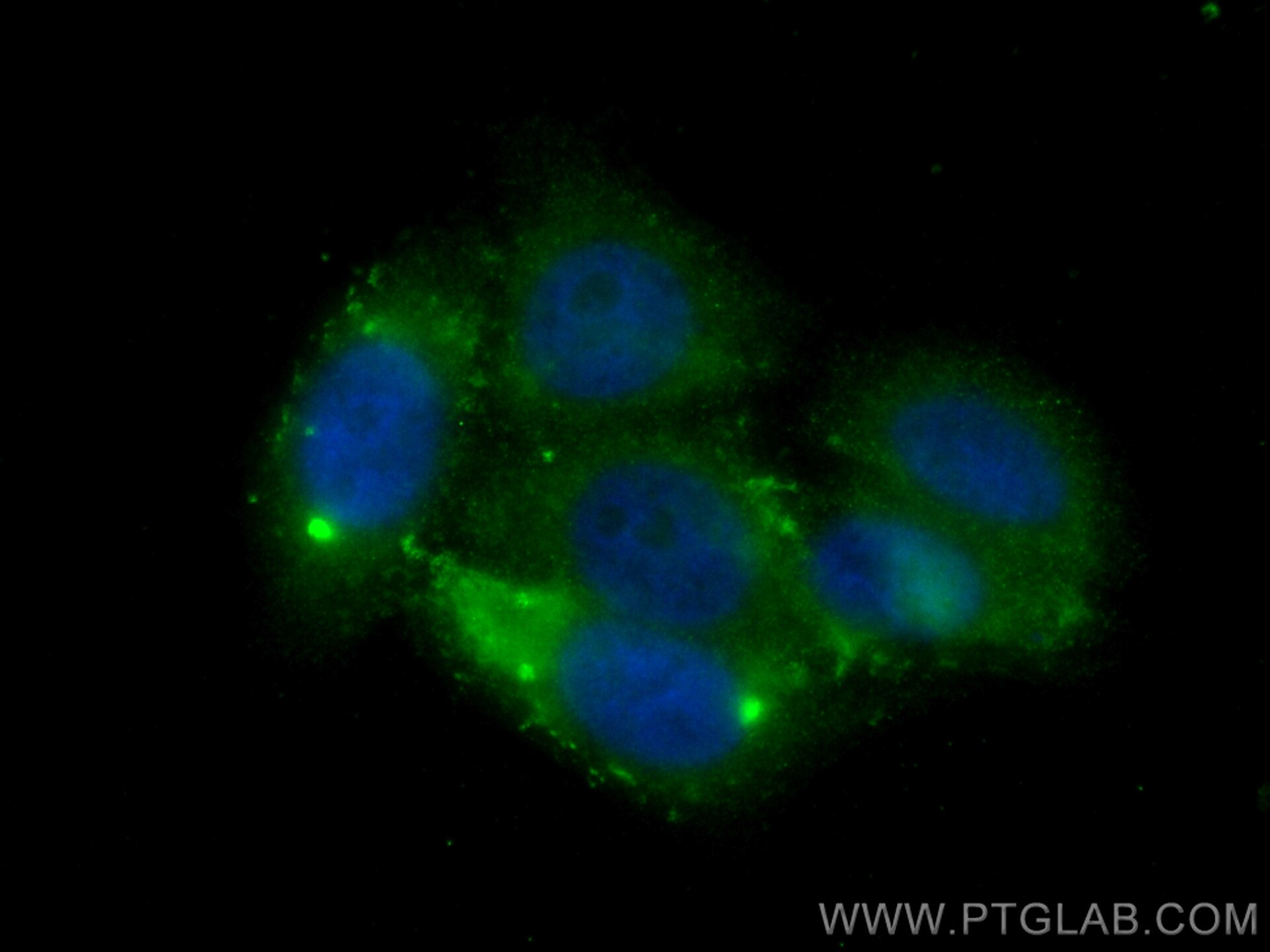
Tested Applications
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
FITC-17996 targets APOA4 in IF/ICC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | APOA4 fusion protein Ag12454 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | apolipoprotein A-IV |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 396 aa, 45 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 45-46 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC074764 |
| Gene Symbol | APOA4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 337 |
| RRID | AB_3673839 |
| Conjugate | FITC Plus Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 495 nm / 524 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
APOA4 is a major protein component of chylomicrons in postprandial lymph and plasma. It is synthesized in the small intestine and the liver, attached to chylomicrons by enterocytes, and secreted into intestinal lymph during fat absorption. APOA4 is intimately involved in metabolism and has protective roles in cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis. APOA4 can promote ins secretion and maintain glucose homeostasis. It also has potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for FITC Plus APOA4 antibody FITC-17996 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |