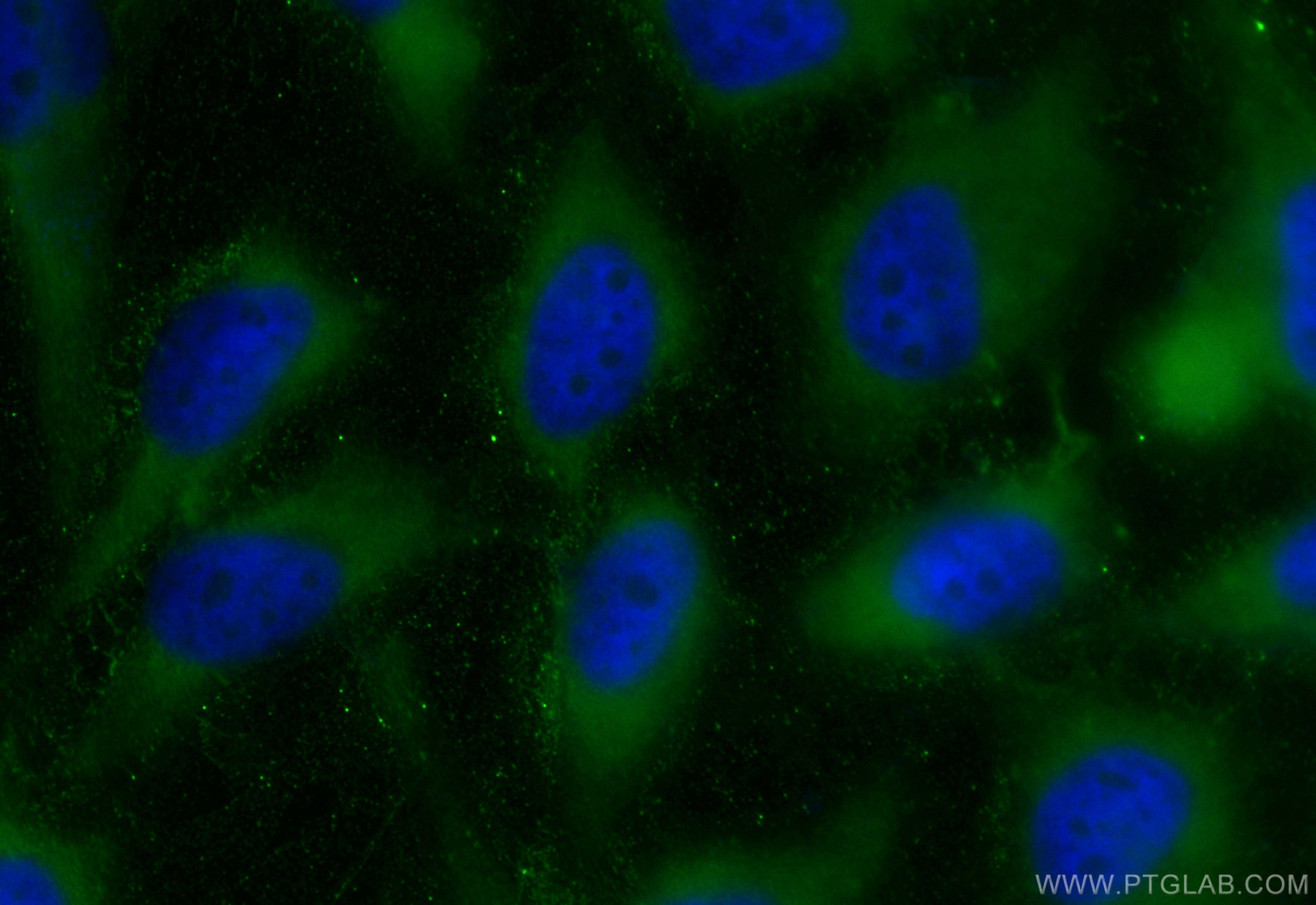
Tested Applications
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL488-84281-5 targets PFKM in IF/ICC applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | PFKM fusion protein Ag30840 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | phosphofructokinase, muscle |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 75-85 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC021203 |
| Gene Symbol | PFKM |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5213 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P08237 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
PFKM, also named as GSD7, PFK-1, PFK-M and PFKX, belongs to the phosphofructokinase family and two domains subfamily. PFKM catalyzes the reaction: ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. It is a key regulatory enzyme in glycolysis. Defects in PFKM cause glycogen storage disease type 7 (GSD7). PFKM has three isoforms with molecular weights of 85, 82, and 93 kDa.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 PFKM antibody CL488-84281-5 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |