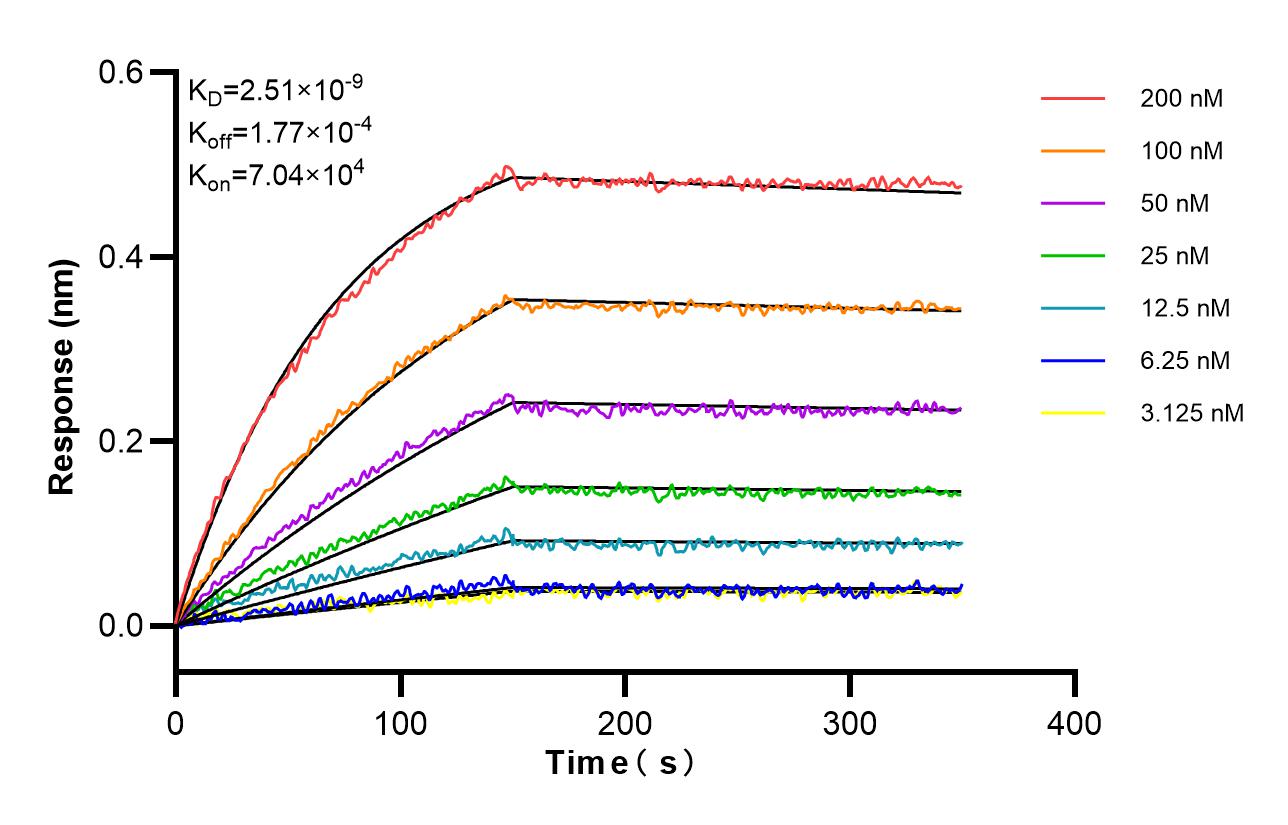
Product Information
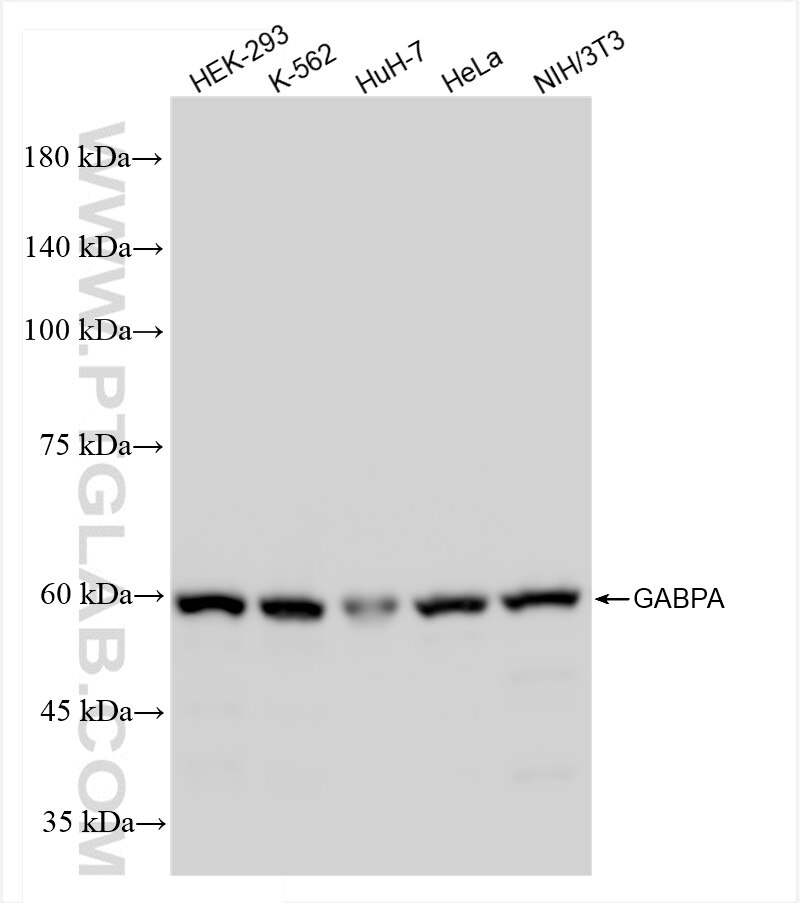
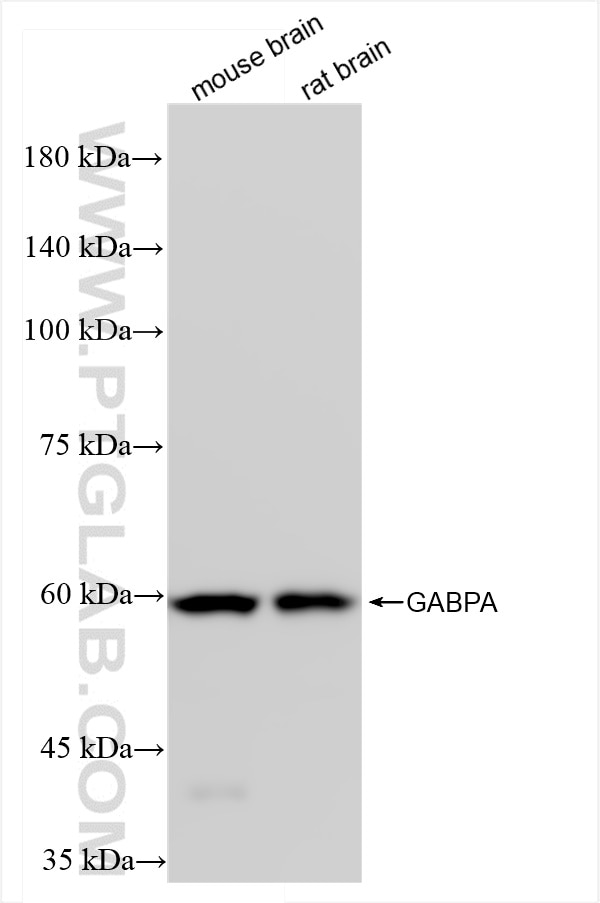
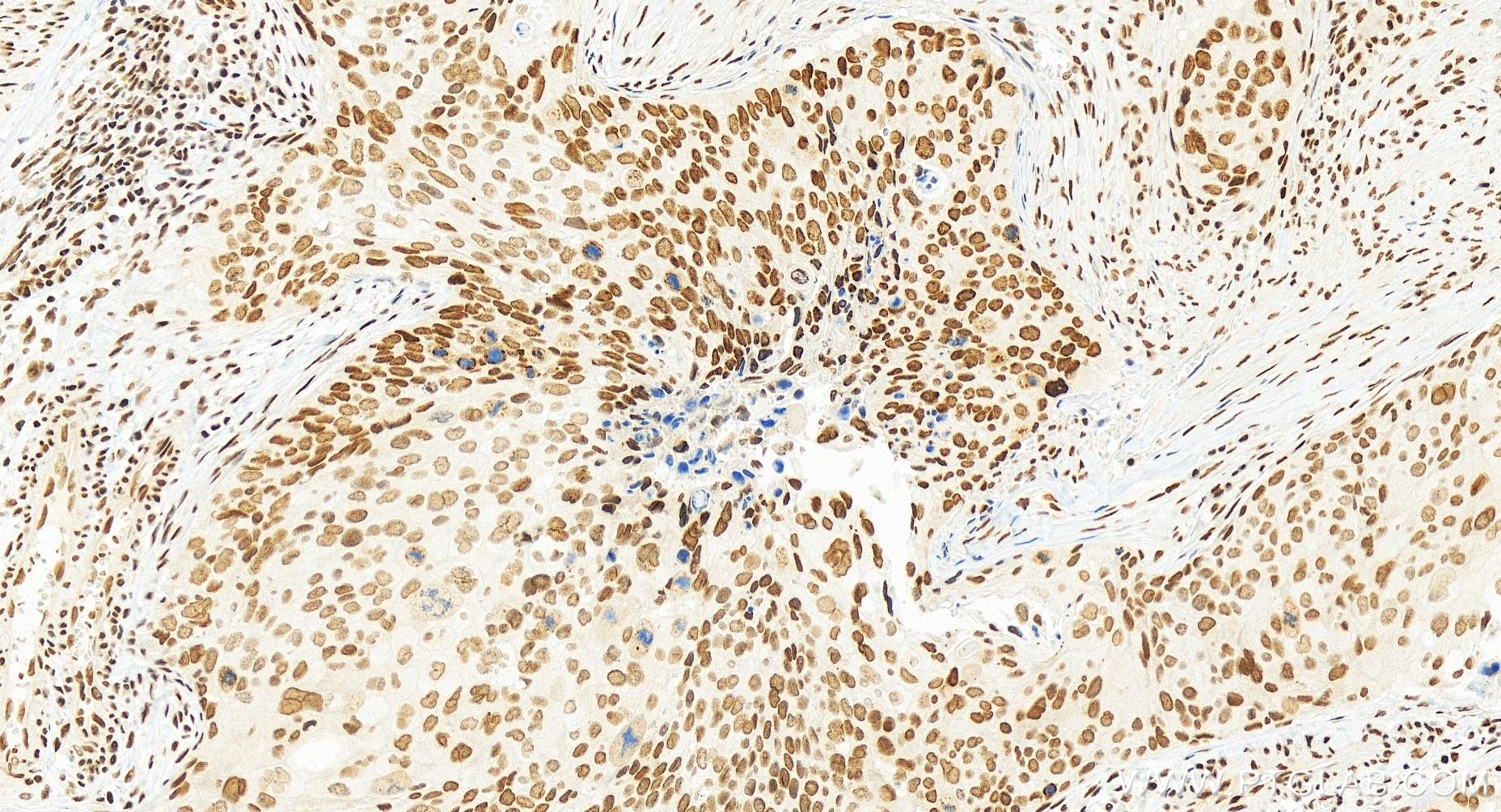
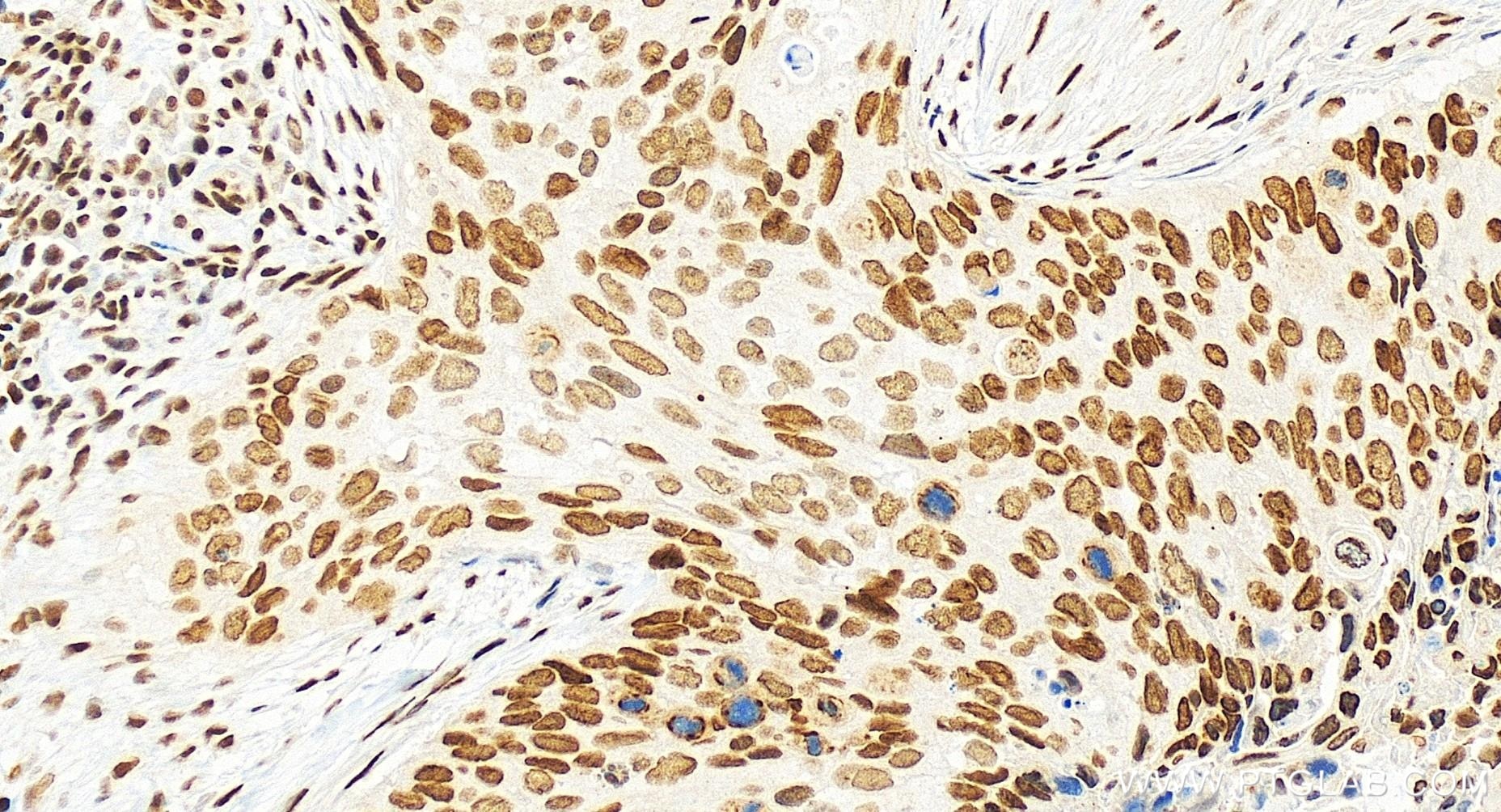
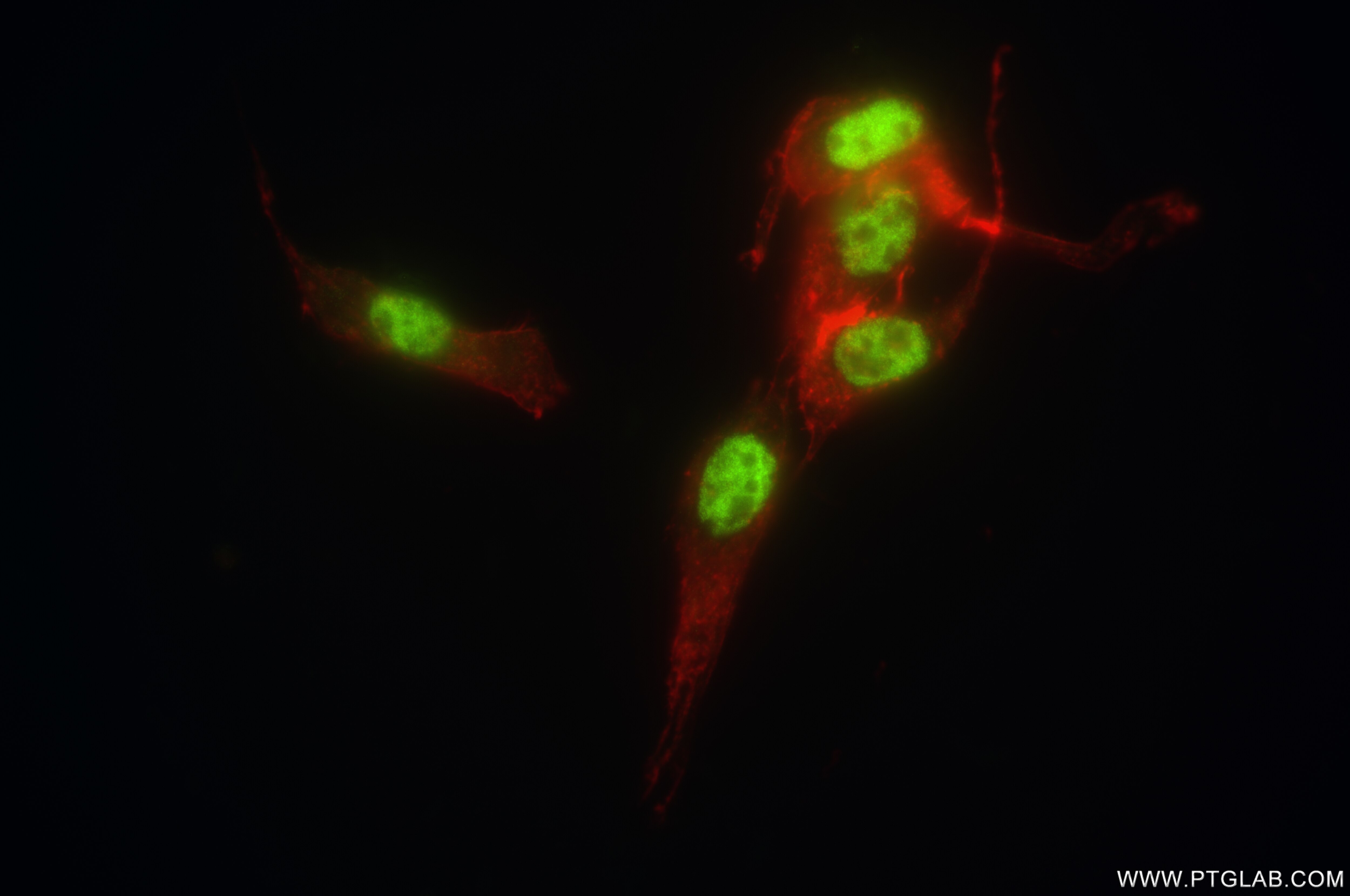
84951-4-PBS targets GABPA in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | GABPA fusion protein Ag16191 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | GA binding protein transcription factor, alpha subunit 60kDa |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 454 aa, 51 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 56-60 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC035031 |
| Gene Symbol | GABPA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2551 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | Q06546 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
GA-binding protein alpha chain (GABP alpha subunit, GABPA, nuclear respiratory factor 2 subunit alpha, transcription factor E4TF1-60) is one of three GA-binding protein transcription factor subunits which functions as a DNA-binding subunit.GABPA is a member of Ets family, binds to the Yap promoter and activates YAP transcription(23684612). Since this subunit shares identity with a subunit encoding the nuclear respiratory factor 2 gene, it is likely involved in activation of cytochrome oxidase expression and nuclear control of mitochondrial function. This subunit also shares identity with a subunit constituting the transcription factor E4TF1, responsible for expression of the adenovirus E4 gene. Because of its chromosomal localization and ability to form heterodimers with other polypeptides, this gene may play a role in the Down Syndrome phenotype.