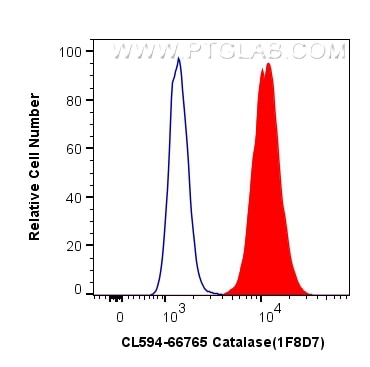
Tested Applications
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.80 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL594-66765 targets Catalase in FC (Intra) applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, pig samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag16916 Product name: Recombinant human Catalase protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 228-527 aa of BC112219 Sequence: EAVYCKFHYKTDQGIKNLSVEDAARLSQEDPDYGIRDLFNAIATGKYPSWTFYIQVMTFNQAETFPFNPFDLTKVWPHKDYPLIPVGKLVLNRNPVNYFAEVEQIAFDPSNMPPGIEASPDKMLQGRLFAYPDTHRHRLGPNYLHIPVNCPYRARVANYQRDGPMCMQDNQGGAPNYYPNSFGAPEQQPSALEHSIQYSGEVRRFNTANDDNVTQVRAFYVNVLNEEQRKRLCENIAGHLKDAQIFIQKKAVKNFTEVHPDYGSHIQALLDKYNAEKPKNAIHTFVQSGSHLAAREKANL Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | catalase |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 60 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 60 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC112219 |
| Gene Symbol | Catalase |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 847 |
| RRID | AB_2934742 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite®594 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 588 nm / 604 nm |
| Excitation Laser | Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm) |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P04040 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Catalase belongs to the catalase family. CAT occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide. CAT promotes growth of cells including T-cells, B-cells, myeloid leukemia cells, melanoma cells, mastocytoma cells and normal and transformed fibroblast cells. CAT catalyzes the reaction: 2 H2O2 = O2 + 2 H2O. Defects in CAT are the cause of acatalasia (ACATLAS) which also known as acatalasemia.