- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-ICAM-1
ICAM-1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain et plus (2)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ELISA, Blocking
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
164
N° de cat : 10831-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
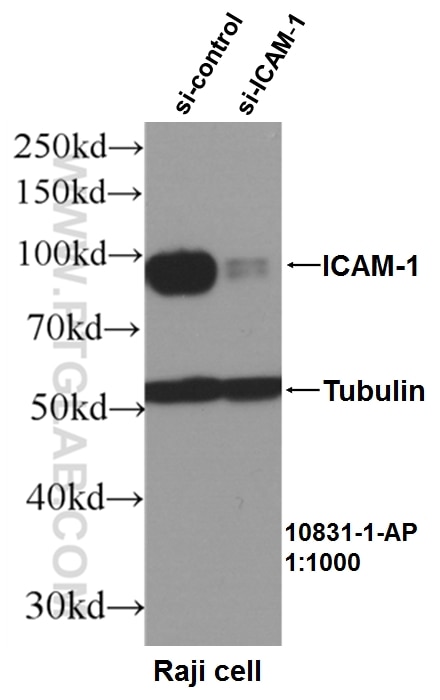
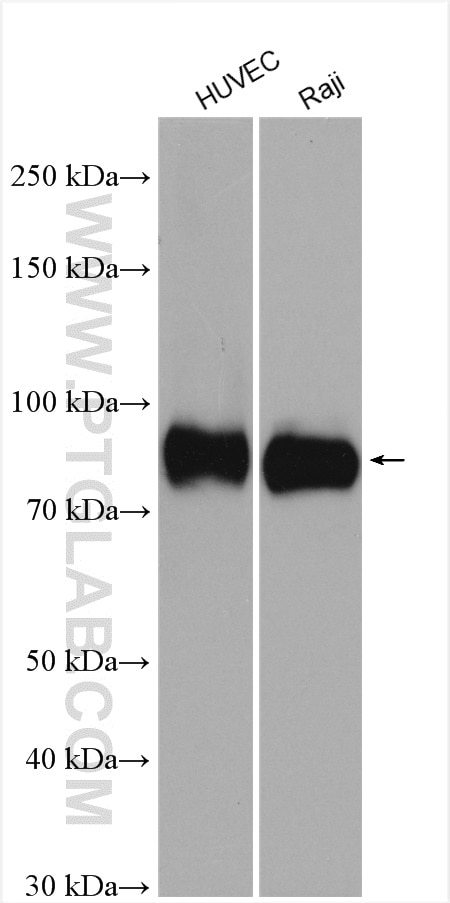
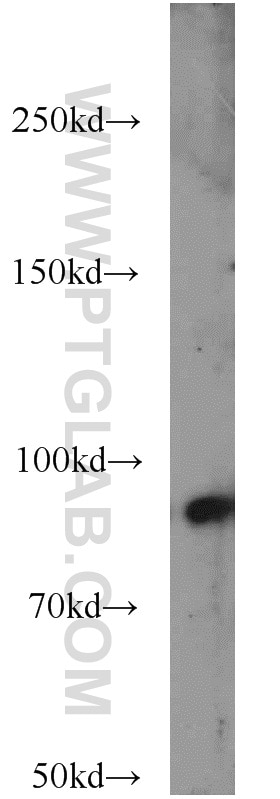
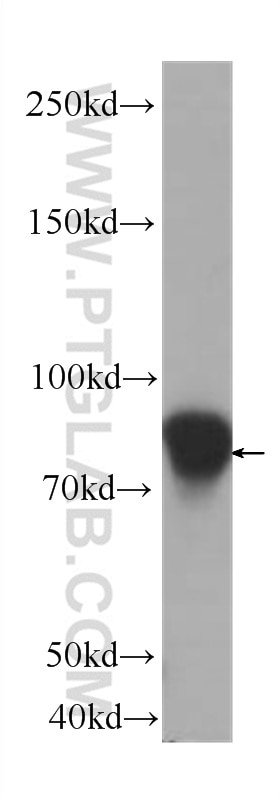
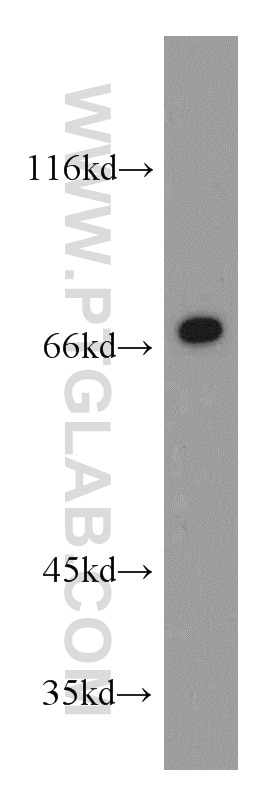
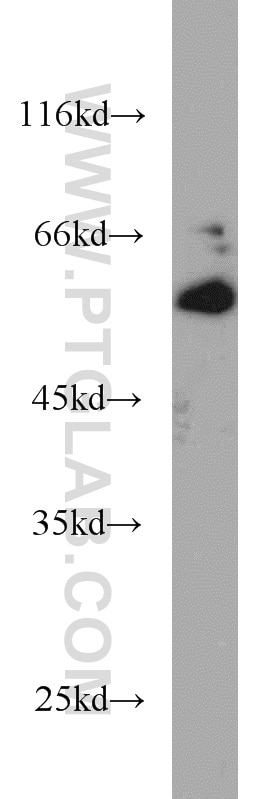
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HUVEC, cellules L02, cellules Raji |
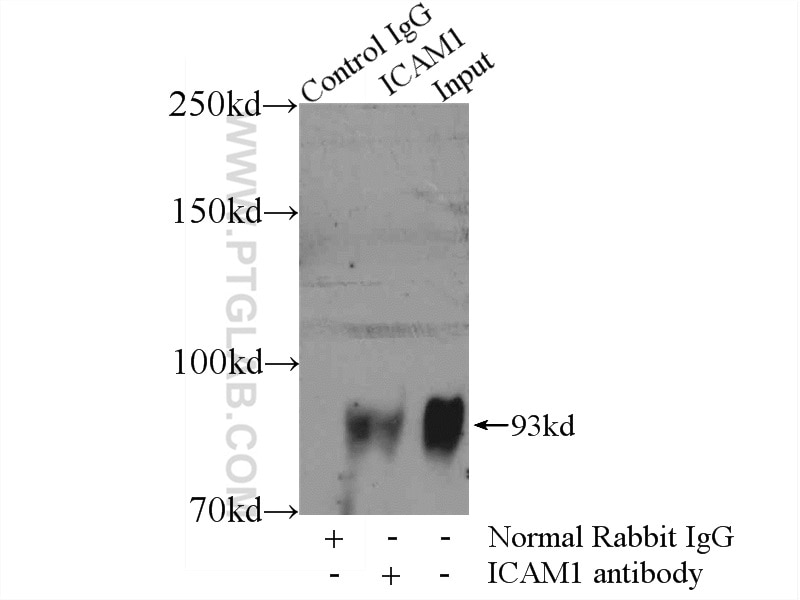
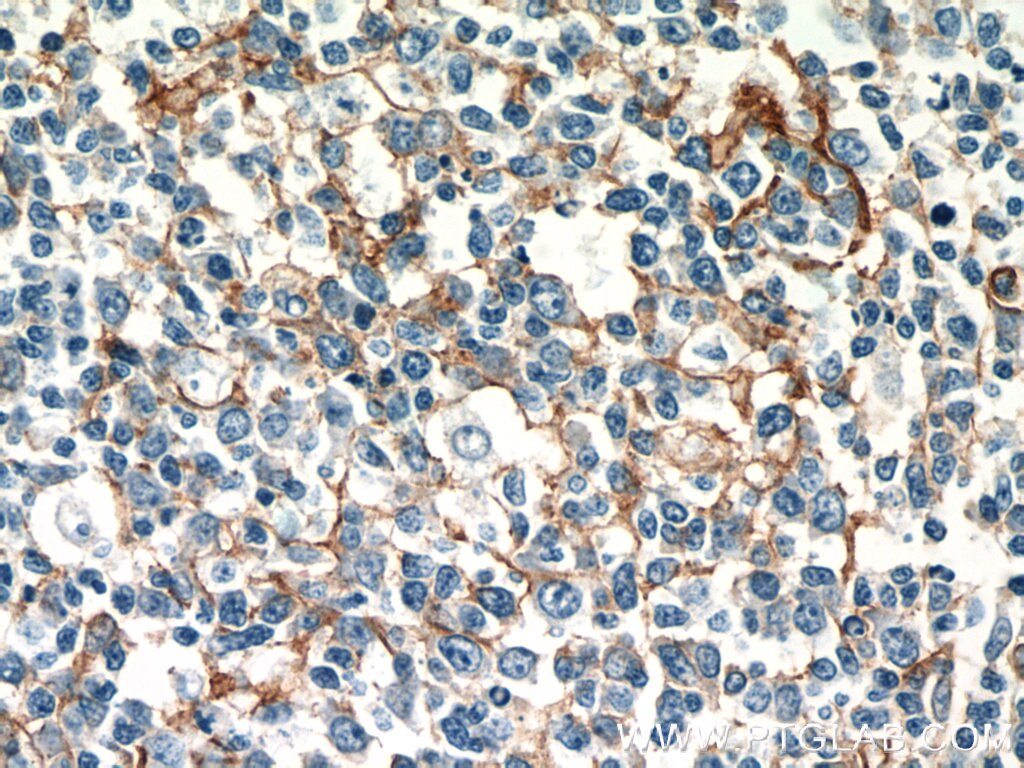
