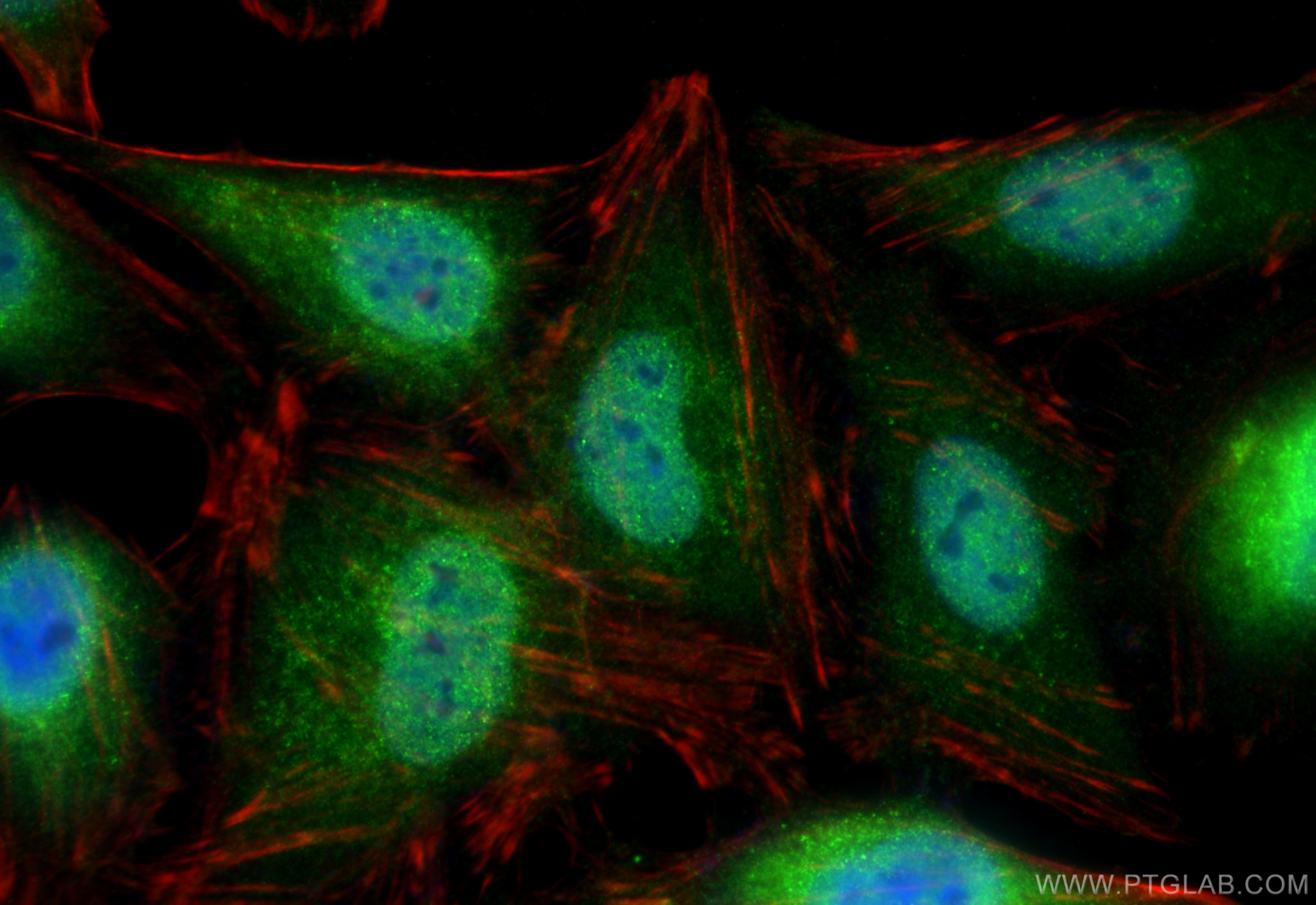
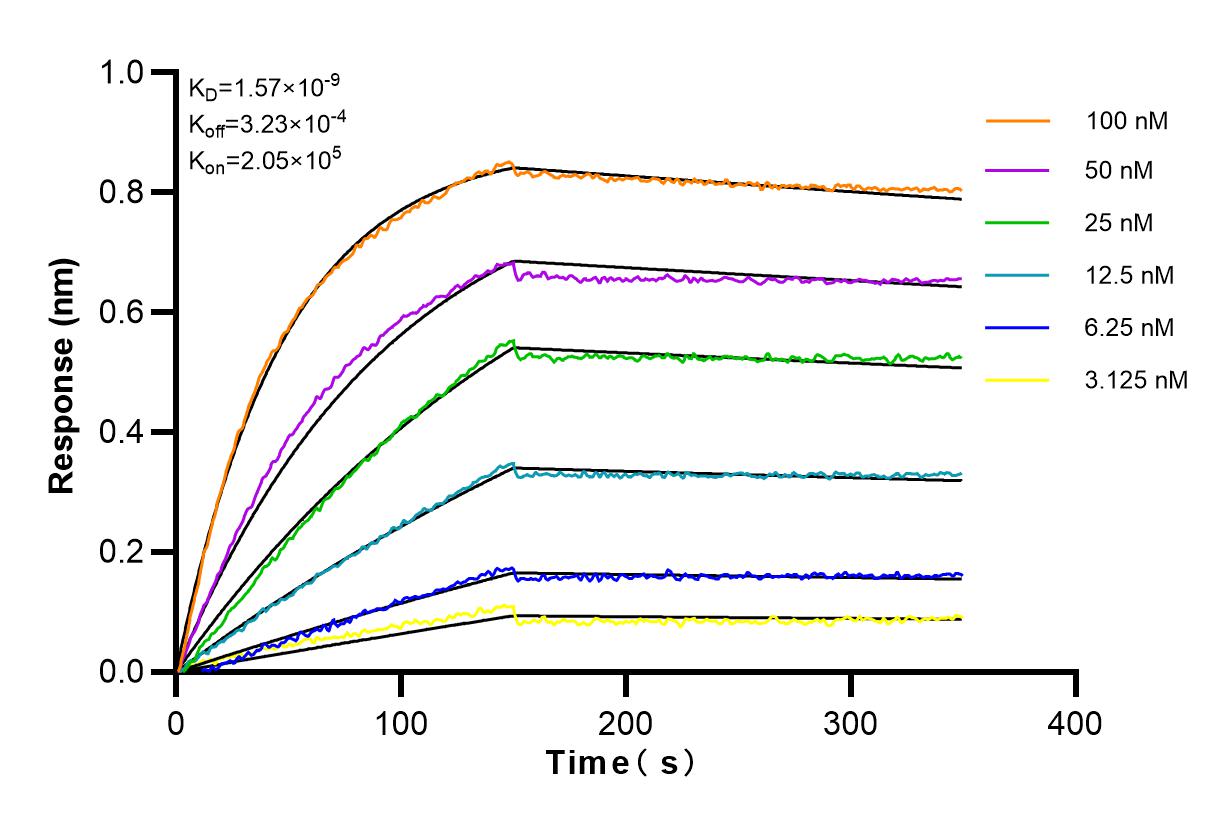
Product Information
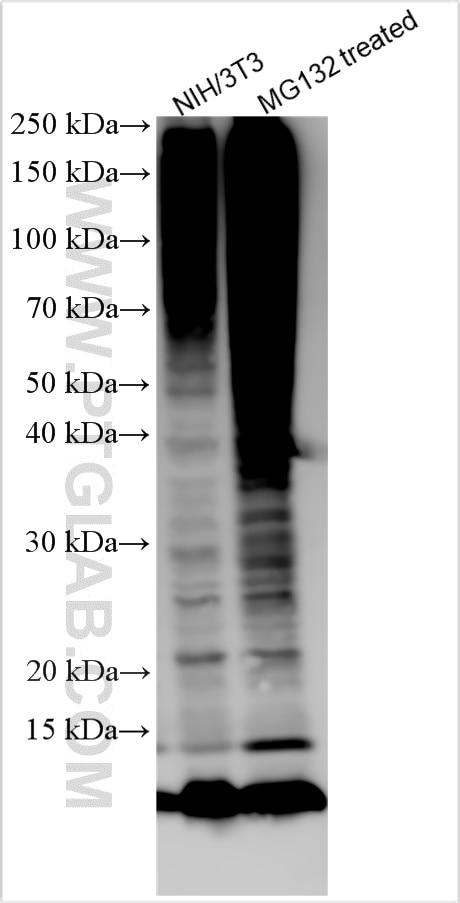
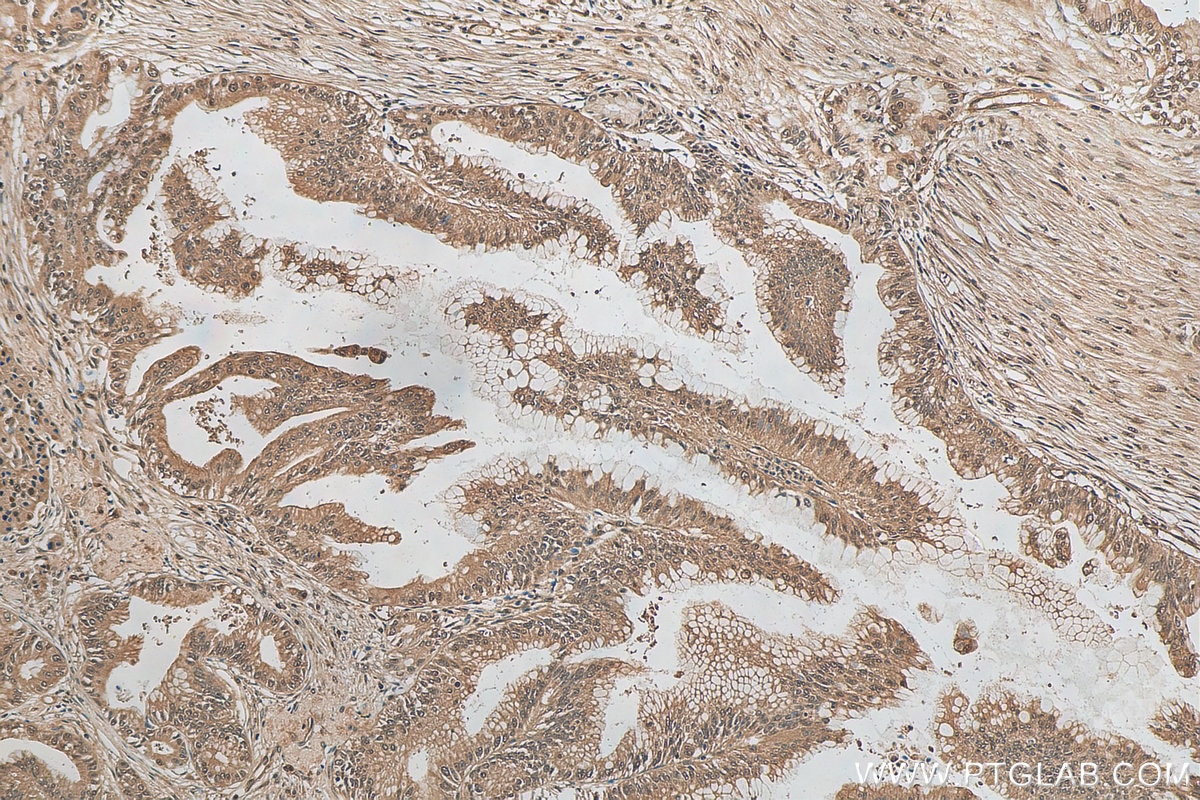
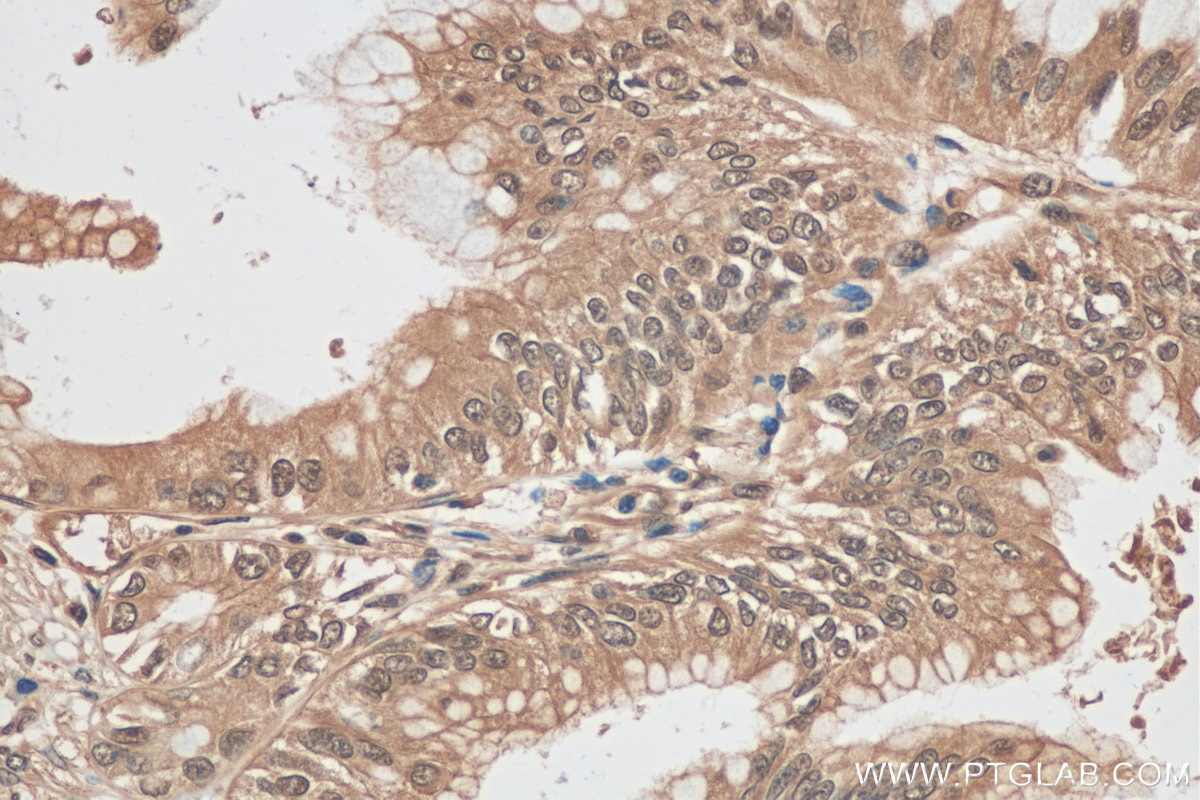
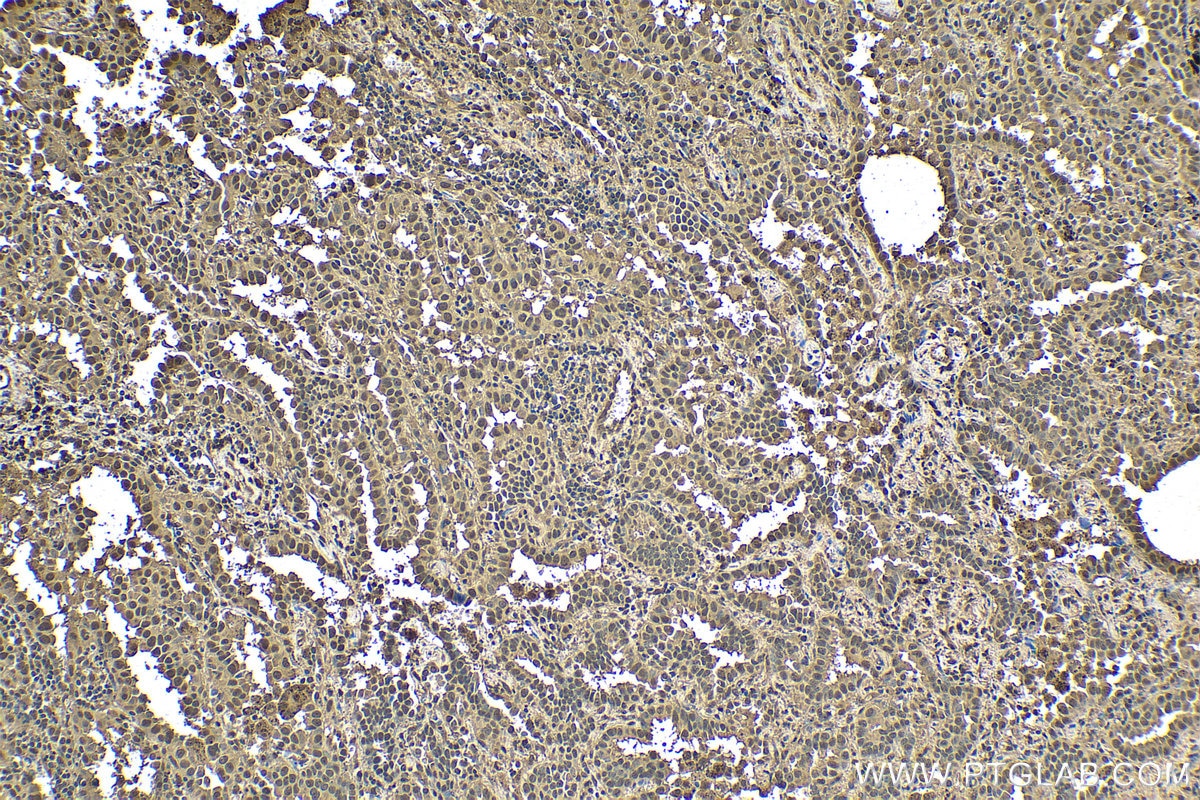
80992-1-PBS targets ubiquitin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster, yeast, spinach samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster, yeast, spinach |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag0260 Product name: Recombinant human ubiquitin protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 103-229 aa of BC000379 Sequence: KAKIQDKEGIPPDQQRLIFAGKQLEDGRTLSDYNIQKESTLHLVLRLRGGMQIFVKTLTGKTITLEVEPSDTIENVKAKIQDKEGIPPDQQRLIFAGKQLEDGRTLSDYNIQKESTLHLVLRLRGGC Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ubiquitin B |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC000379 |
| Gene Symbol | ubiquitin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7314 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P0CG47 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Ubiquitin B (UBB) is a member of ubiquitin family, one of the most conserved proteins known. Ubiquitin B is required for ATP-dependent, non-lysosomal intracellular protein degradation of abnormal proteins and normal proteins with a rapid turnover. Ubiquitin B is covalently bound to proteins to be degraded, and presumably labels these proteins for degradation. Ubiquitin also binds to histone H2A in actively transcribed regions but does not cause histone H2A degradation, suggesting that ubiquitin is also involved in regulation of gene expression.When polyubiquitin is free (unanchored-polyubiquitin), it also has distinct roles, such as in activation of protein kinases, and in signaling. This gene consists of three direct repeats of the ubiquitin coding sequence with no spacer sequence. Consequently, the protein is expressed as a polyubiquitin precursor with a final amino acid after the last repeat. Aberrant form of this protein has been noticed in patients with Alzheimer's and Down syndrome. Interestingly ubiquitin also becomes covalently bonded to many types of pathological inclusions which appear to be resistant to normal degradation.