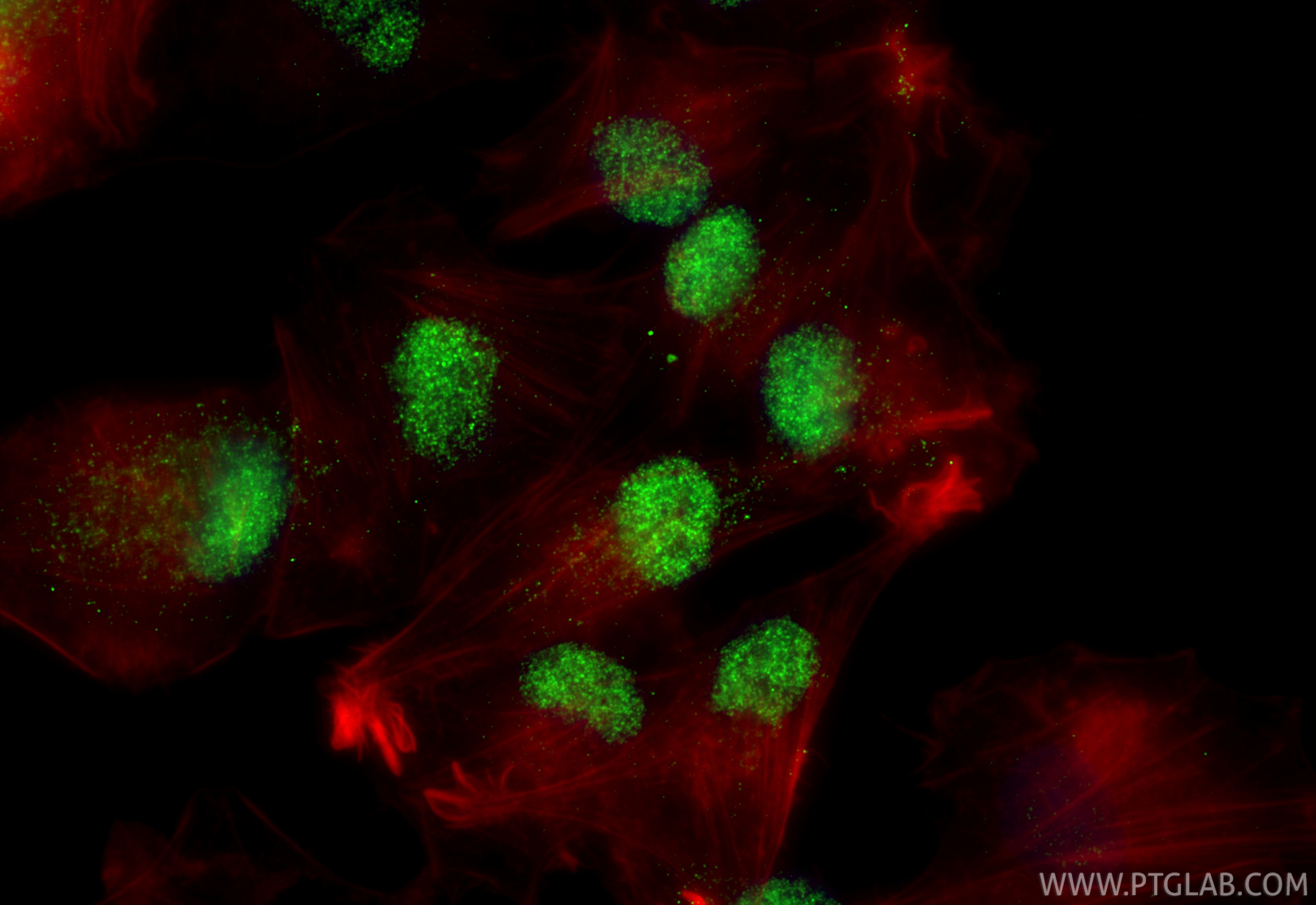
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | ROS1728 cells |
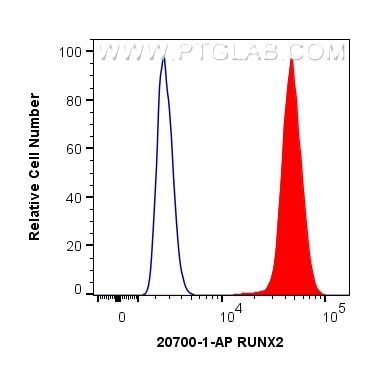
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:200-1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 4 publications below |
| WB | See 209 publications below |
| IHC | See 34 publications below |
| IF | See 56 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| ChIP | See 3 publications below |
Product Information
20700-1-AP targets RUNX2 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, chIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit, chicken |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | runt-related transcription factor 2 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 57 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 57-60 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_004348 |
| Gene Symbol | RUNX2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 860 |
| RRID | AB_2722783 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q13950 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
RUNX2, also named as AML3, CBFA1, OSF2 and PEBP2A, is a Transcription factor which involved in osteoblastic differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis. It is essential for the maturation of osteoblasts and both intramembranous and endochondral ossification. CBF binds to the core site, 5'-PYGPYGGT-3', of a number of enhancers and promoters, including murine leukemia virus, polyomavirus enhancer, T-cell receptor enhancers, osteocalcin, osteopontin, bone sialoprotein, alpha 1(I) collagen, LCK, IL-3 and GM-CSF promoters By similarity. RUNX2 inhibits MYST4-dependent transcriptional activation. The antibody is specific to RUNX2.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for RUNX2 antibody 20700-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for RUNX2 antibody 20700-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for RUNX2 antibody 20700-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for RUNX2 antibody 20700-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for RUNX2 antibody 20700-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Bioact Mater 3D Printed Biomimetic Metamaterials with Graded Porosity and Tapering Topology for Improved Cell Seeding and Bone Regeneration | ||
Small Honeycomb Bionic Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot/Layered Double Hydroxide Composite Nanocoating Promotes Osteoporotic Bone Regeneration via Activating Mitophagy | ||
Sci Adv Multiomic identification of senescent stem cell populations critical for osteoarthritis progression and therapy in subchondral bones | ||
Redox Biol Endogenous hydrogen sulfide accelerated trauma-induced heterotopic ossification through the Ca2+/ERK pathway-enhanced aberrant osteogenic activity | ||
Mater Today Bio Sustained release of naringin from silk-fibroin-nanohydroxyapatite scaffold for the enhancement of bone regeneration. | ||
Mater Today Bio A biomimetic multimodal nanoplatform combining neutrophil-coated two-dimensional metalloporphyrinic framework nanosheet and exendin-4 to treat obesity-related osteoporosis |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH YINGJIAN (Verified Customer) (08-15-2025) | high specificity, strong/robust signal, low background, consistent results, reproducible performance, good lot-to-lot consistency
 |