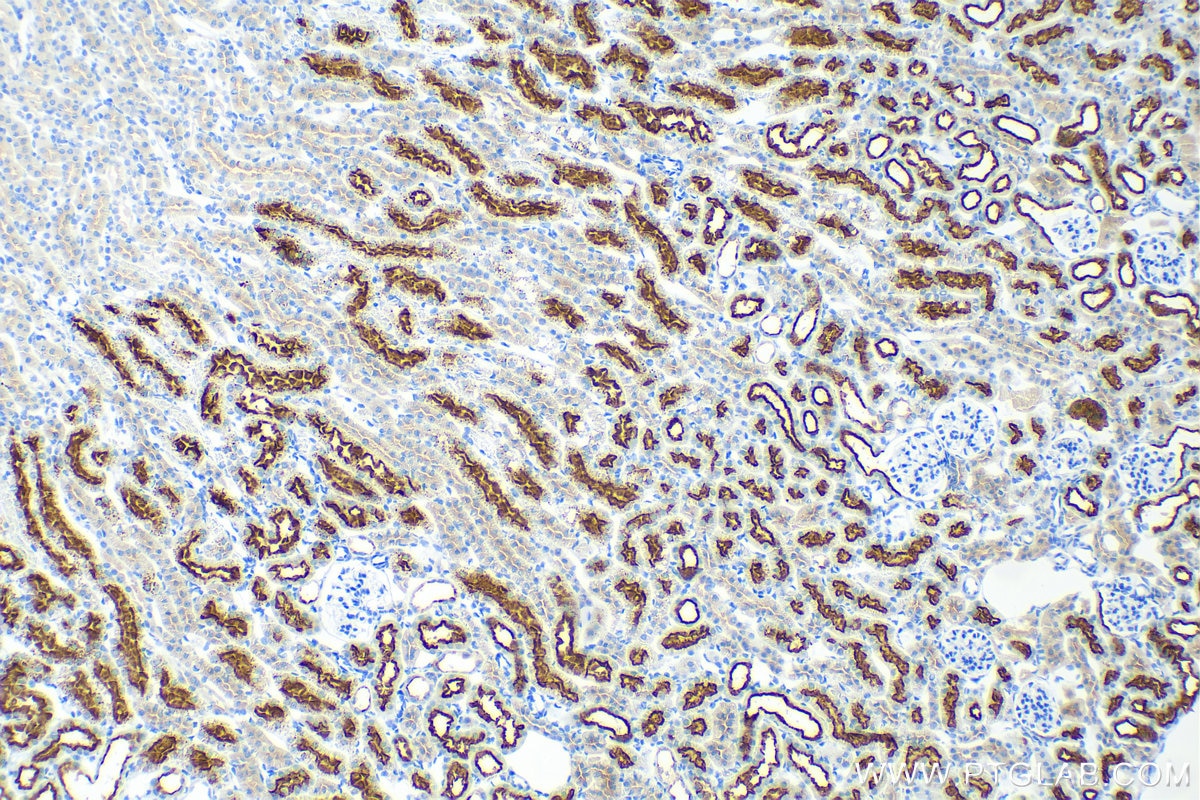
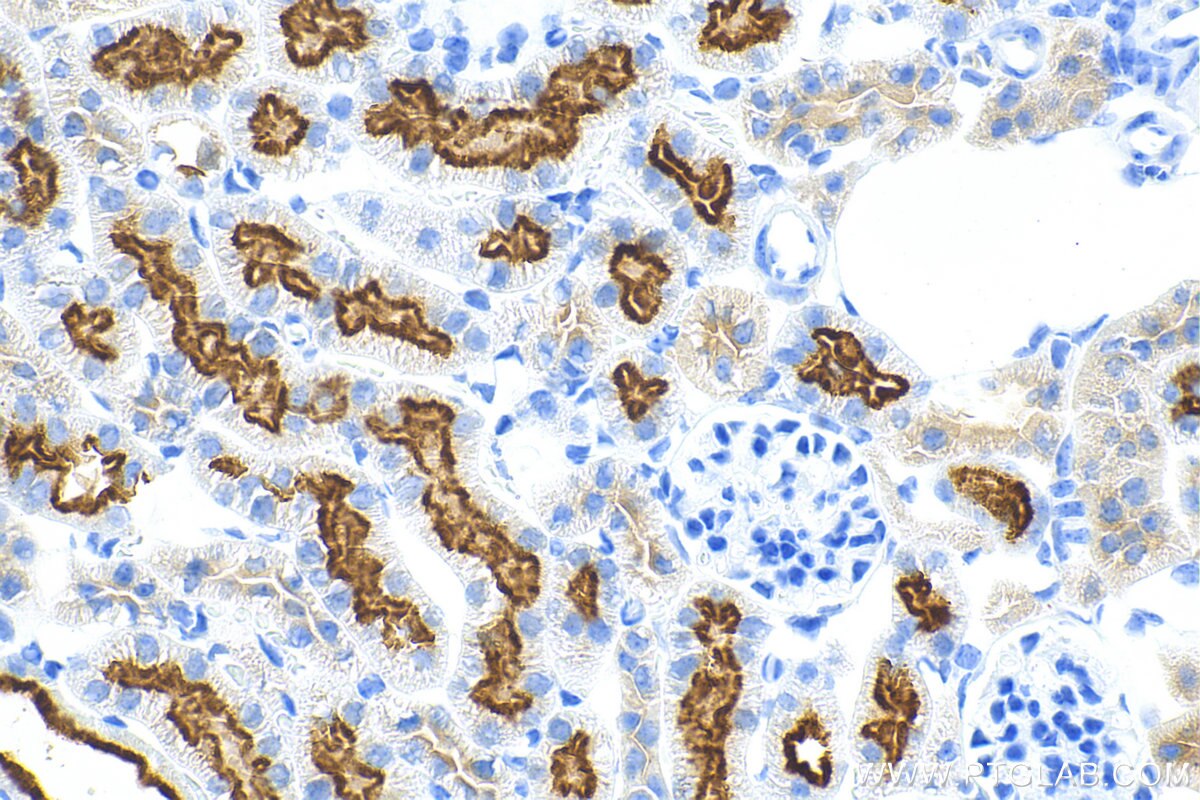
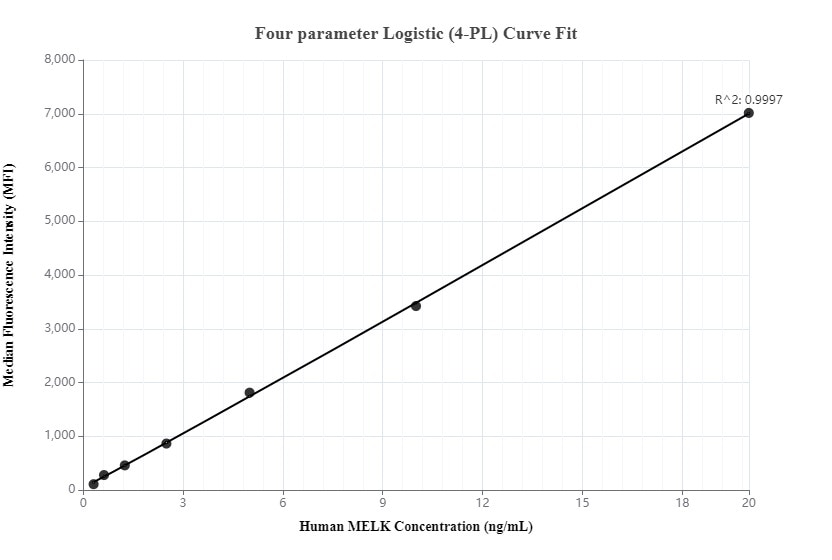
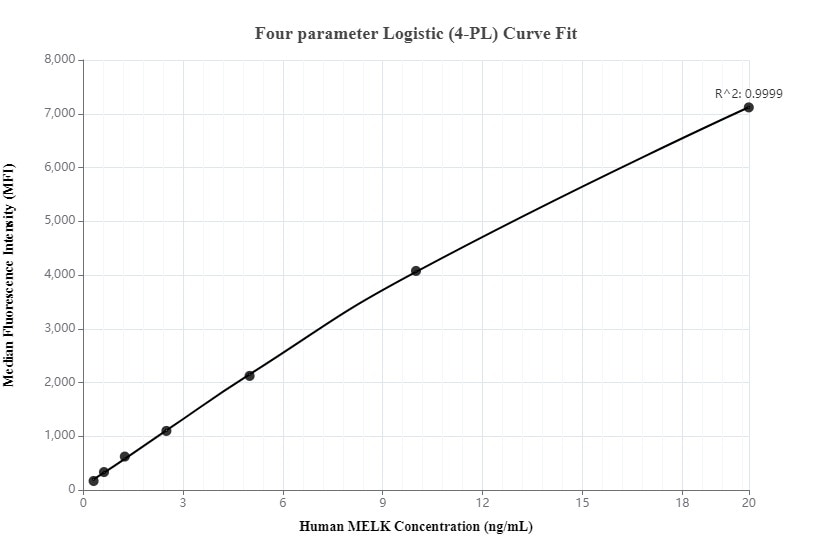
Product Information
82893-2-PBS targets MELK as part of a matched antibody pair:
MP00075-1: 82893-2-PBS capture and 82893-3-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
MP00075-2: 82893-4-PBS capture and 82893-2-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
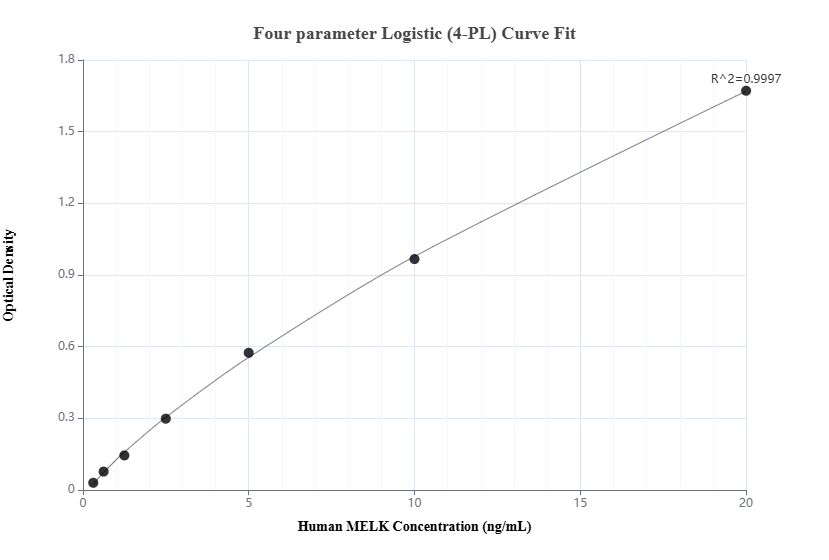
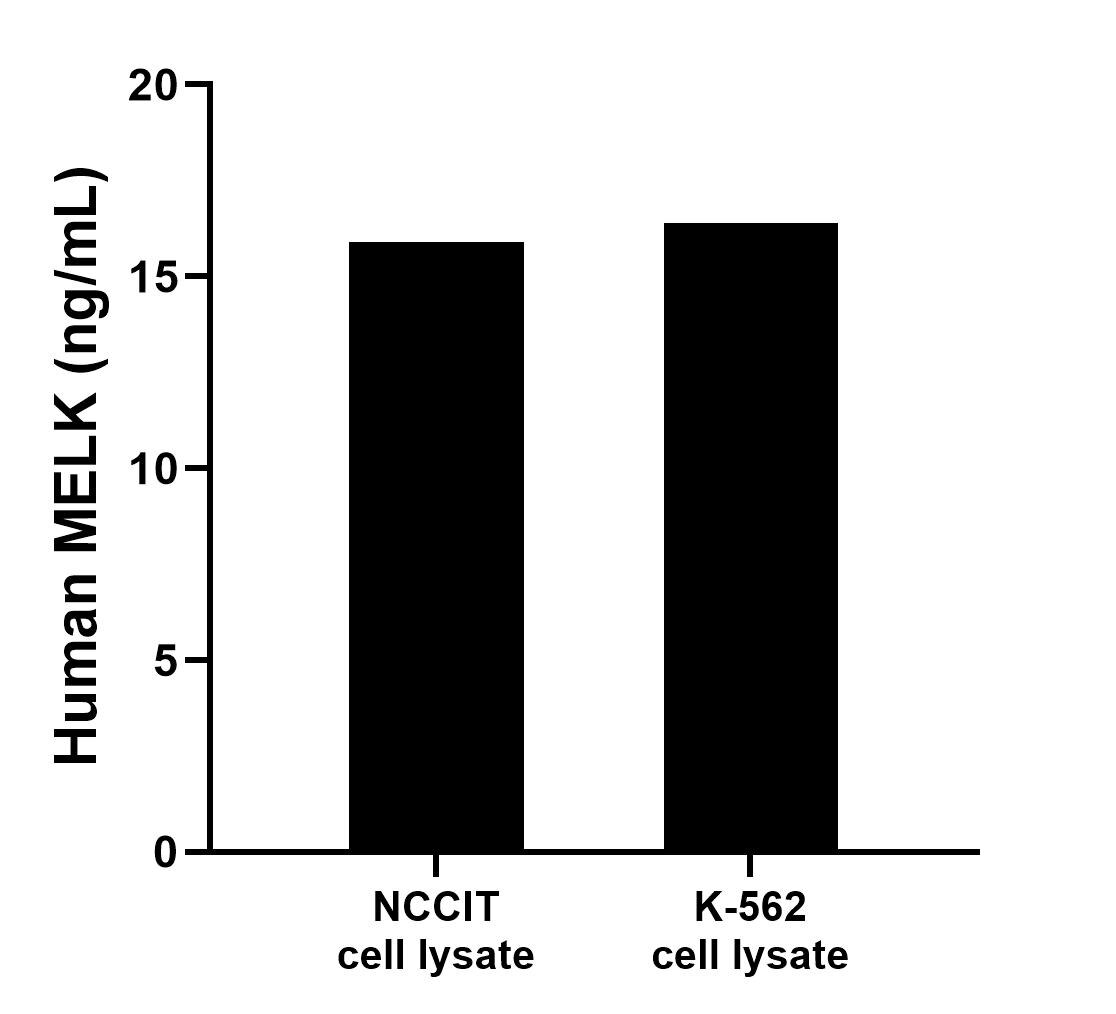
MP00075-4: 82893-2-PBS capture and 82893-6-PBS detection (validated in Sandwich ELISA)
Unconjugated rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation. Created using Proteintech’s proprietary in-house recombinant technology. Recombinant production enables unrivalled batch-to-batch consistency, easy scale-up, and future security of supply.