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules Raji |
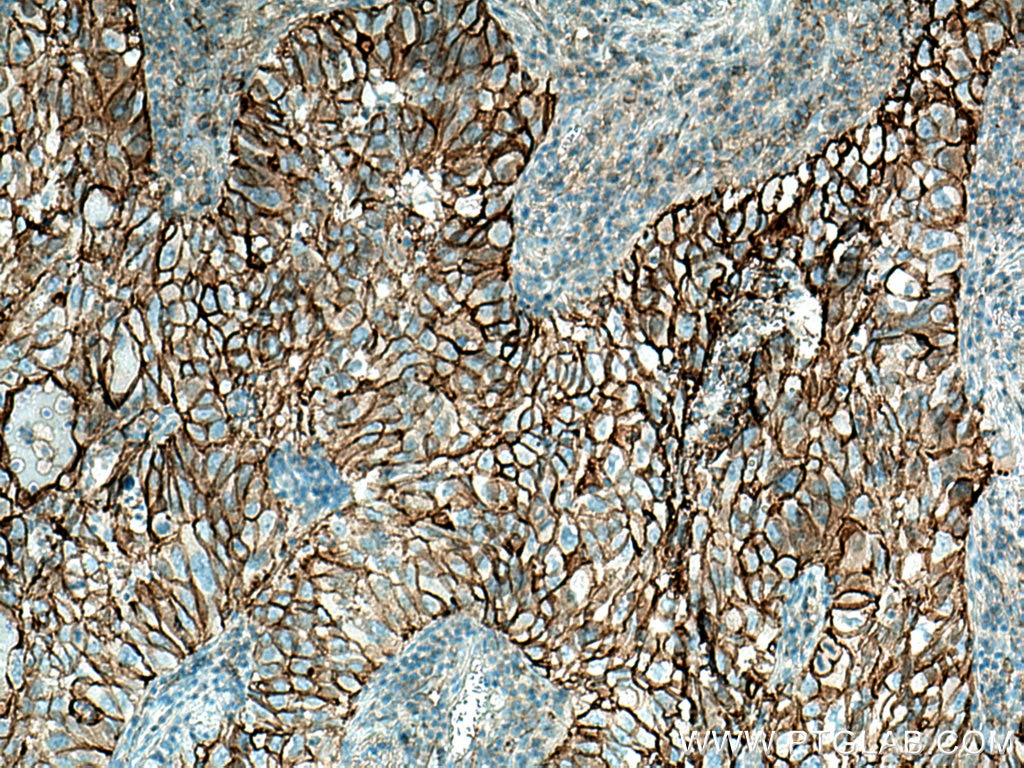
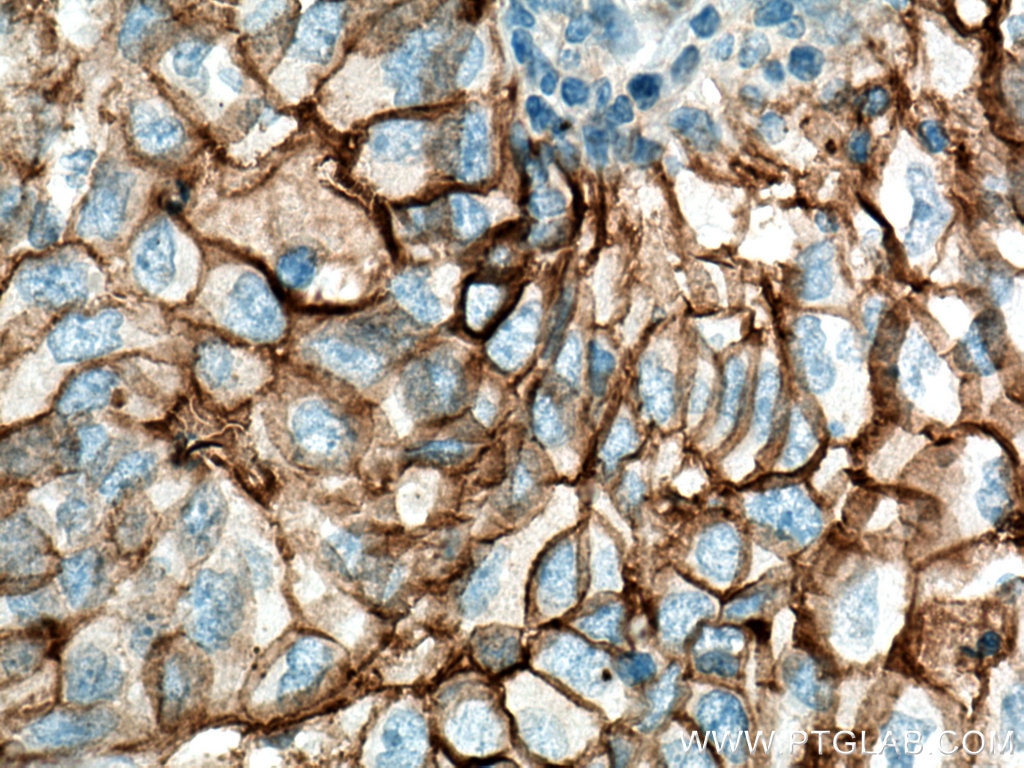
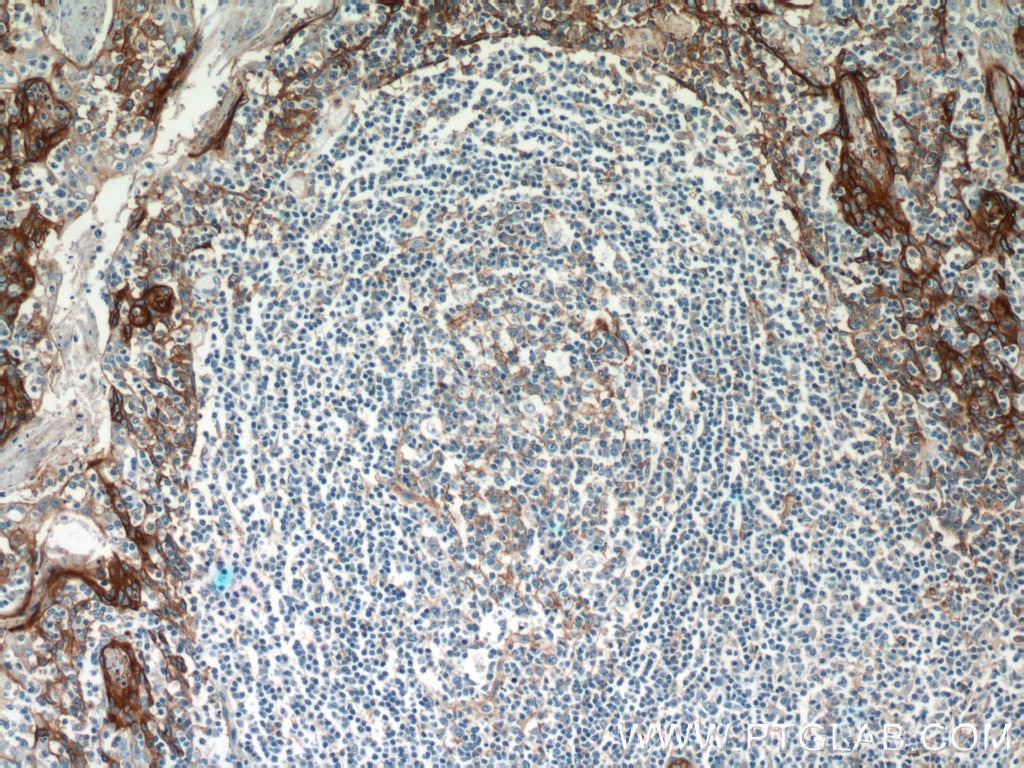
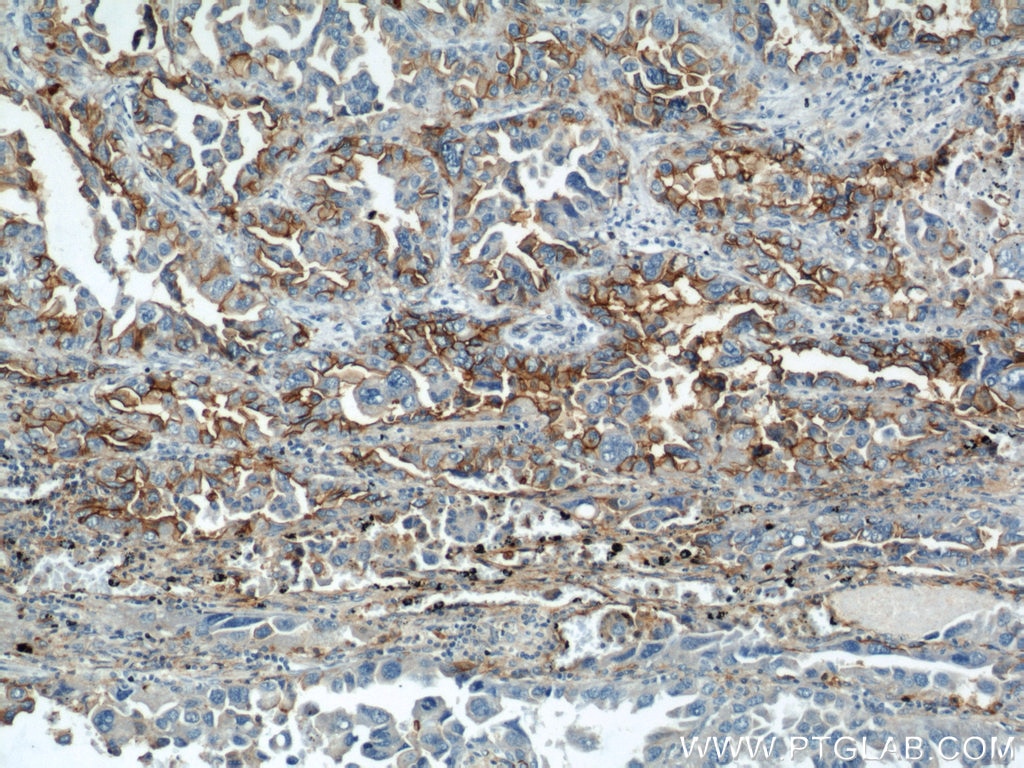
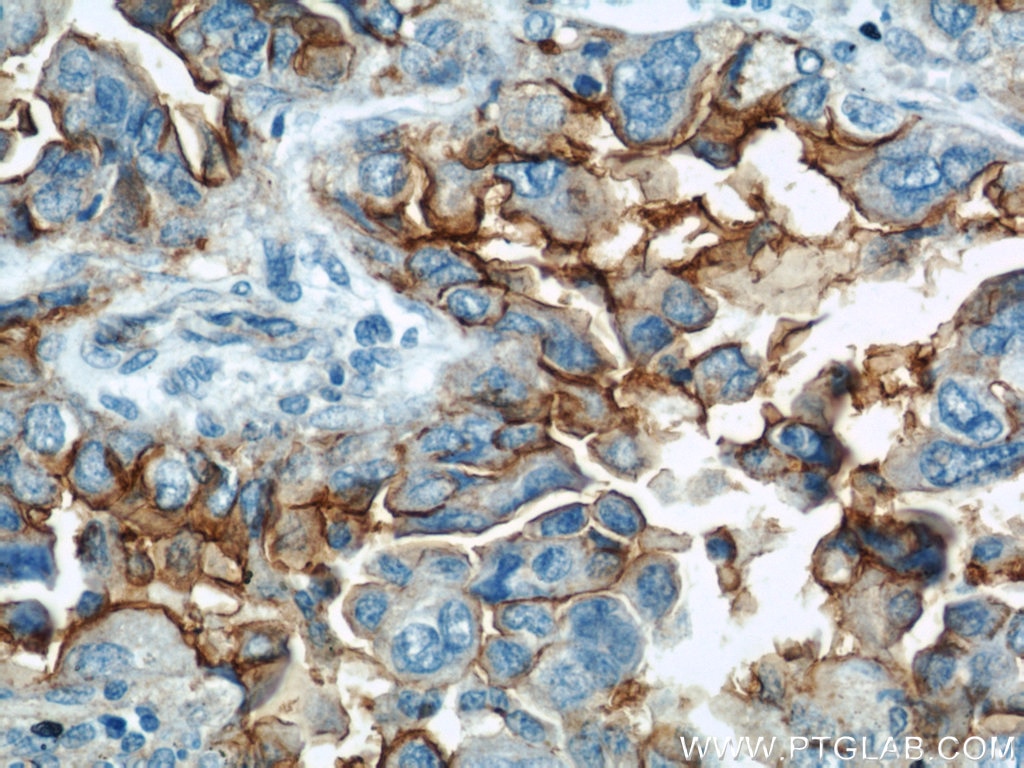
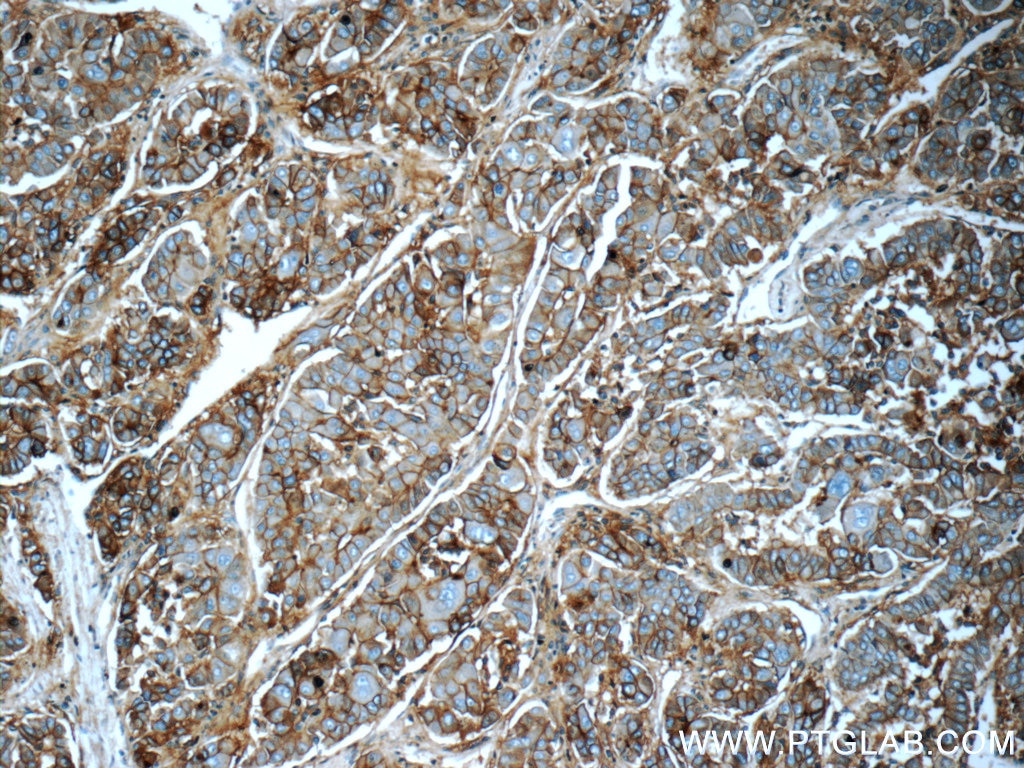
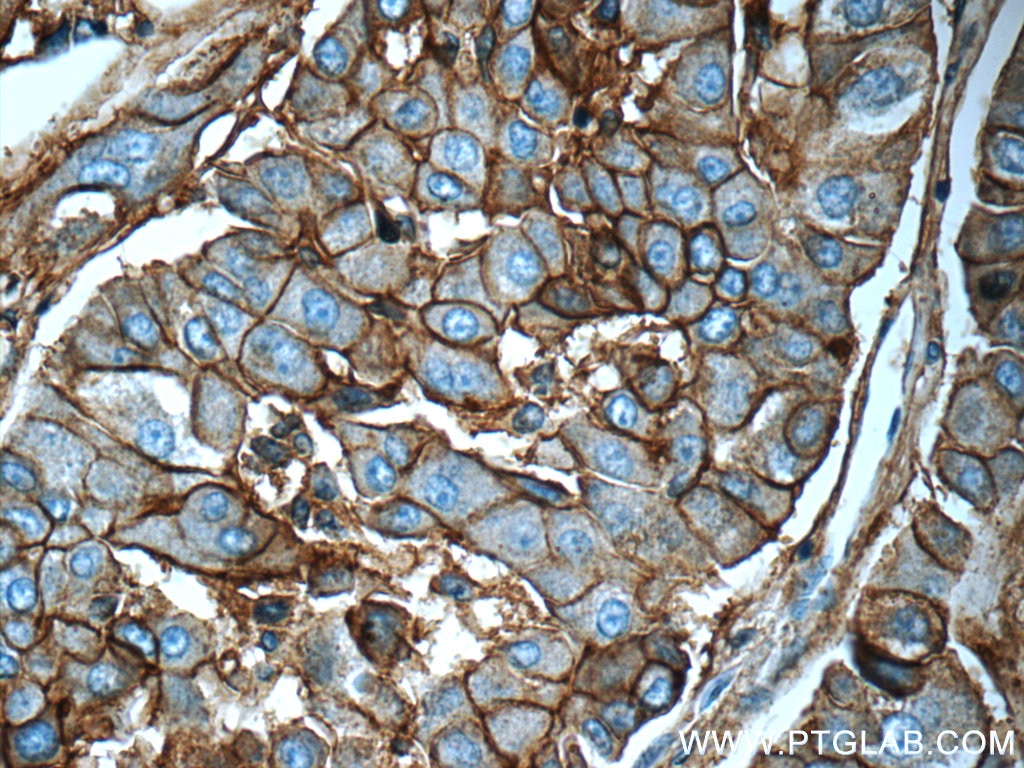
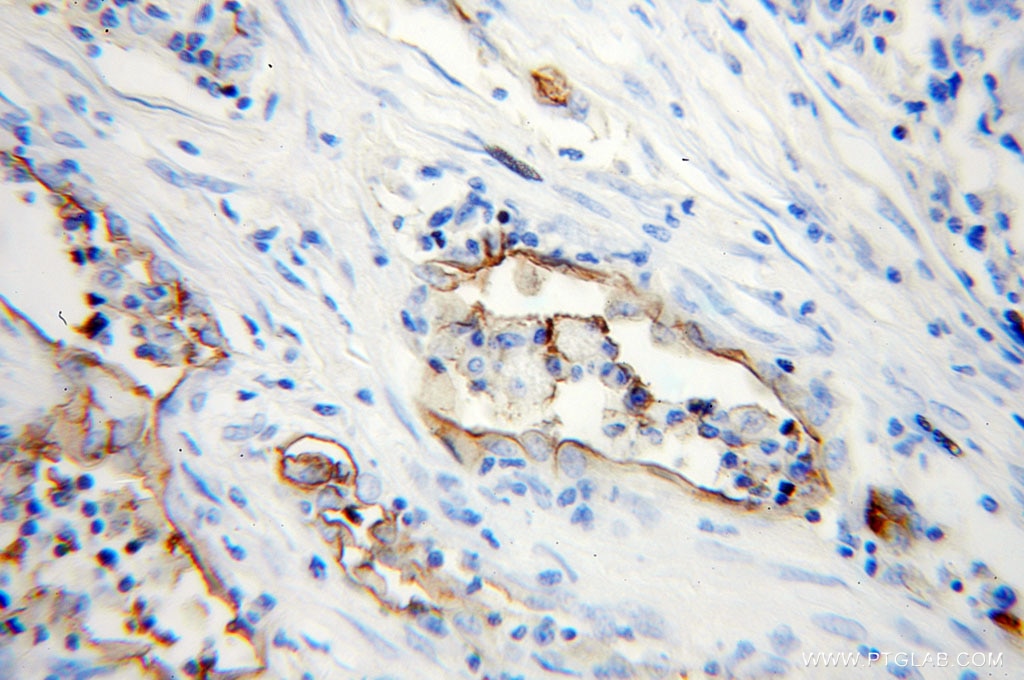
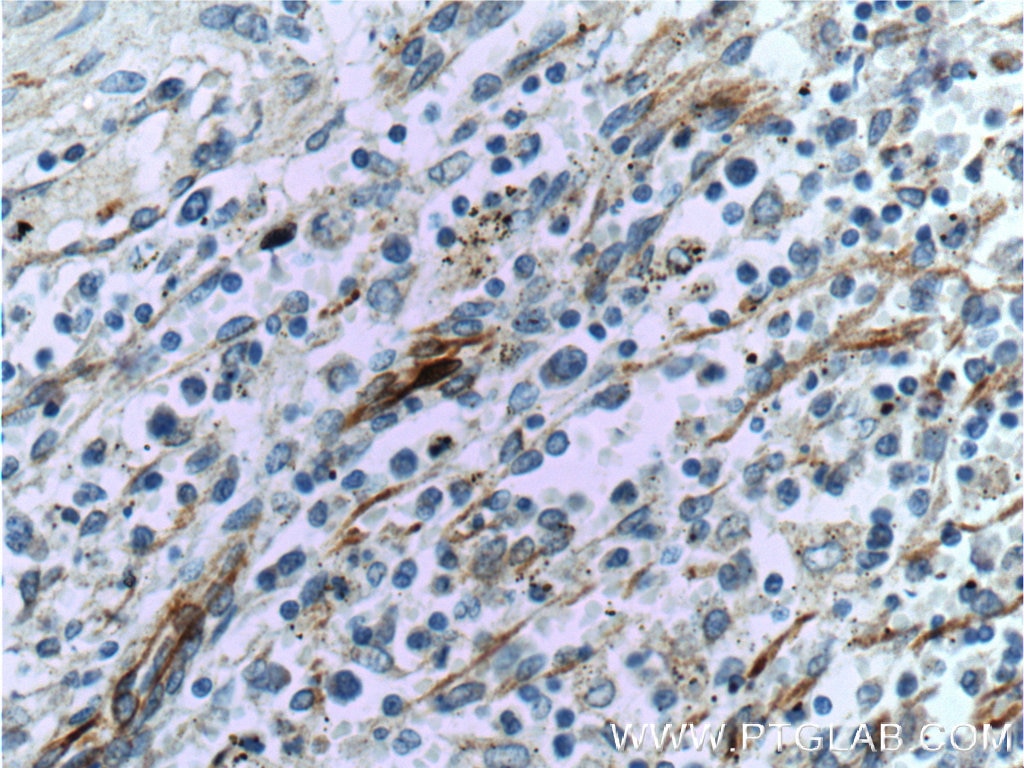
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du poumon humain, tissu d'amygdalite humain, tissu de cancer du foie humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
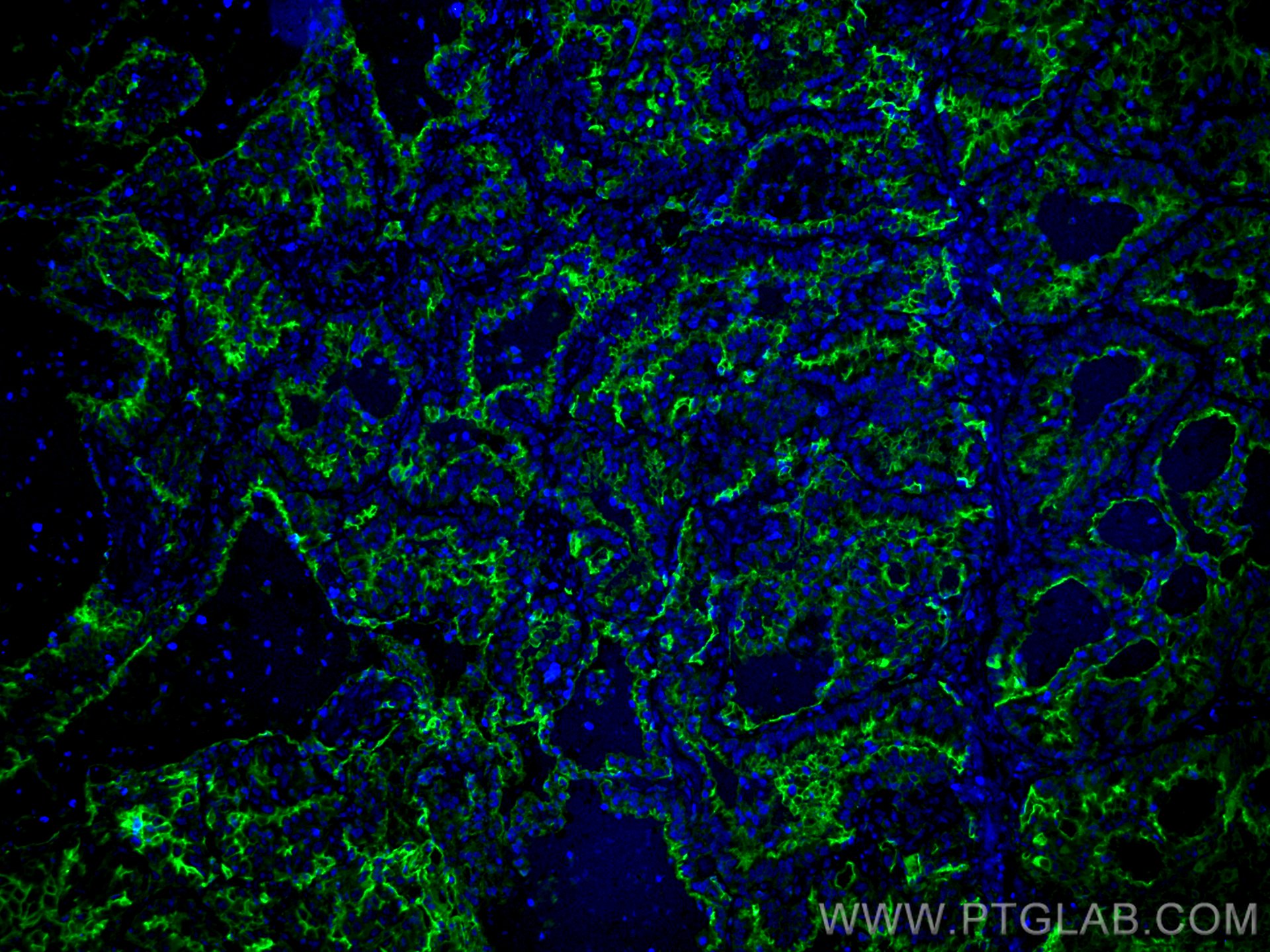
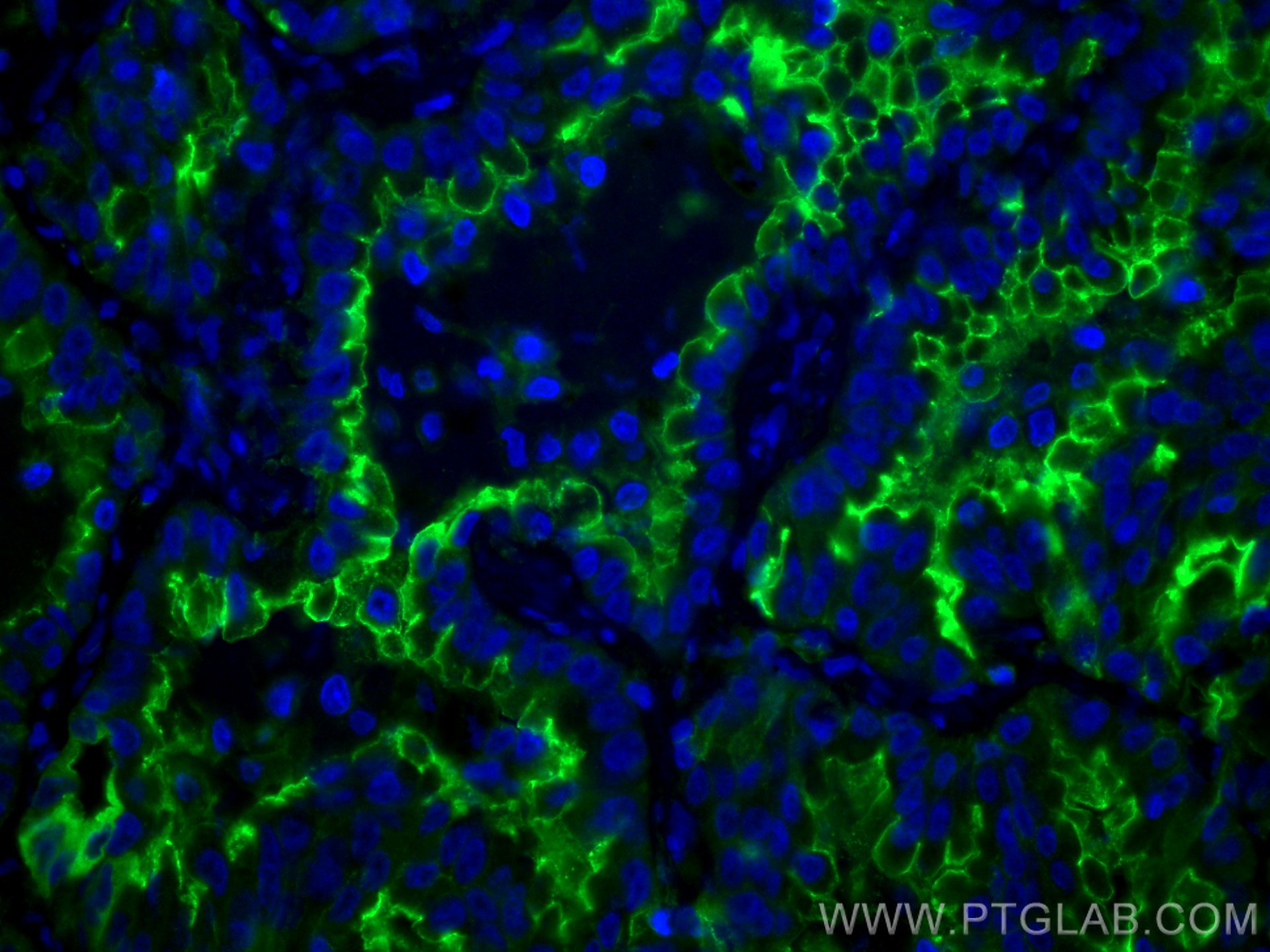
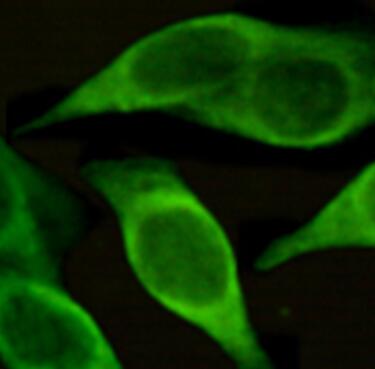
