Product Information
83894-1-PBS targets IL-4 as part of a matched antibody pair:
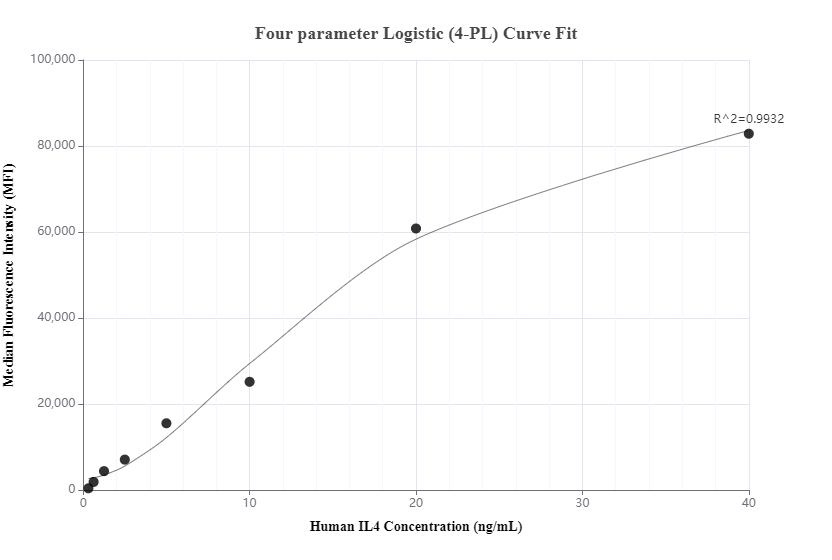
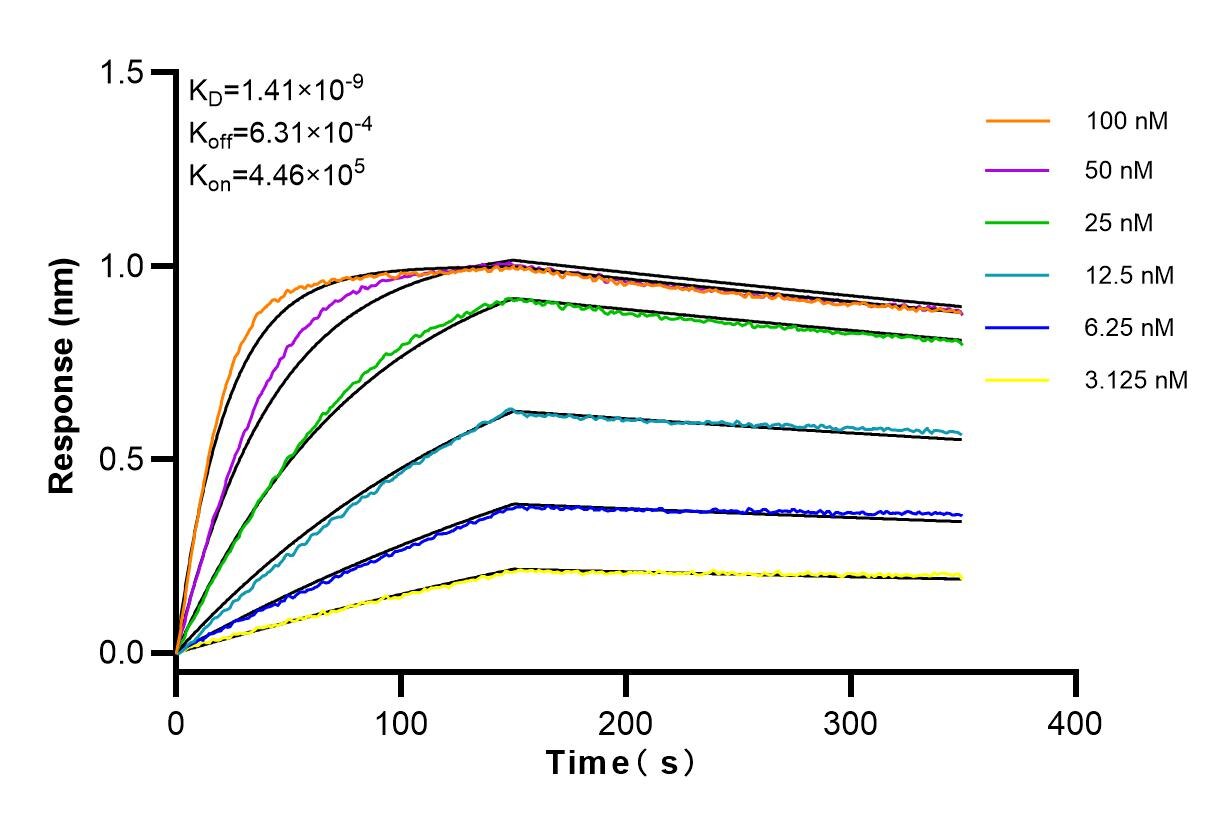
MP00829-1: 83894-1-PBS capture and 83894-4-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation. Created using Proteintech’s proprietary in-house recombinant technology. Recombinant production enables unrivalled batch-to-batch consistency, easy scale-up, and future security of supply.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | interleukin 4 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 153 aa, 17 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC070123 |
| Gene Symbol | IL-4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3565 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P05112 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
IL4 is a cytokine produced by CD4+ T cells in response to helminthes and other extracellular parasites. It promotes the proliferation and differentiation of antigen presenting cells. IL4 also plays a pivotal role in antibody isotype switching and stimulates the production of IgE. This cytokine has been applied in the treatment of autoimmune disorder like multiple myeloma, cancer, psoriasis, and arthritis. IL4 has also been extensively applied to inhibit detrimental effect of Th1. It may promote the growth of epithelial tumors by mediating increased proliferation and survival.