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | MELK fusion protein Ag1897 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 651 aa, 75 kDa |
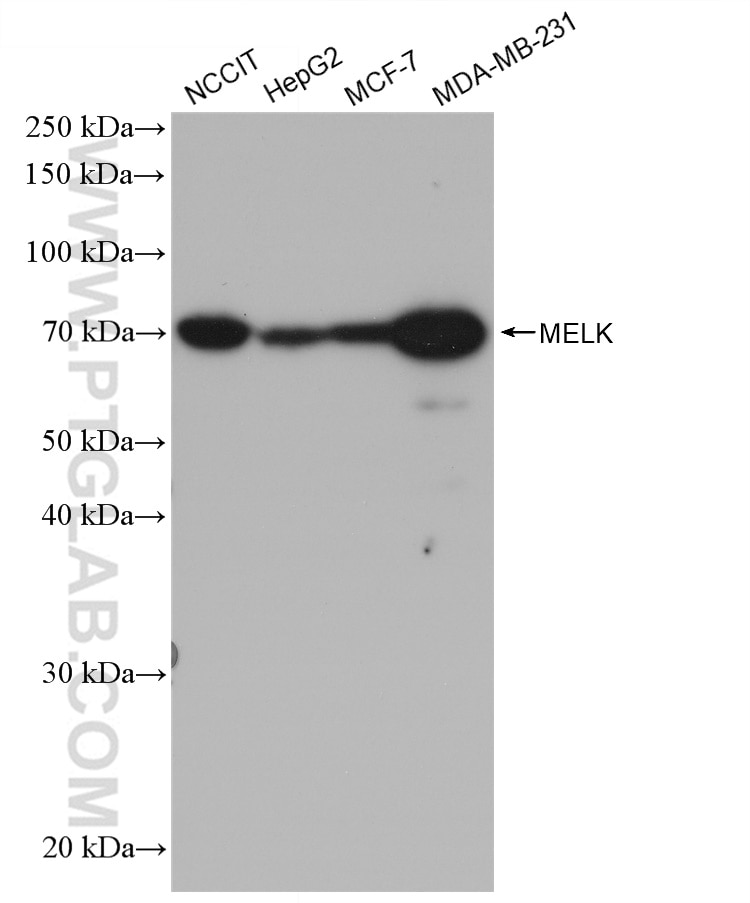
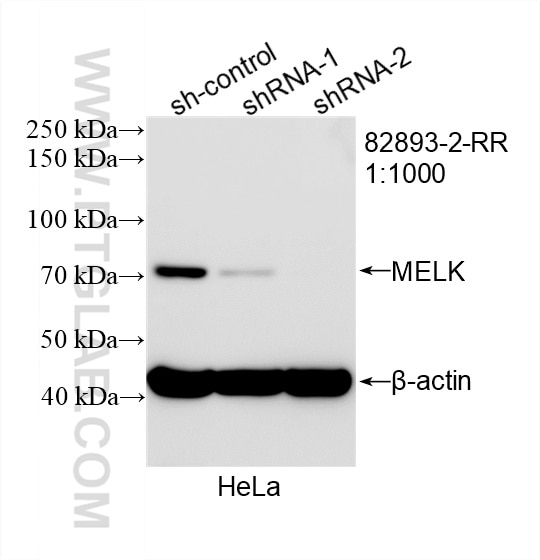
| Observed Molecular Weight | 50-70 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC014039 |
| Gene Symbol | MELK |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9833 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14680 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
MELK is involved in various processes such as cell cycle regulation, self-renewal of stem cells, apoptosis and splicing regulation. It also plays a key role in cell proliferation and carcinogenesis, and it is required for proliferation of embryonic and postnatal multipotent neural progenitors.