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu de cancer du poumon humain, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:12000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 4 publications below |
| WB | See 134 publications below |
| IHC | See 28 publications below |
| IF | See 23 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
10831-1-AP cible ICAM-1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ELISA, Blocking et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | bovin, Humain, porc |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | ICAM-1 Protéine recombinante Ag1188 |
| Nom complet | intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 90 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 85-95 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC015969 |
| Symbole du gène | ICAM-1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 3383 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Where is ICAM-1 expressed?
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM-1), also known as Cluster of Differentiation 54 (CD54) is a transmembrane glycoprotein constitutively expressed at low levels in endothelial cells, pericytes and on some lymphocytes and monocytes1. It is located at the cytoplasmic membrane, with a large extracellular region of mainly hydrophobic amino acids joined to a small transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail. It has a molecular weight of 75 to 115 kDa depending on the level of glycosylation.
What is the function of ICAM-1?
ICAM-1 is important in both innate and adaptive immune responses as an adhesion molecule. Although it is constitutively expressed, in the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα the endothelial cells are activated and upregulate expression of ICAM-12. In blood vessels lined with endothelial cells, leukocytes that are rolling over the surface are able to bind to ICAM-1 and transmigrate through the endothelial barrier and into the tissue. The initial binding of the leukocytes to ICAM-1 causes a Ca2+ release that initiates endothelial cell contraction and weakening of the intercellular tight junctions3, 4. This protein can be used as an indicator of endothelial activation and of vascular inflammation.
What is the role of ICAM-1 in disease?
