Tested Applications
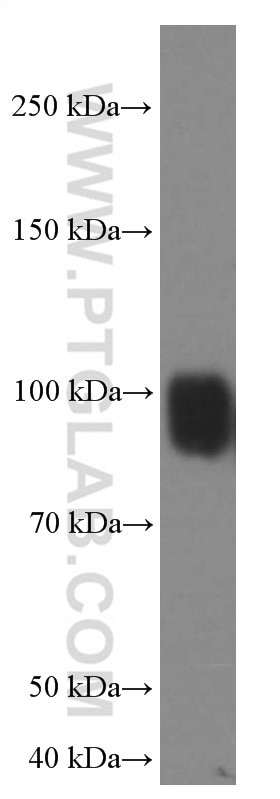
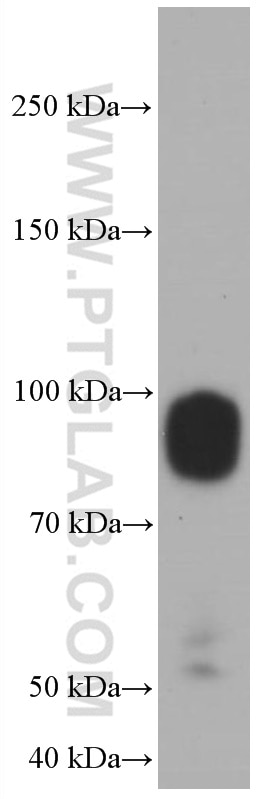
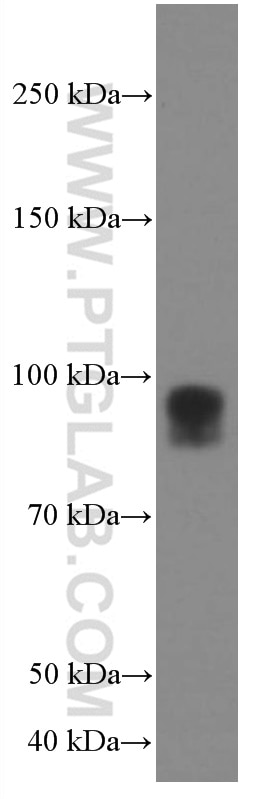
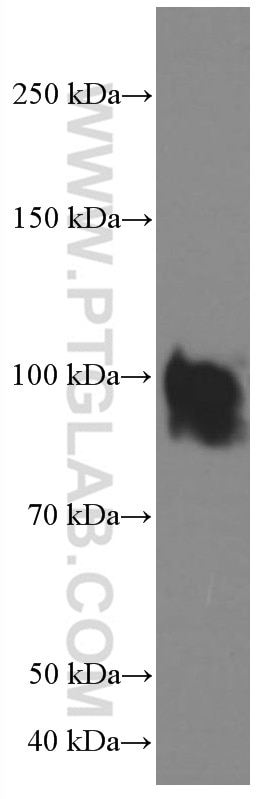
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, HEK-293 cells, T-47D cells, Jurkat cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
66704-1-Ig targets IFNGR1 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | IFNGR1 fusion protein Ag27085 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | interferon gamma receptor 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 54 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 90 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC005333 |
| Gene Symbol | IFNGR1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3459 |
| RRID | AB_2882056 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P15260 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is a cytokine critical for innate and adaptive immunity against viral and intracellular bacterial infections and for tumor control. Cellular responses to IFN-γ are activated through its interaction with a heterodimeric receptor consisting of two subunits, IFNGR1 (CD119) and IFNGR2. IFNGR1 is the ligand-binding subunit which binds IFN-γ with high affinity, whereas IFNGR2 serves as the accessory subunit. Two subunits bind one IFN-γ dimer. Defects in IFNGR1 are a cause of mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD), also known as familial disseminated atypical mycobacterial infection. (PMID: 17981204; 946248; 10888113)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for IFNGR1 antibody 66704-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |