CRM1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
CRM1 Polyklonal Antikörper für ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 12915-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
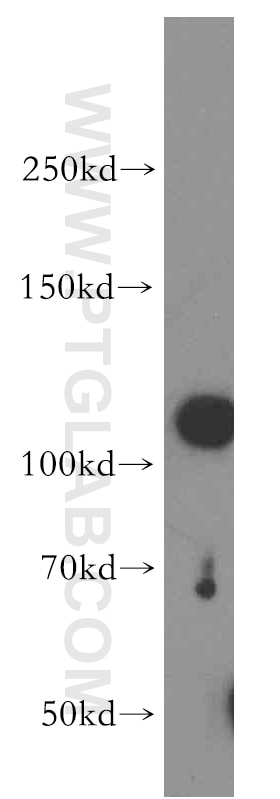
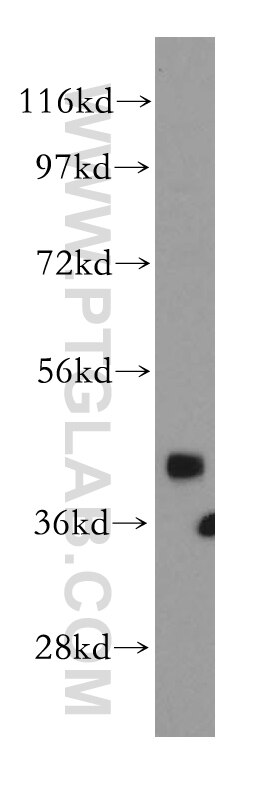
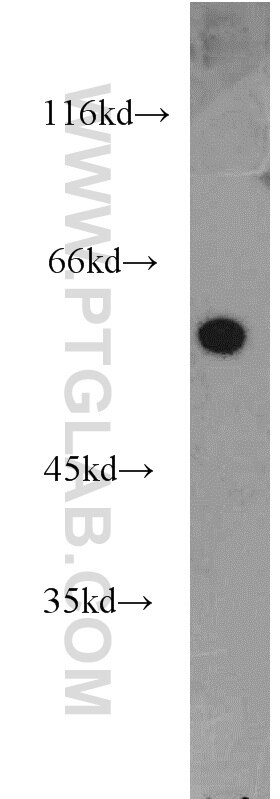
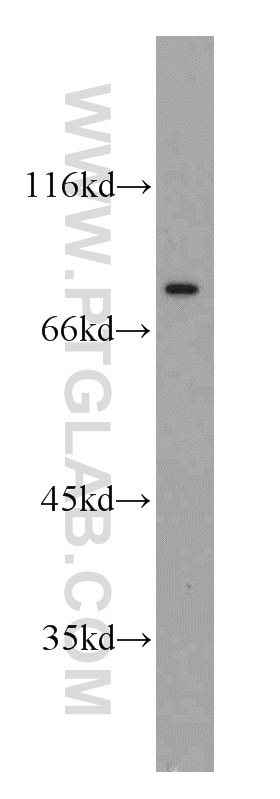
12915-1-AP bindet in WB, ELISA CRM1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | CRM1 fusion protein Ag3488 |
| Vollständiger Name | exportin 1 (CRM1 homolog, yeast) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 1071 aa, 123 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 100-110 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC032847 |
| Gene symbol | CRM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7514 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
CRM1 (chromosome region maintenance 1, also known as exportin-1 or XPO1), a member of the karyopherin β family of transport receptors, is an important nuclear export receptor recognizing proteins bearing a leucine-rich nuclear export signal (PMID: 9323133). CRM1 is the major receptor for the export of proteins out of the nucleus and is also required for transport of many RNAs (PMID: 17317185). In addition to nuclear export, CRM1 also plays a role in centrosome duplication and spindle assembly (PMID: 22773955). Elevated CRM1 expression has been reported in several cancers, which implicates CRM1 as a potential anti-cancer drug target (PMID: 22677130; 21683812 ).
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Toxicology Tetrachlorobenzoquinone induces Nrf2 activation via rapid Bach1 nuclear export/ubiquitination and JNK-P62 signaling. |