Product Information
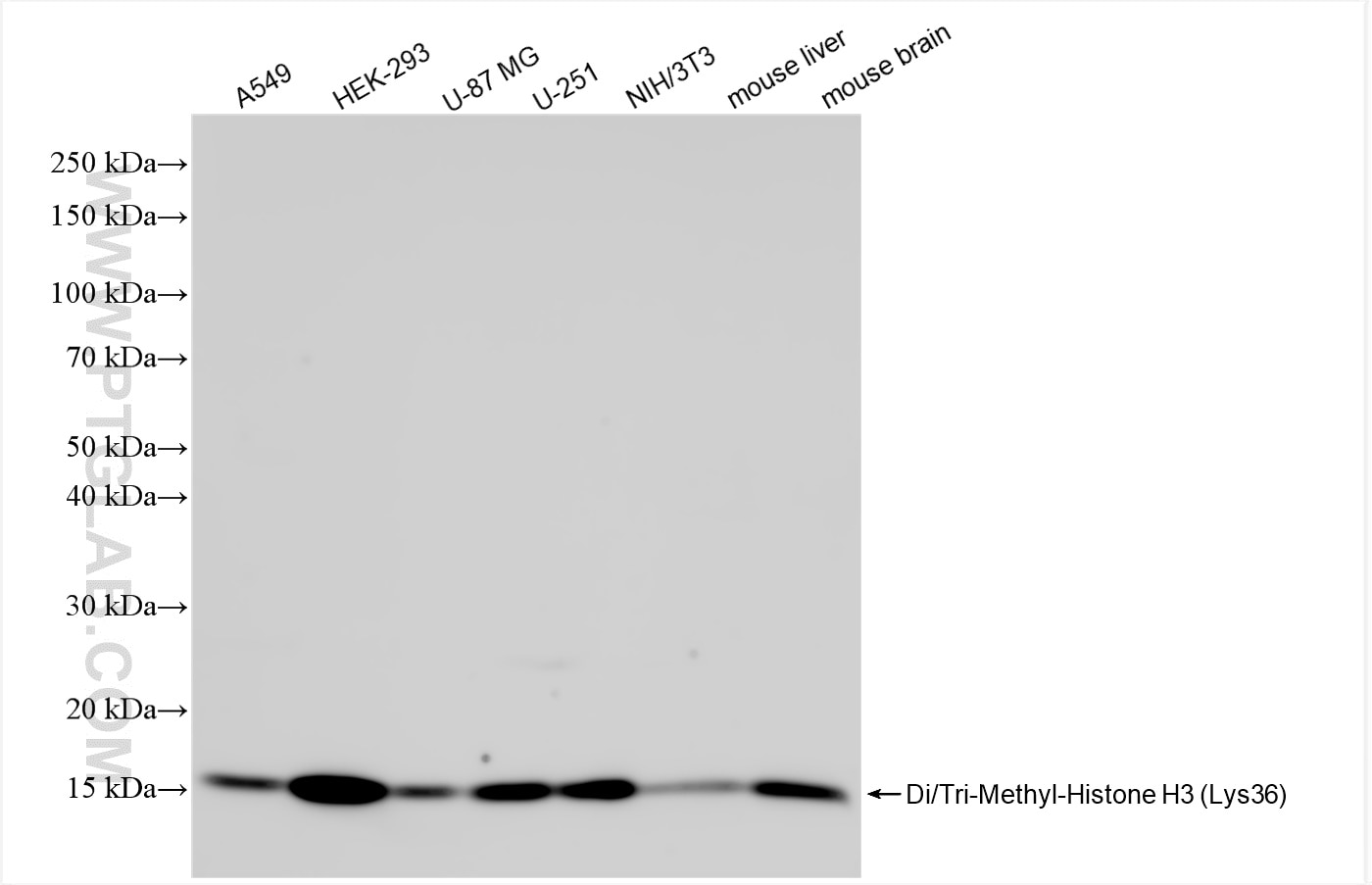
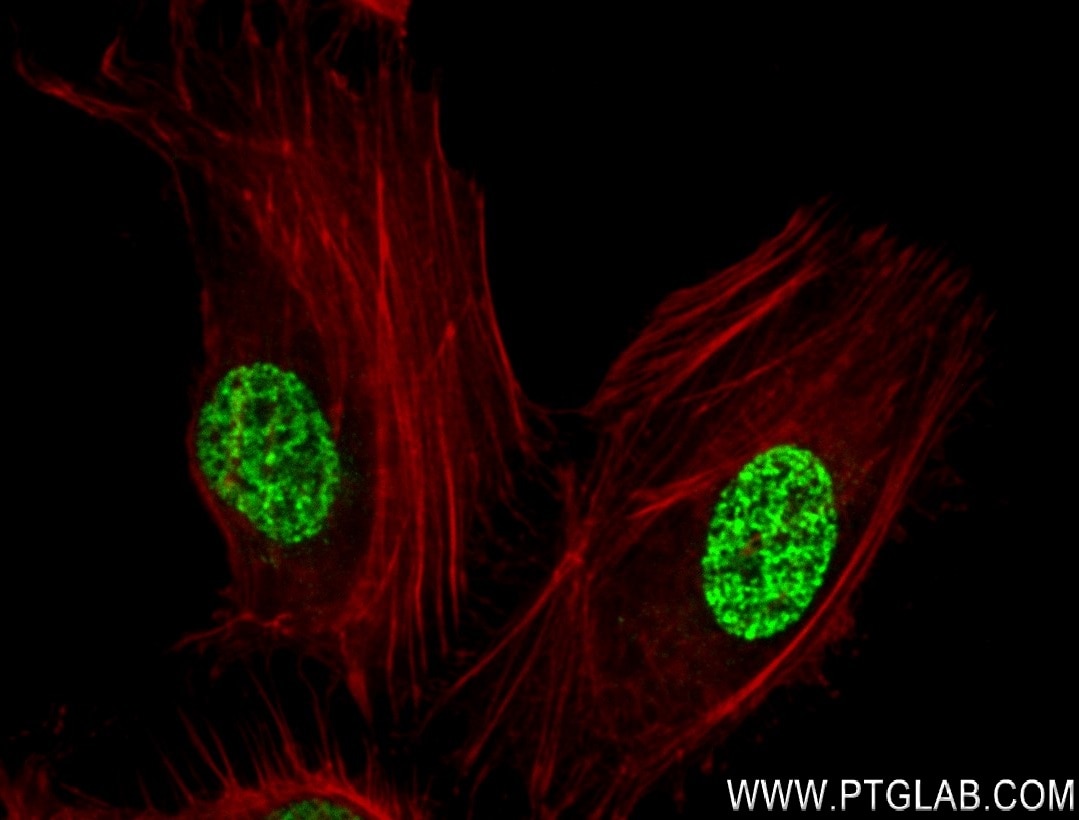
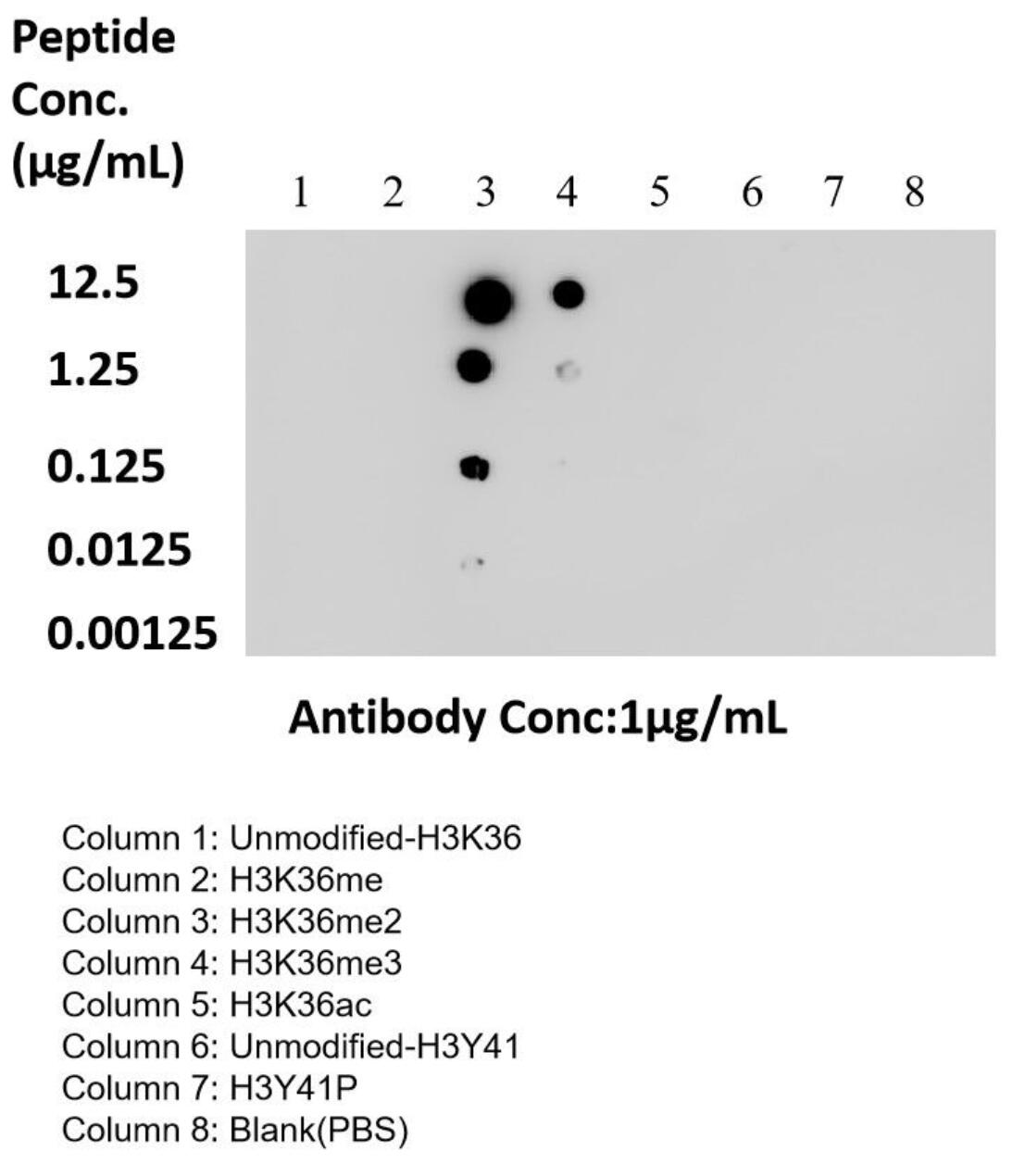
84329-1-PBS targets Di/Tri-Methyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) in WB, IF/ICC, Dot Blot, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | histone cluster 1, H3a |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 15 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC066245 |
| Gene Symbol | HIST1H3A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8350 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P68431 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS Only |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Histones are small, highly basic proteins that consist of a globular domain with unstructured N- and C-terminal tails protruding from the main structure. Histone H3 is one of the five main histones that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form an octamer, around which approximately 146 bp of DNA is wrapped in repeating units, called nucleosomes. In addition to their role in DNA compartmentalization, histones also play crucial roles in various biologic processes, including gene expression and regulation, DNA repair, chromatin condensation, cell cycle progression, chromosome segregation, and apoptosis. The ability of histones to regulate chromatin dynamics primarily originates from various posttranslational modifications carried out by histone-modifying enzymes.