Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-FABP4
FABP4 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 15872-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
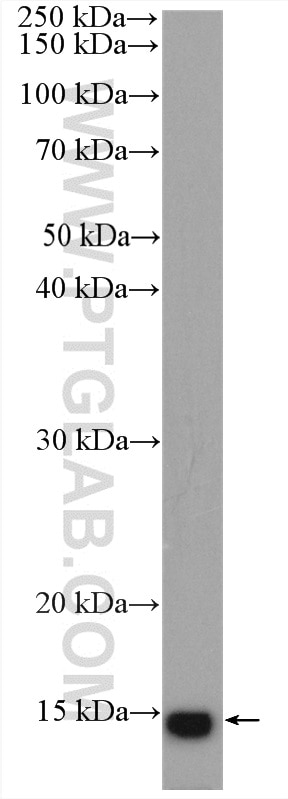
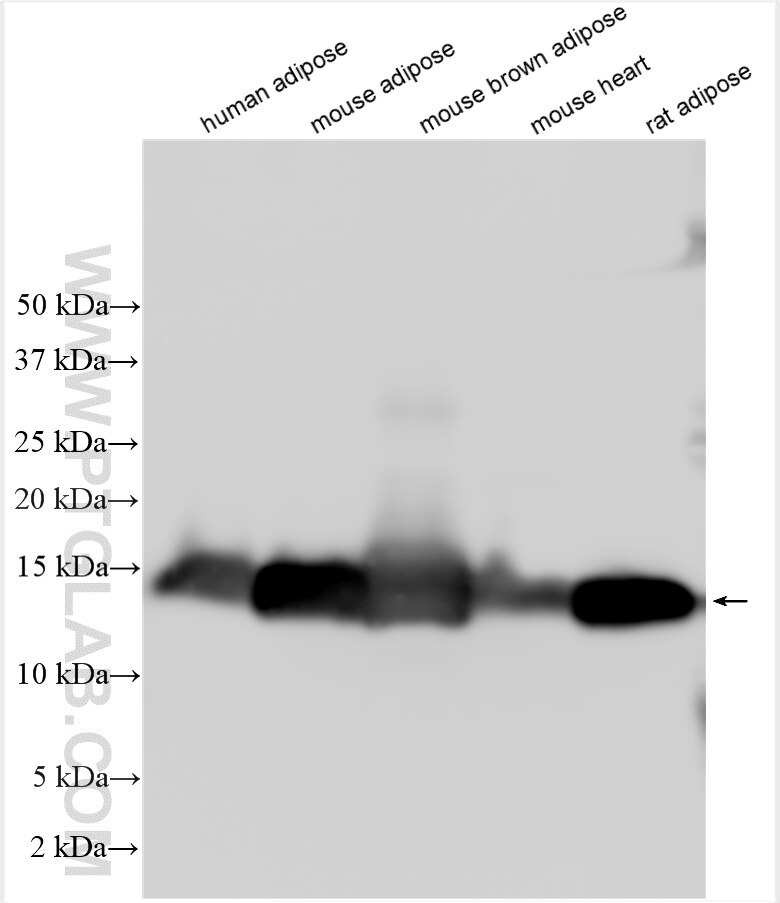
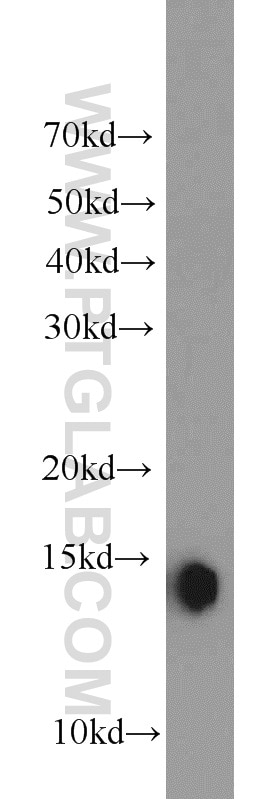
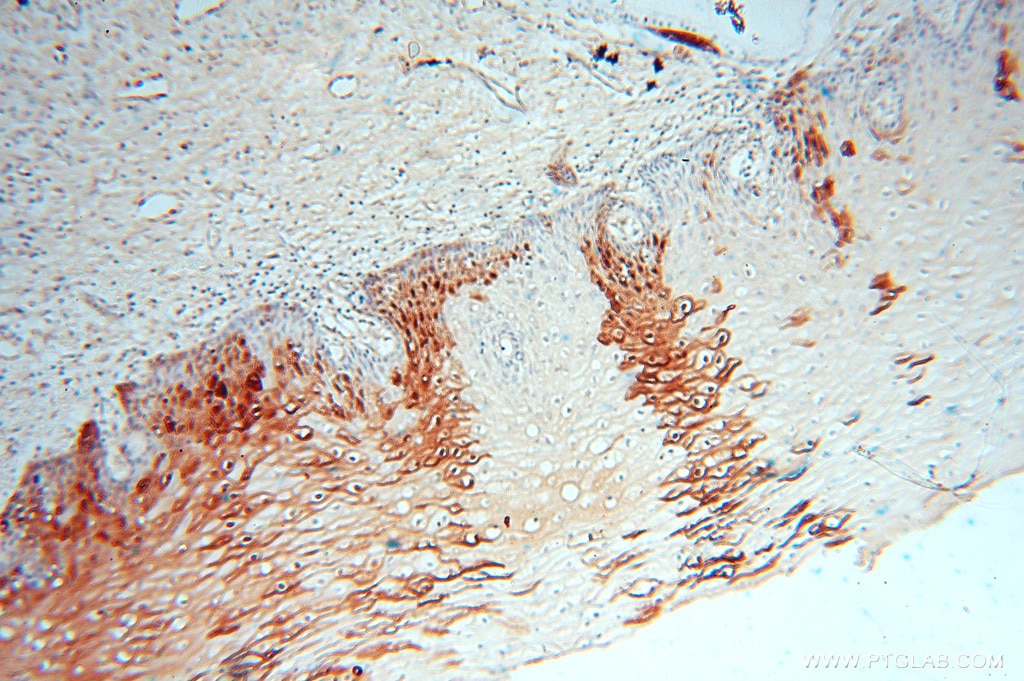
Applications testées
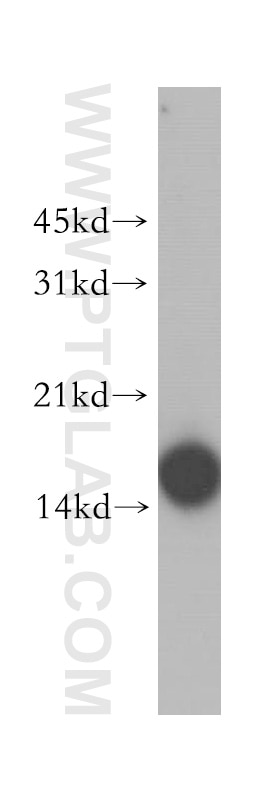
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu de muscle squelettique de rat, tissu adipeux brun de souris, tissu adipeux de souris, tissu