Product Information
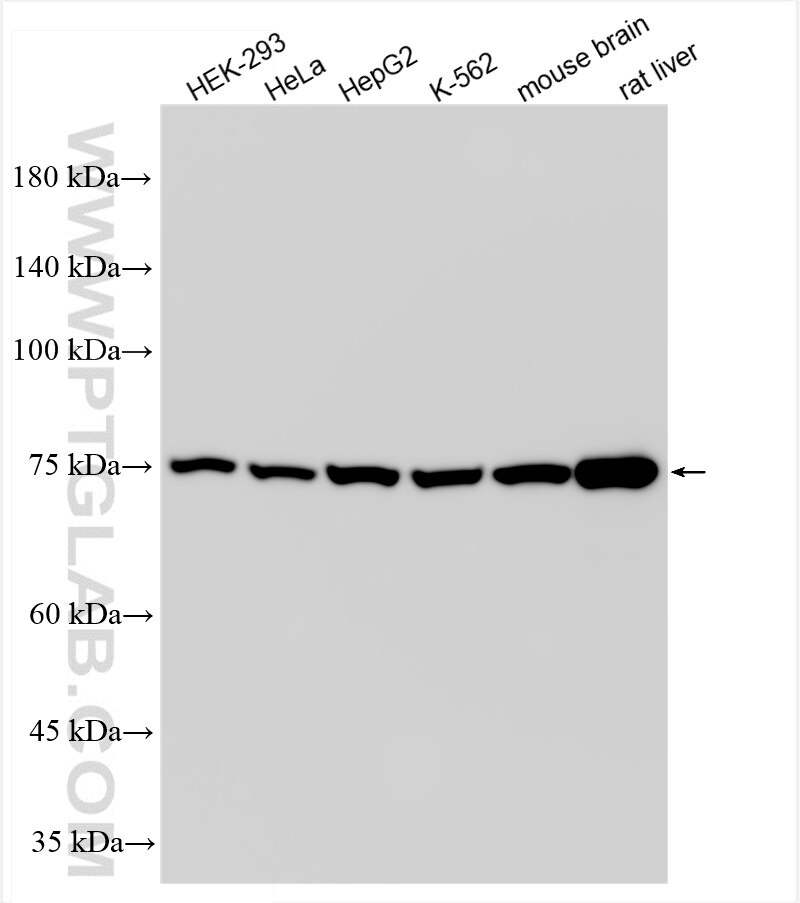
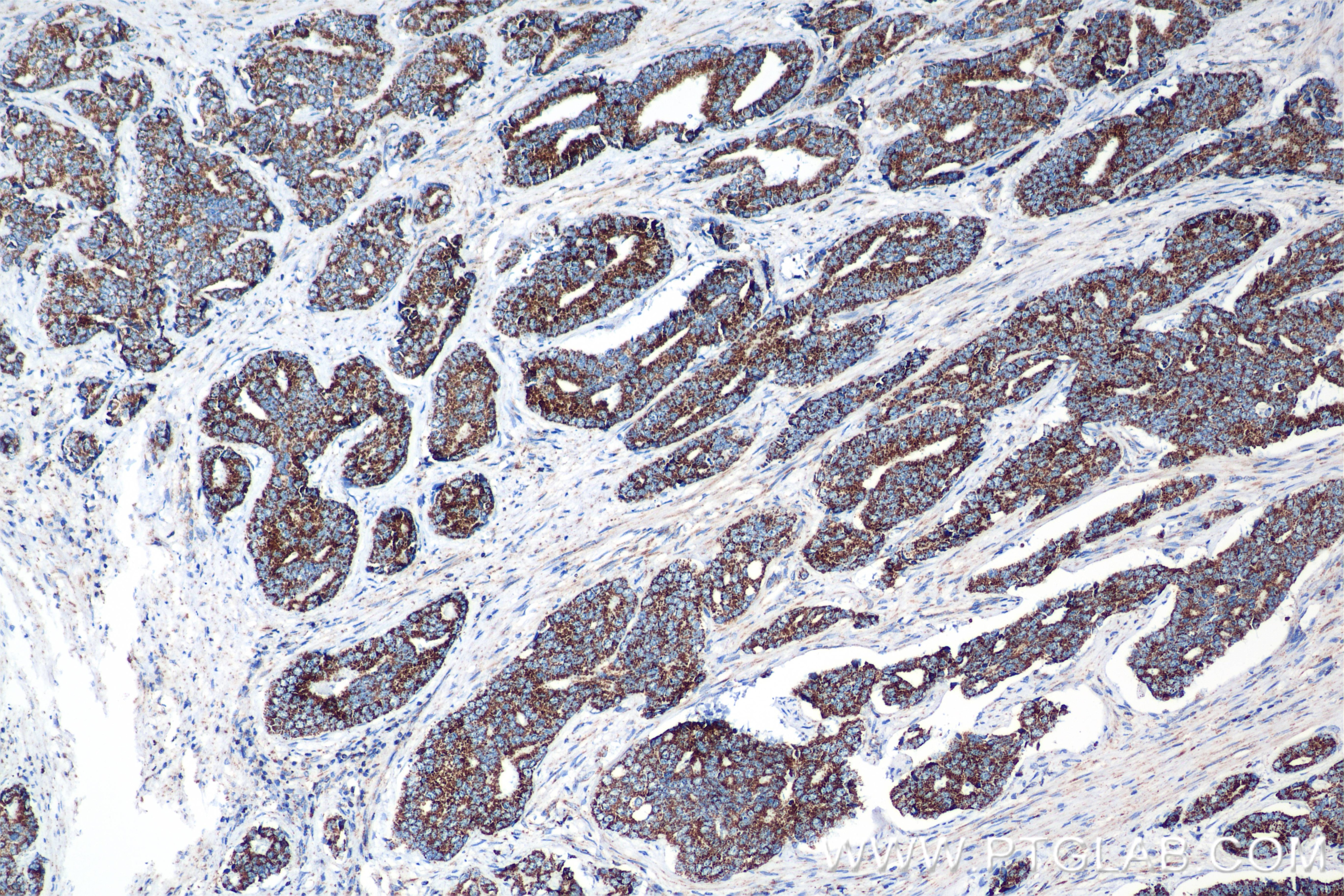
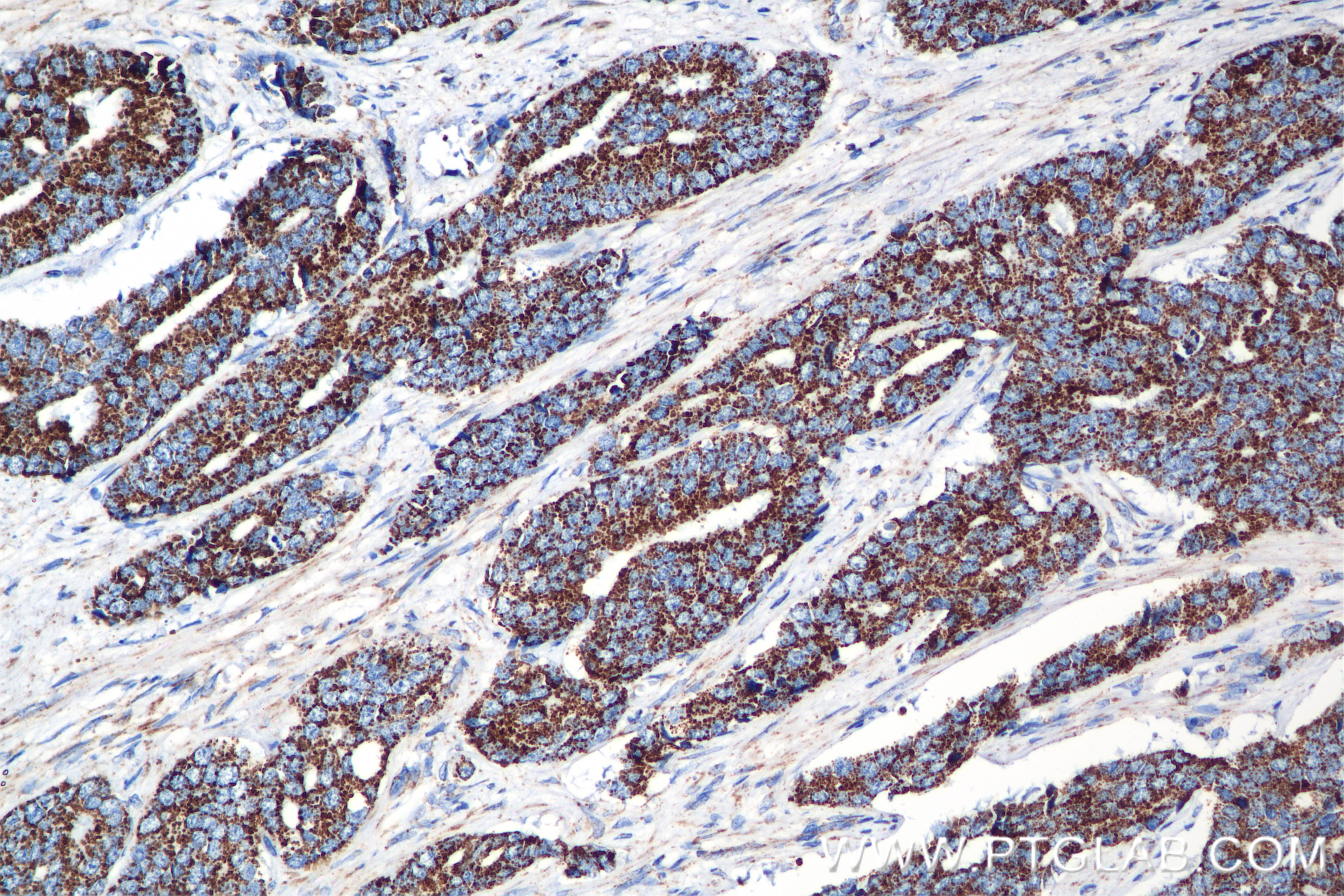
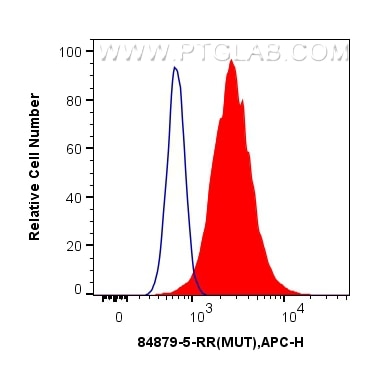
84879-5-PBS targets Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase/MUT fusion protein Ag10523 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 750 aa, 83 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 78 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC016282 |
| Gene Symbol | MUT |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4594 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P22033 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase (MUT) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of certain amino acids and fatty acids. Mutations in the MUT gene can lead to methylmalonic acidemia, a metabolic disorder characterized by the accumulation of toxic compounds such as methylmalonyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA. This condition can cause severe health issues including developmental delays, metabolic acidosis, and neurological problems. MUT is essential for maintaining normal metabolic processes and its dysfunction can have significant health implications, highlighting its importance in both basic metabolism and clinical medicine.