Tested Applications
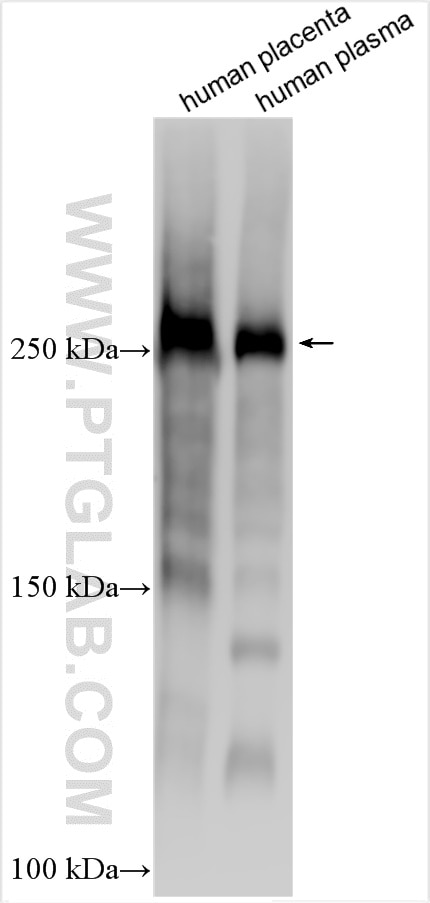
| Positive WB detected in | human placenta tissue, human plasma |
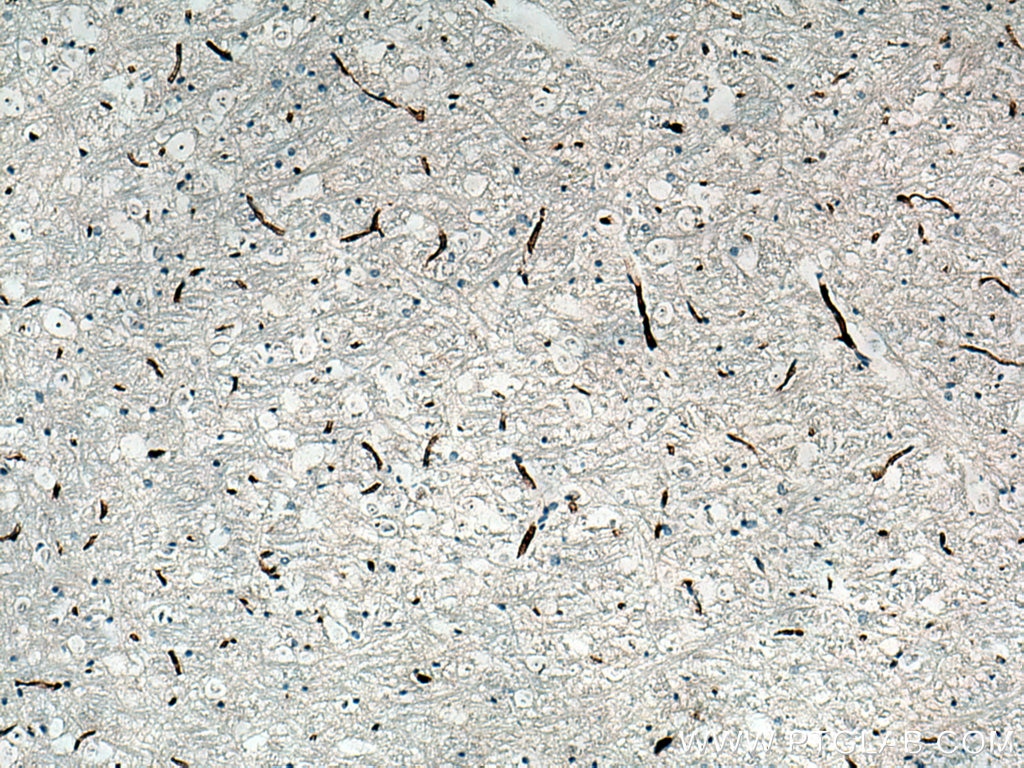
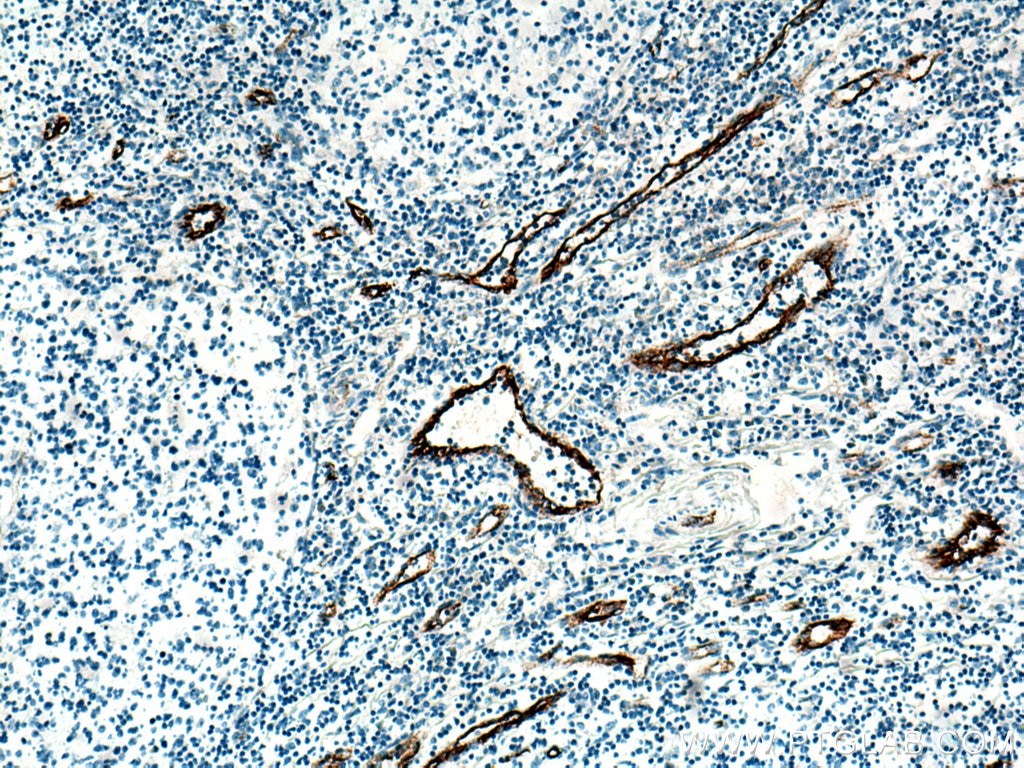
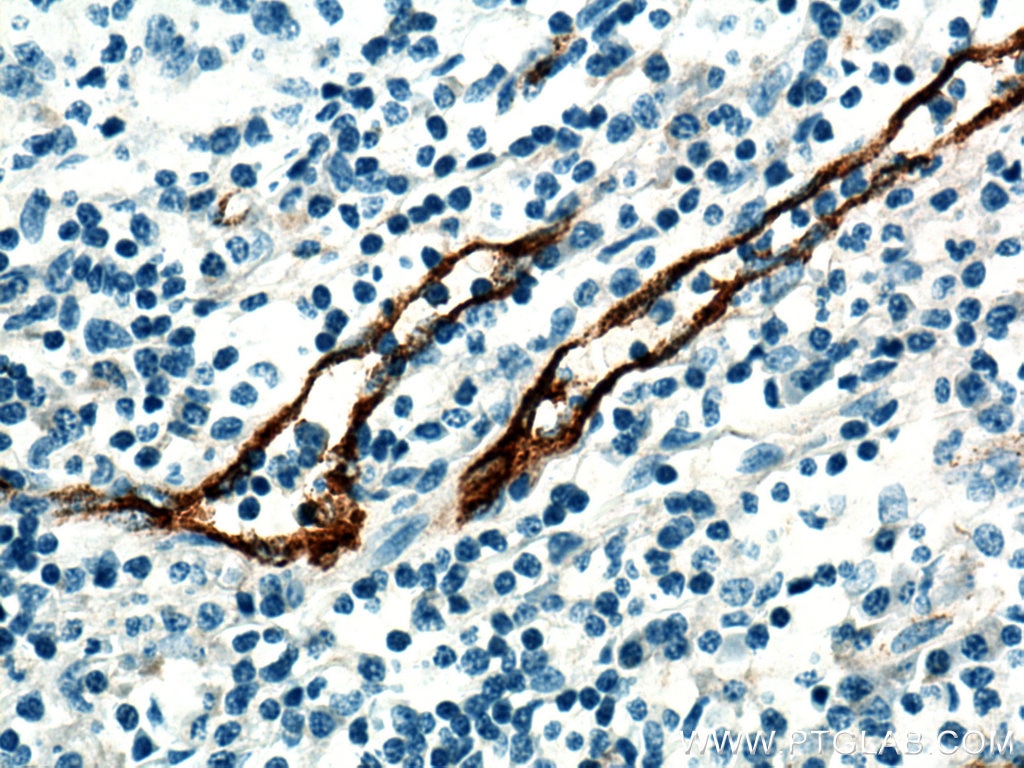
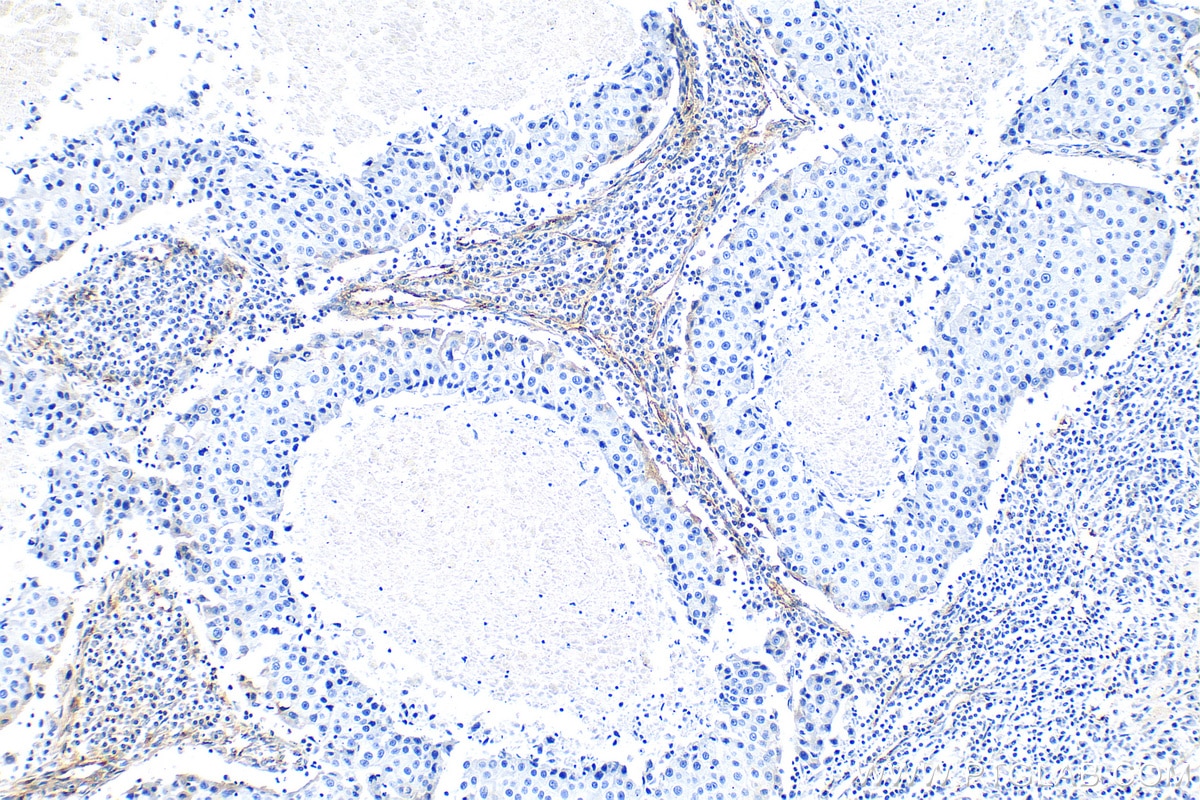
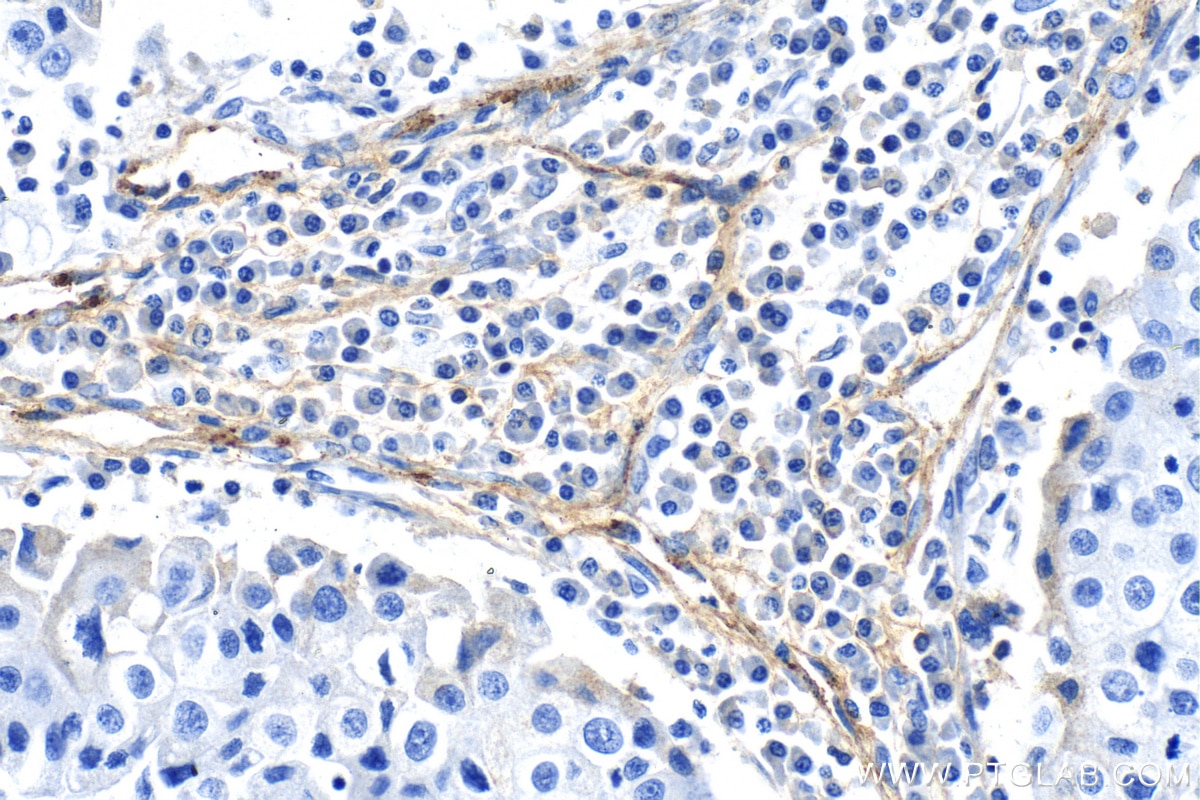
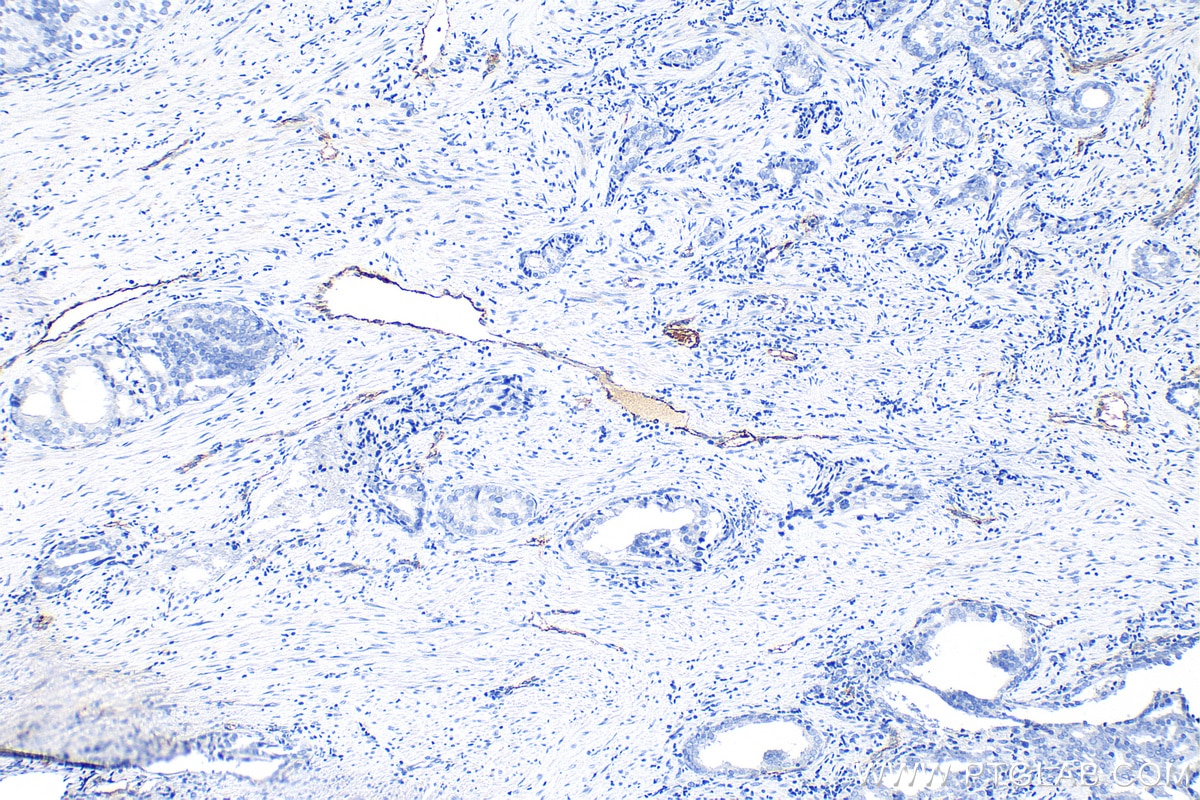
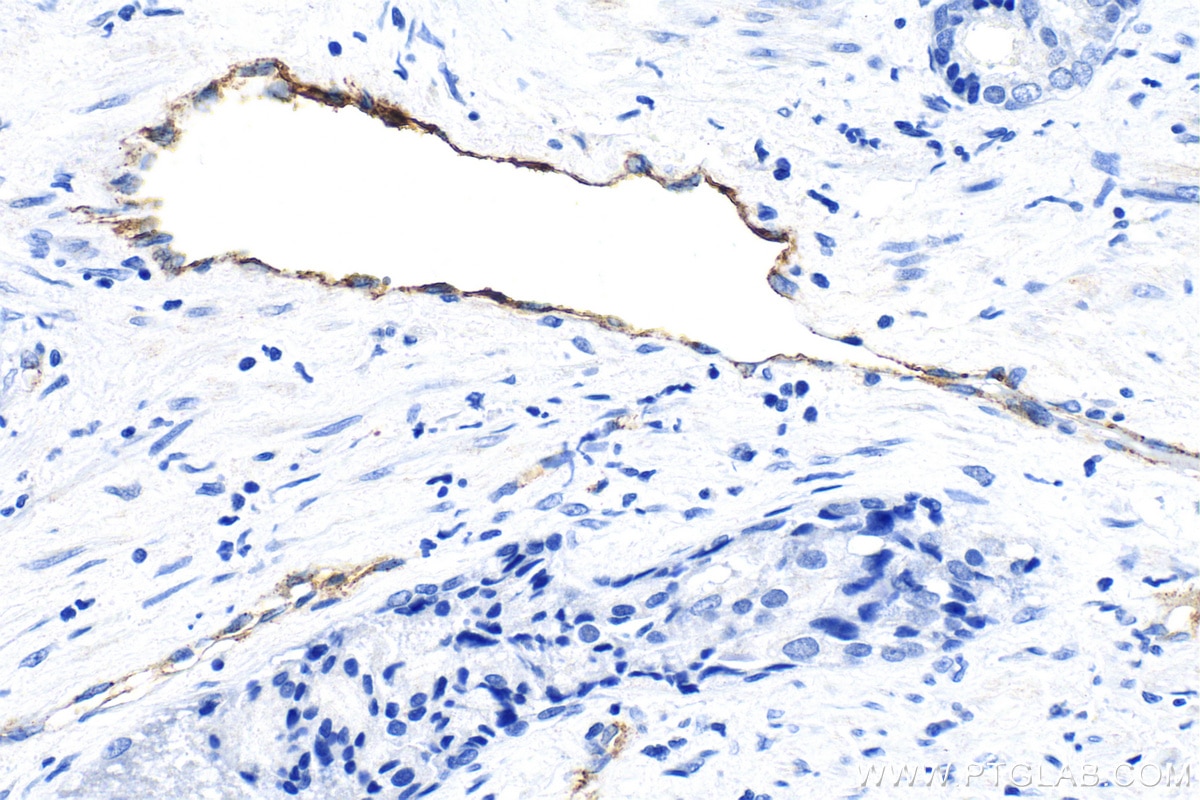
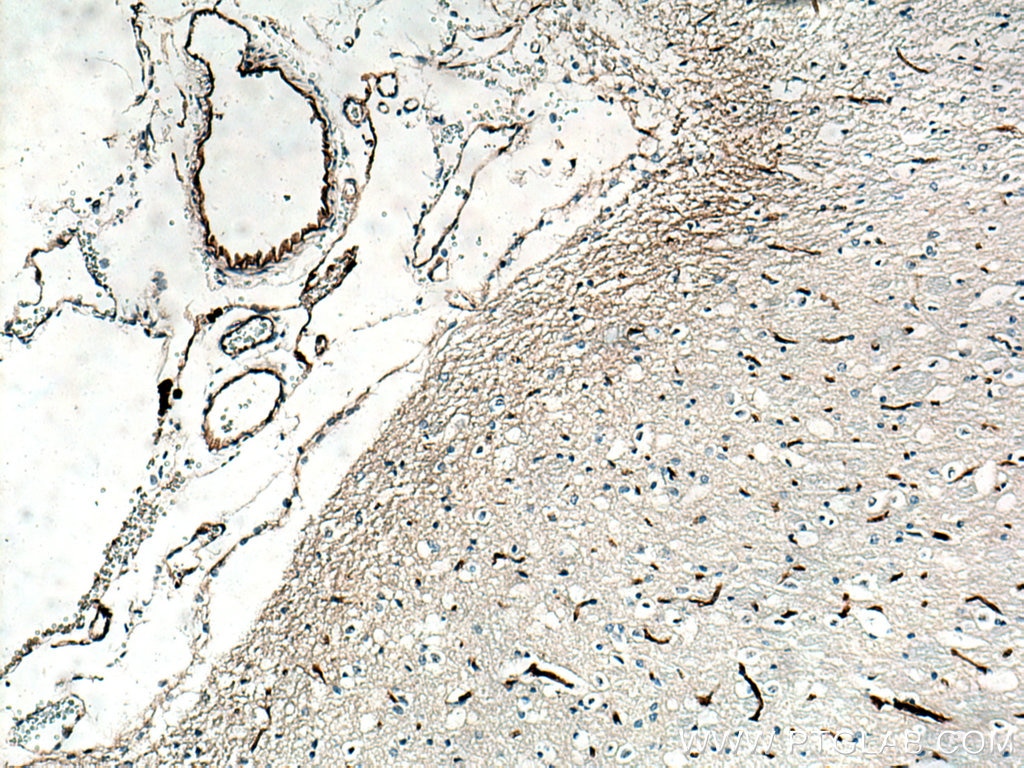
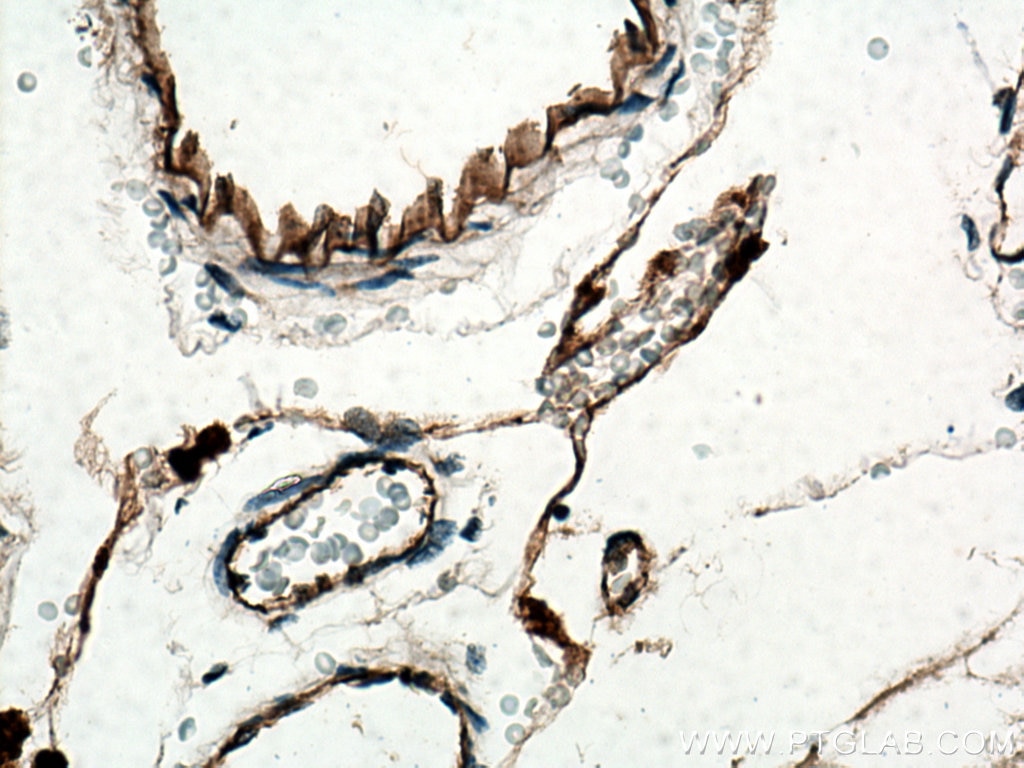
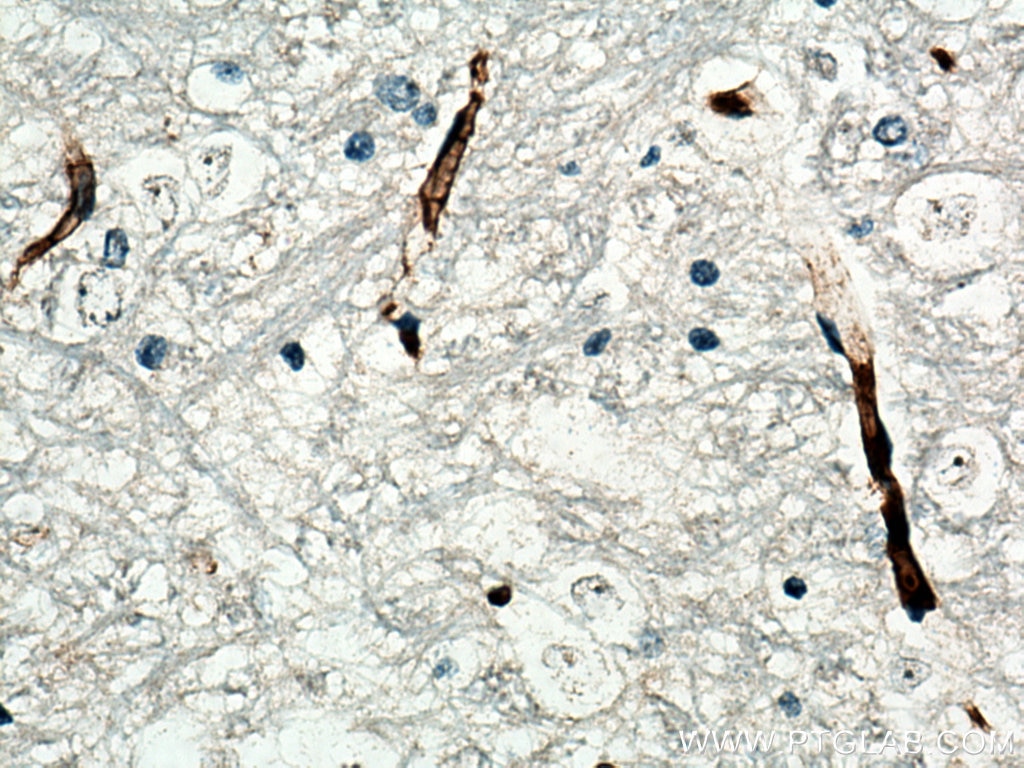
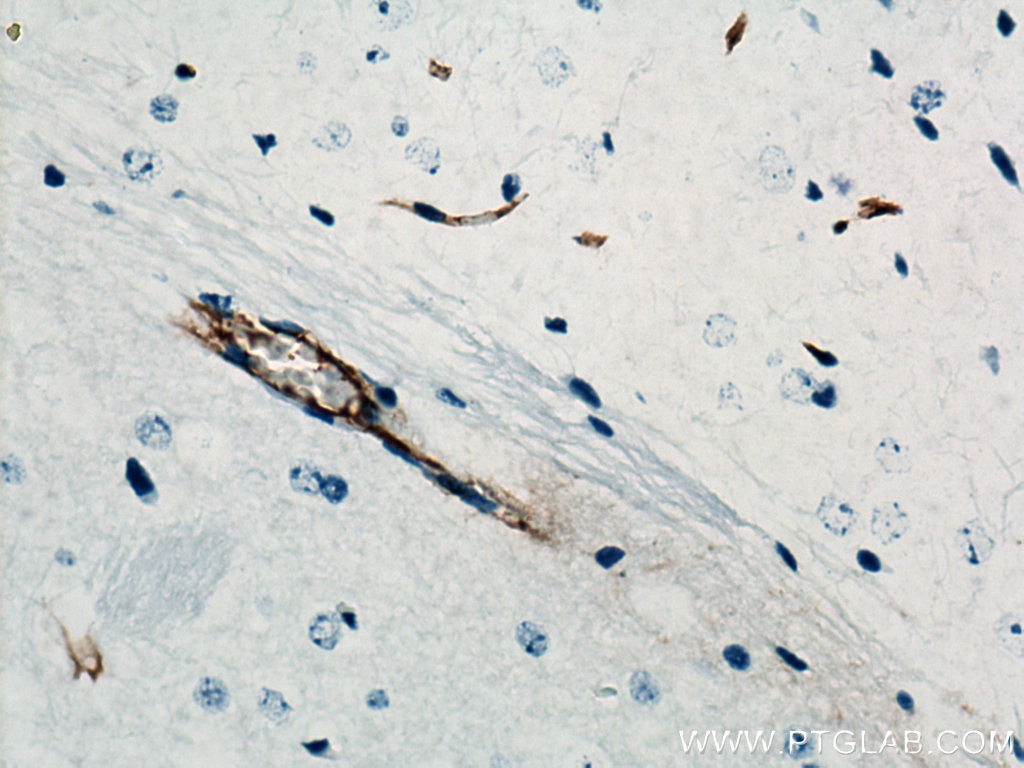
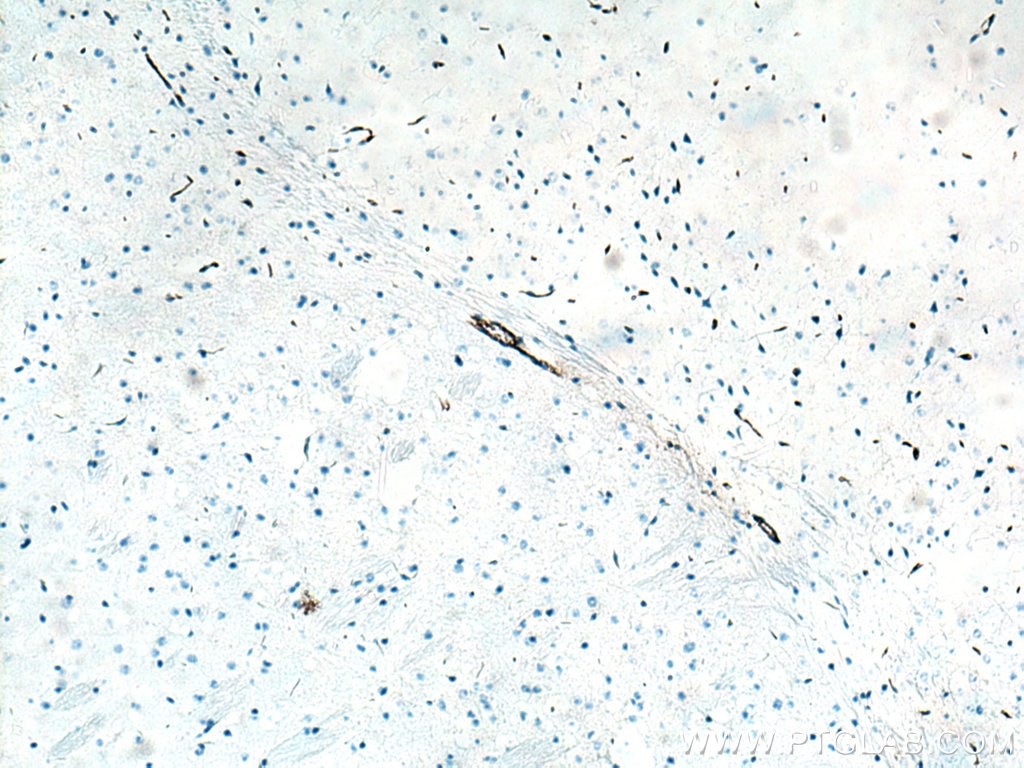
| Positive IHC detected in | human tonsillitis tissue, mouse brain tissue, rat brain tissue, human prostate cancer tissue, human breast cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
| Positive IF-P detected in | human tonsillitis tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 3 publications below |
| IHC | See 7 publications below |
| IF | See 38 publications below |
Product Information
27186-1-AP targets VWF in WB, IHC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag25578 Product name: Recombinant human vwf protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Sequence: MSSPLSHRSKRSLSCRPPMVKLVCPADNLRAEGLECTKTCQNYDLECMSMGCVSGCLCPPGMVRHENRCVALERCPCFHQGKEYAPGETVKIGCNTCVCQD Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | von Willebrand factor |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 220-250 kDa |
| Gene Symbol | VWF |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7450 |
| RRID | AB_2880791 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P04275 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a large multimeric glycoprotein found in blood plasma involved in hemostasis following vascular injury.
What is the molecular weight of VWF?
Due to the multimeric nature of VWF, it can range in size from 500 to 20,000 kDa due to the differences in the number of subunits comprising the protein. Each subunit is approximately 250 kDa (PMID: 9759493).
What is the tissue specificity of VWF?
The biosynthesis of VWF in vivo is limited to endothelial cells (PMID: 4209883) and megakaryocytes (PMID: 2413071). VWF synthesized in endothelial cells is either released directly into the plasma via a secretory pathway, or tubulized and stored in organelles unique to this cell type called Weibel-Palade bodies (PMID: 16459301). Whereas VWF synthesized in megakaryocytes is stored in the alpha granules of platelets (PMID: 2046403).
What is the function of VWF?
The primary function of VWF is as an adhesive plasma glycoprotein, particularly factor VIII; an essential blood-clotting protein (PMID: 6982084). VWF is also important in platelet adhesion to wound sites by binding specifically to type I and type III collagen (PMID: 11098050), with larger VWF multimers being most effective (PMID: 24448155).
What is the importance of post-translational modifications (PTMs) on VWF function?
During the synthesis of VWF, it must undergo extensive PTMs. The VWF monomers are subsequently N-glycosylated with the addition of a 12 N-linked high-mannose-containing oligosaccharide after the cleavage of the signal peptide in the endoplasmic reticulum. Dimerization of the pro-VWF follows glycosylation via carboxyl-termini disulphide bond formation. In the Golgi apparatus, the oligosaccharide chains are further modified into complex carbohydrates and multimerization of pro-VWF dimers occurs after another round of disulphide bond formation at the amino-termini end of the subunits (PMID: 6334089).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for VWF antibody 27186-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for VWF antibody 27186-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for VWF antibody 27186-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Biomaterials Oriented nanofibrous P(MMD-co-LA)/Deferoxamine nerve scaffold facilitates peripheral nerve regeneration by regulating macrophage phenotype and revascularization. | ||
Mater Today Bio Endoscopic nasal delivery of engineered endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes improves angiogenesis and neurological deficits in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage | ||
Adv Healthc Mater Platelet Membrane-Fused Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Protect the Heart from Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury | ||
Acta Biomater Selective inhibition of glycolysis in hepatic stellate cells and suppression of liver fibrogenesis with vitamin A-derivative decorated camptothecin micelles | ||
Front Immunol Fatty acid synthase inhibition improves hypertension-induced erectile dysfunction by suppressing oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis through activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway | ||
Regen Biomater Microvascular network based on the Hilbert curve for nutrient transport in thick tissue |