adipeux humain, tissu cardiaque de souris, tissu de muscle squelettique de souris |
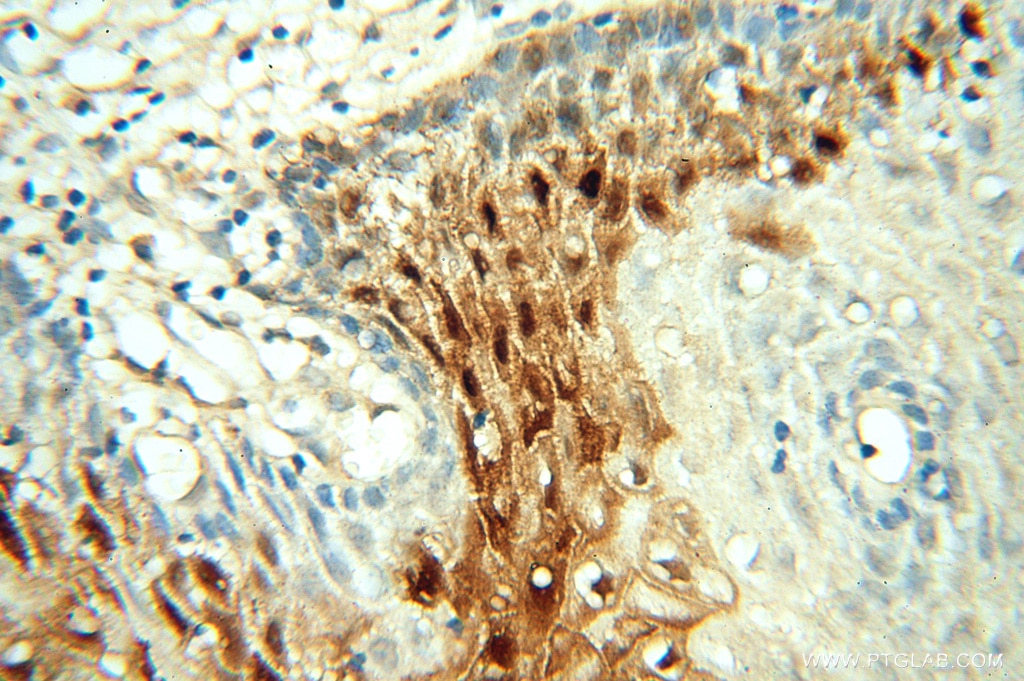
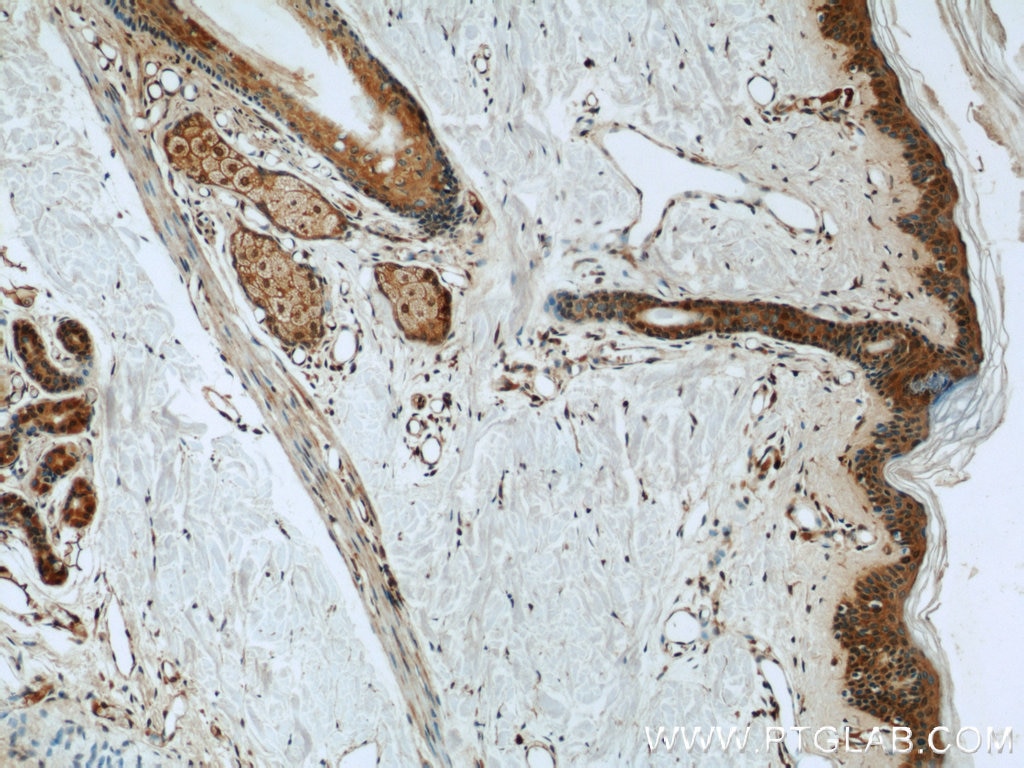
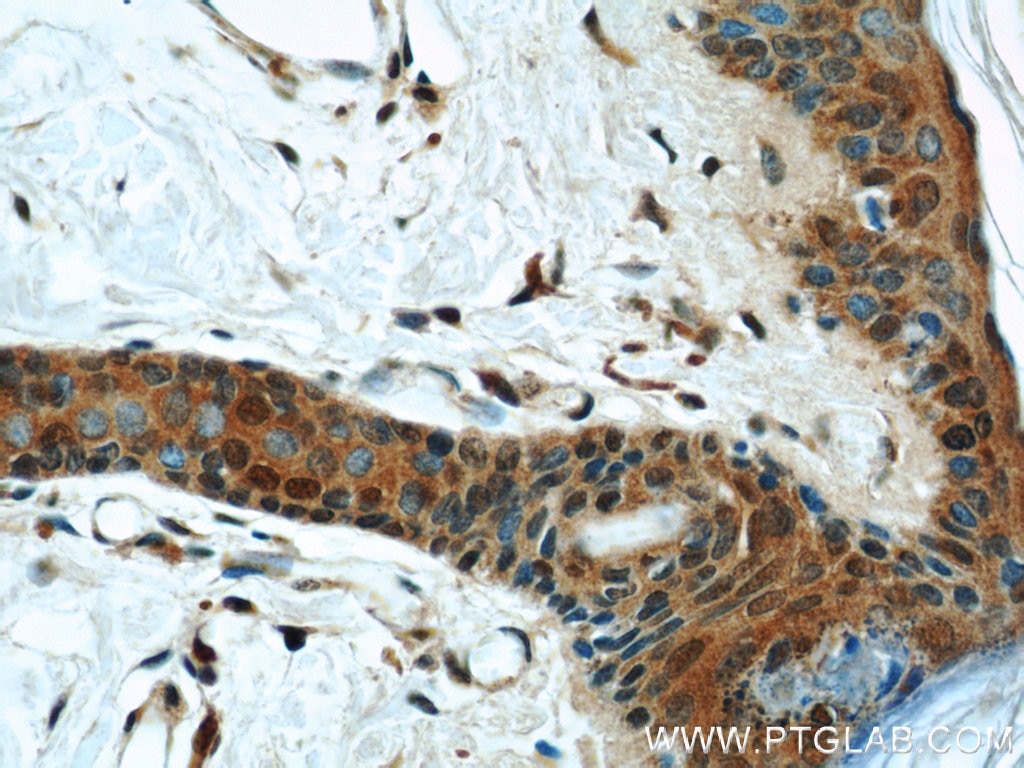
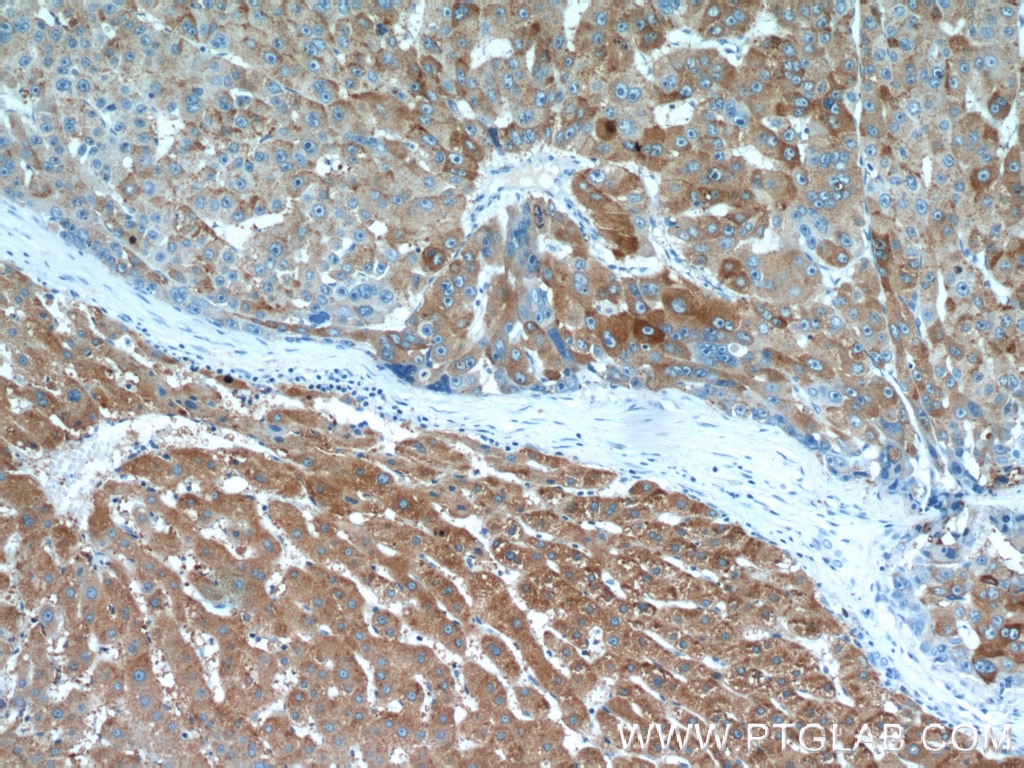
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de col de l'utérus humain, tissu cutané humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
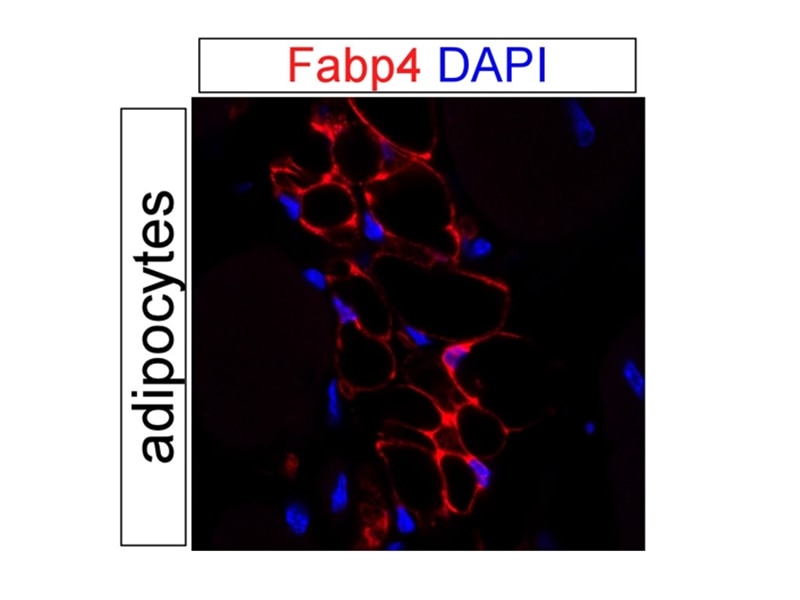
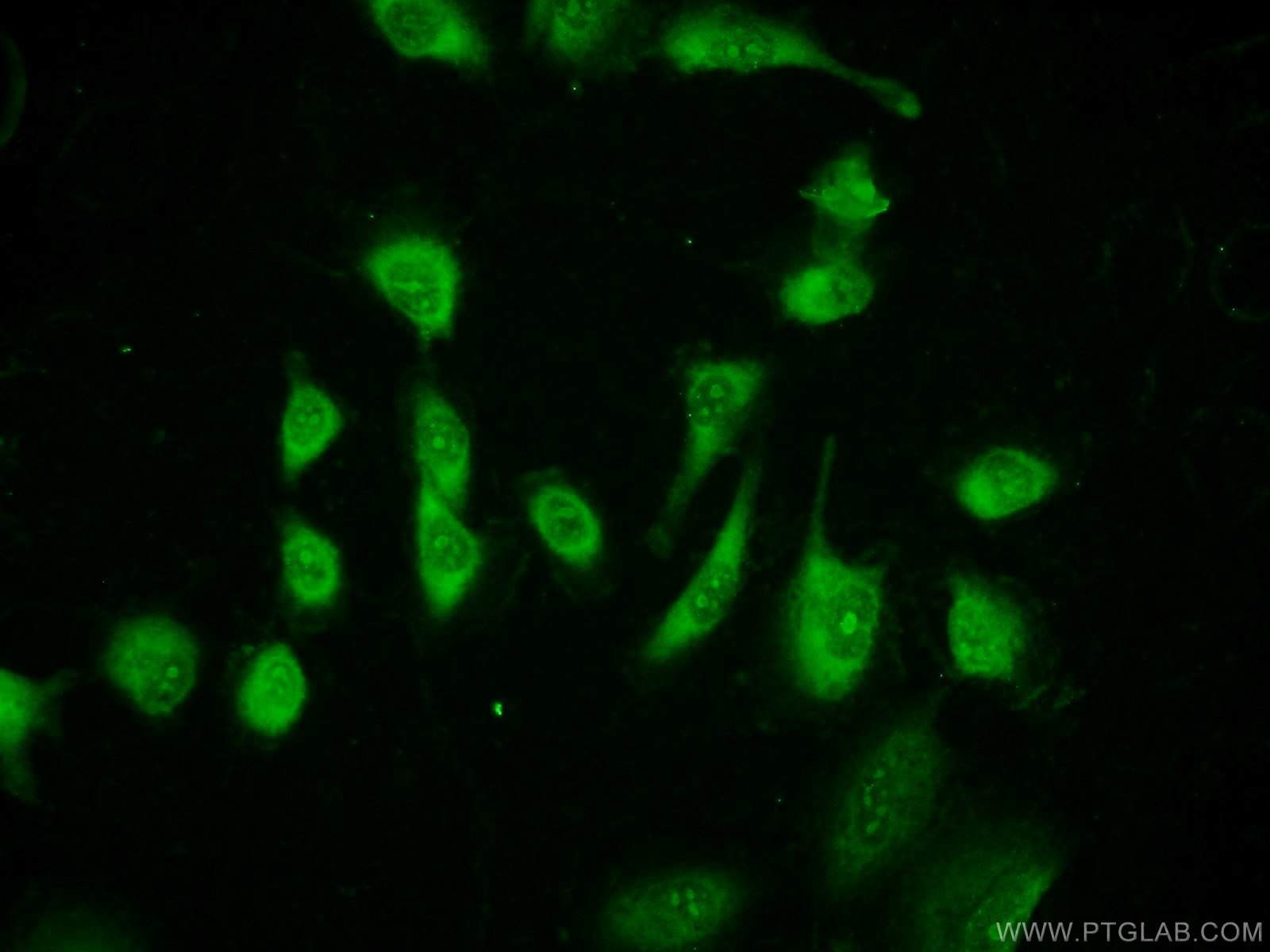
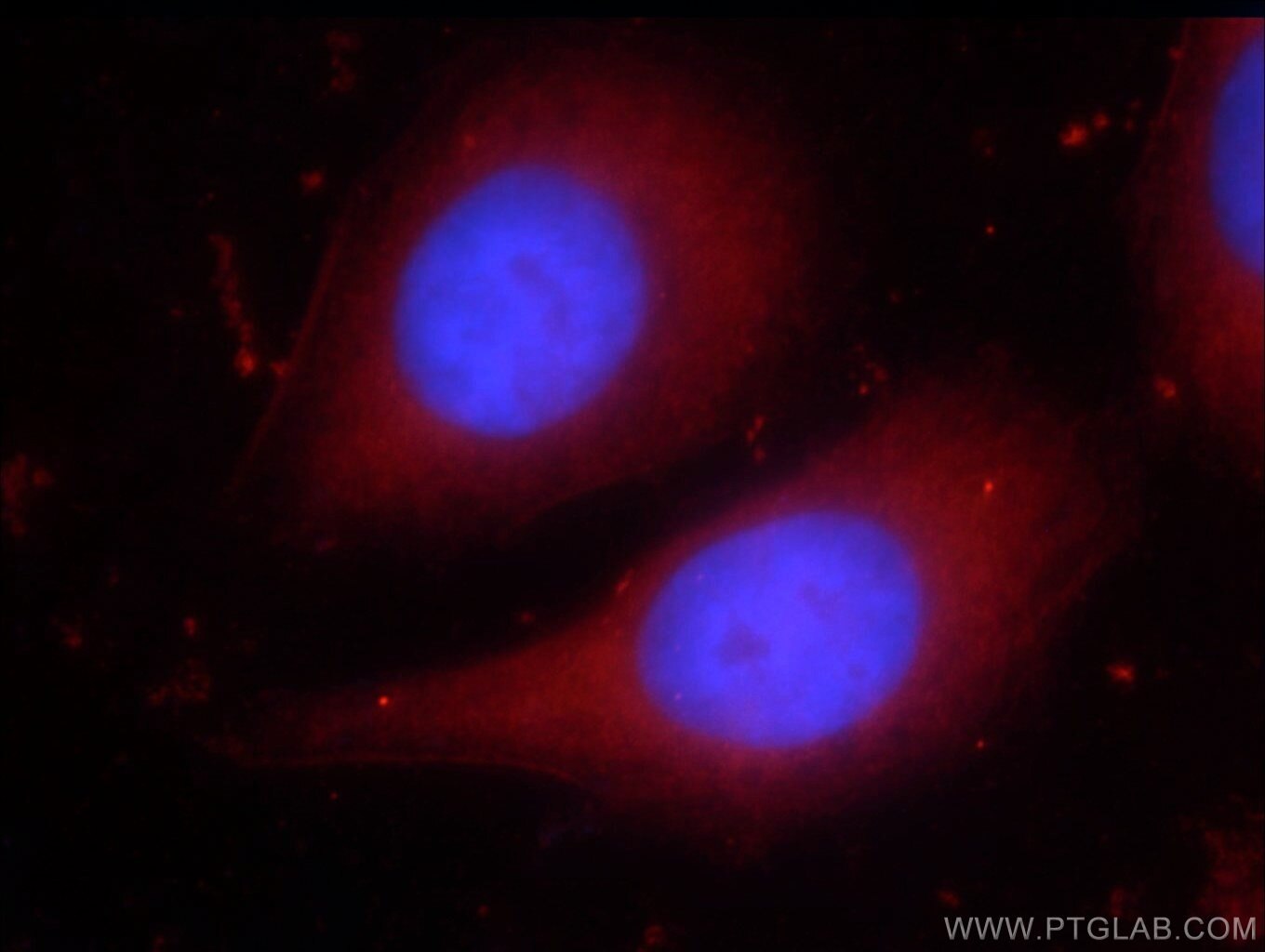