Beyond the role in the immune response, ICAM-1 has also been identified as the target of attachment for the human rhinovirus, the cause of the common cold. Binding of the virus to ICAM-1 causes the viral capsid to uncoat and leads to release of the genetic material5.
Hubbard, A. K. & Rothlein, R. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression and cell signaling cascades. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 28, 1379-86 (2000).
Long, E. O. ICAM-1: getting a grip on leukocyte adhesion. J. Immunol. 186, 5021-3 (2011).
Lawson, C. & Wolf, S. ICAM-1 signaling in endothelial cells. (2009).
Lyck, R. & Enzmann, G. The physiological roles of ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in neutrophil migration into tissues. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 22, 53-59 (2015).
Xing, L., Casasnovas, J. M. & Cheng, R. H. Structural analysis of human rhinovirus complexed with ICAM-1 reveals the dynamics of receptor-mediated virus uncoating. J. Virol. 77, 6101-7 (2003).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for ICAM-1 antibody 10831-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for ICAM-1 antibody 10831-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for ICAM-1 antibody 10831-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Adv Mater Biomimetic Immunosuppressive Exosomes that Inhibit Cytokine Storms Contribute to the Alleviation of Sepsis. | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Engineered Cell-Derived Microparticles Bi2Se3/DOX@MPs for Imaging Guided Synergistic Photothermal/Low-Dose Chemotherapy of Cancer. | ||
Hepatology Dysregulation of the unfolded protein response in db/db mice with diet-induced steatohepatitis. | ||
Nat Commun Tumor exosome-based nanoparticles are efficient drug carriers for chemotherapy. | ||
Mater Today Bio Neutrophil membrane-mimicking nanodecoys with intrinsic anti-inflammatory properties alleviate sepsis-induced acute liver injury and lethality in a mouse endotoxemia model. | ||
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces Inflammation-Driven Nanohitchhiker Enhances Postoperative Immunotherapy by Alleviating Prostaglandin E2-Mediated Immunosuppression |
Avis
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive forproviding their feedback.
FH Uthra (Verified Customer) (10-03-2022) | Good!!!
 |