| Résultats positifs en IF | tissu adipeux de souris, cellules HUVEC |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | IF : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
15872-1-AP cible FABP4 dans les applications de WB, IF, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | FABP4 Protéine recombinante Ag8631 |
| Nom complet | fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 132 aa, 15 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 15 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC003672 |
| Symbole du gène | FABP4 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 2167 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 4 is a member of the FABP family which abundantly expressed, fatty acid carrier proteins. FABPs are capable of binding a variety of hydrophobic molecules such as long-chain fatty acids and are important for their uptake and intracellular trafficking. It was first identified as an adipocyte-specific protein, important for the maintenance of lipid and glucose metabolism. It is also detected in macrophages, where it participates in regulating inflammation and cholesterol trafficking via NFκB and PPAR. In more recent studies, FABP4 has been found in a variety of endothelial cells, where it has been identified as a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation and possibly angiogenesis. Pathologically, FABP4 has been associated with the development of metabolic syndrome, diabetes and cancer and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. FABP4 has been identified as a novel prognostic factor for both adverse cardiovascular events and breast cancer.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for FABP4 antibody 15872-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for FABP4 antibody 15872-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for FABP4 antibody 15872-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Eur Heart J Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in atherosclerotic plaques is associated with local vulnerability and is predictive for the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events. | ||
Autophagy Autophagy loss impedes cancer-associated fibroblast activation via downregulating proline biosynthesis. | ||
PLoS Biol Single-cell mapping reveals new markers and functions of lymphatic endothelial cells in lymph nodes. | ||
Int J Obes (Lond) miR-20a regulates adipocyte differentiation by targeting lysine-specific demethylase 6b and transforming growth factor-β signaling. | ||
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol Human Adipocytes from the Subcutaneous Superficial Layer have Greater Adipogenic Potential and Lower PPAR-γ DNA Methylation Levels than Deep Layer Adipocytes. |