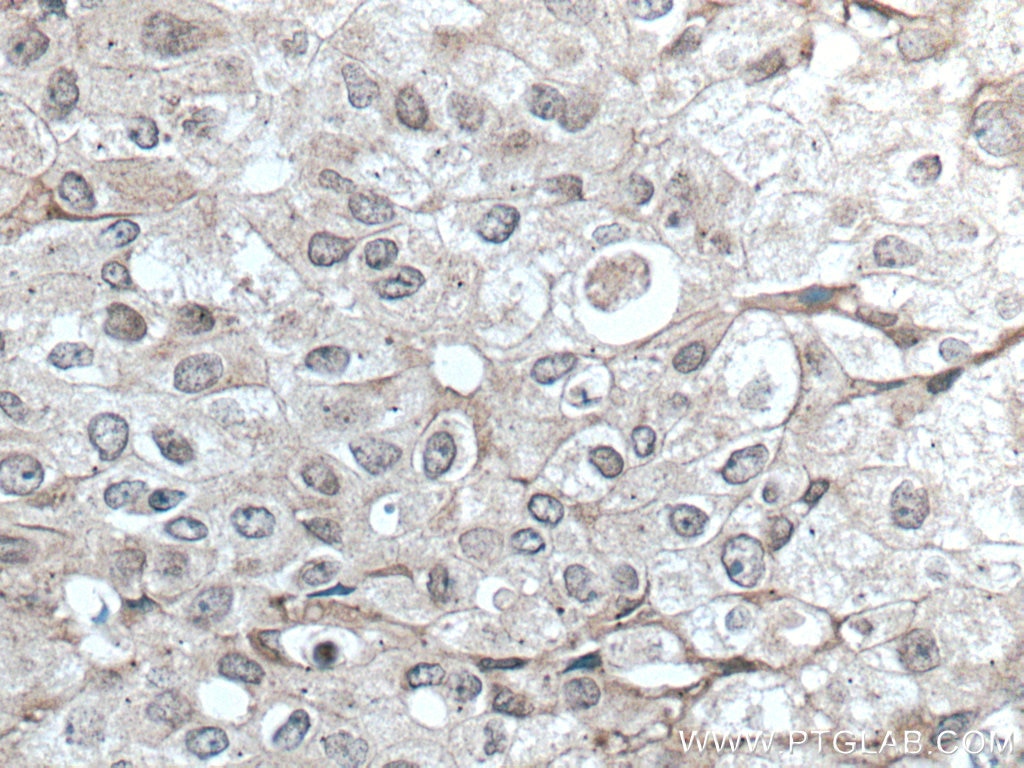
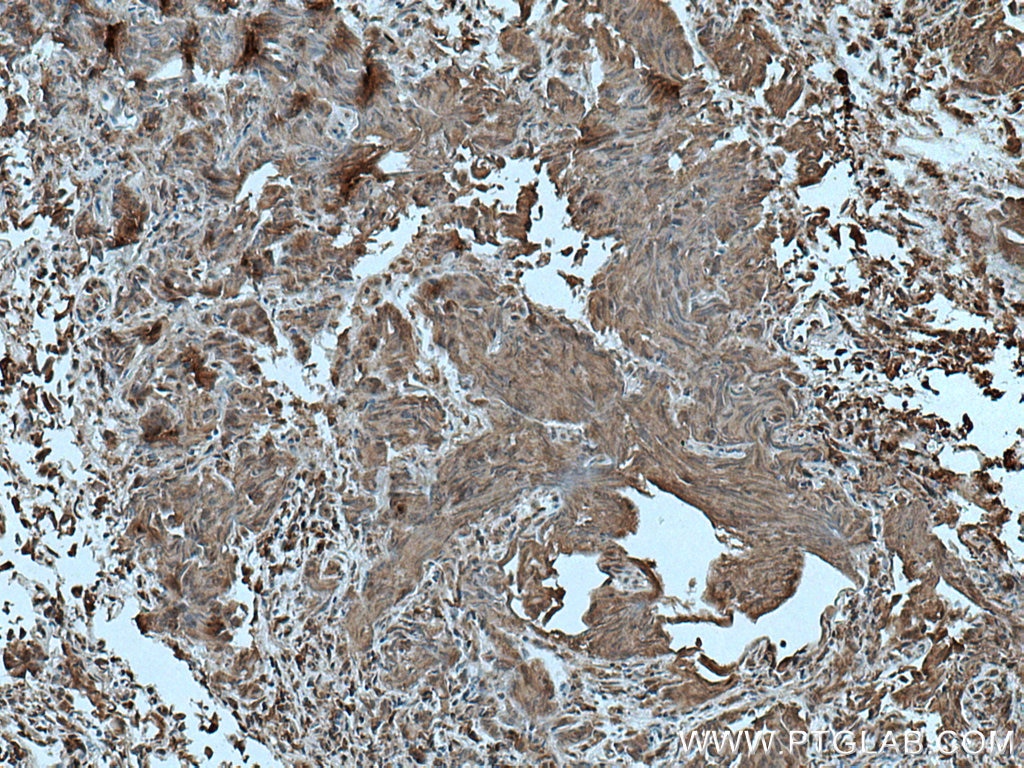
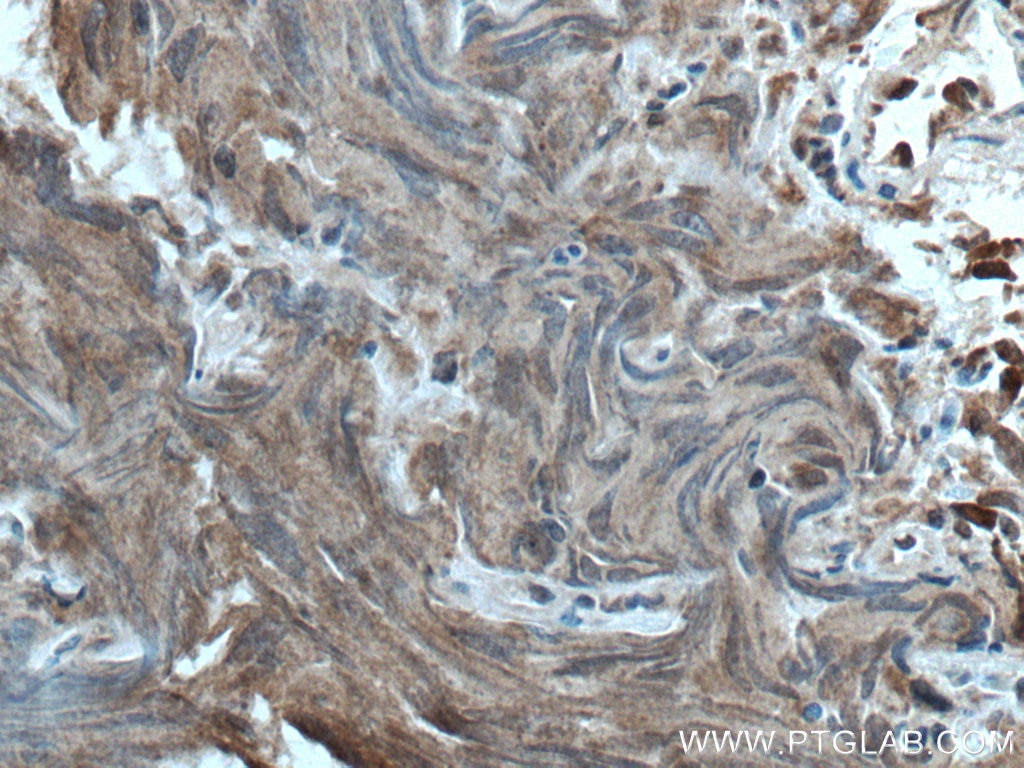
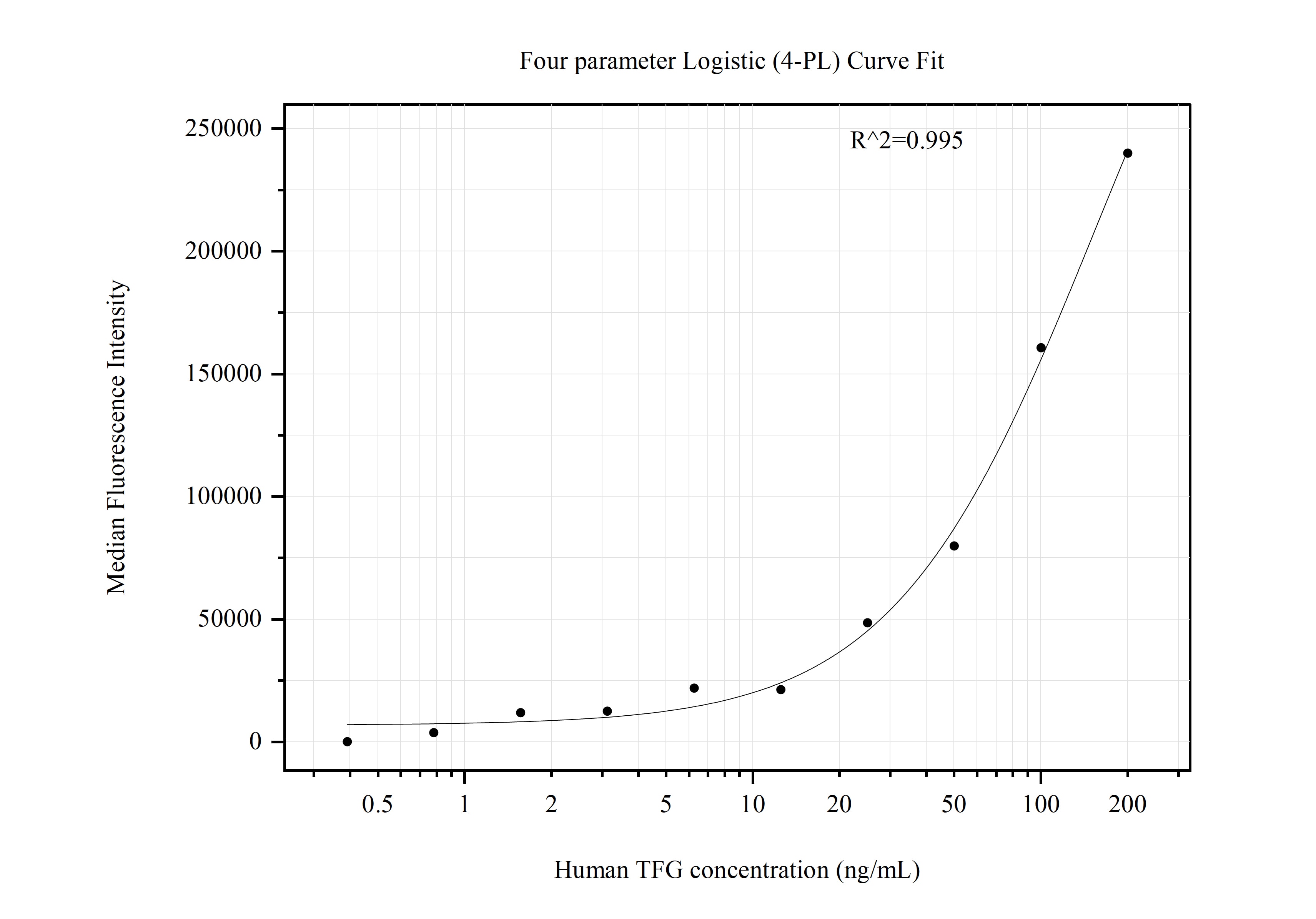
Product Information
66916-1-PBS targets TFG as part of a matched antibody pair:
MP50894-1: 66916-1-PBS capture and 66916-2-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, pig |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | TFG fusion protein Ag27697 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | TRK-fused gene |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 400 aa, 43 kDa |
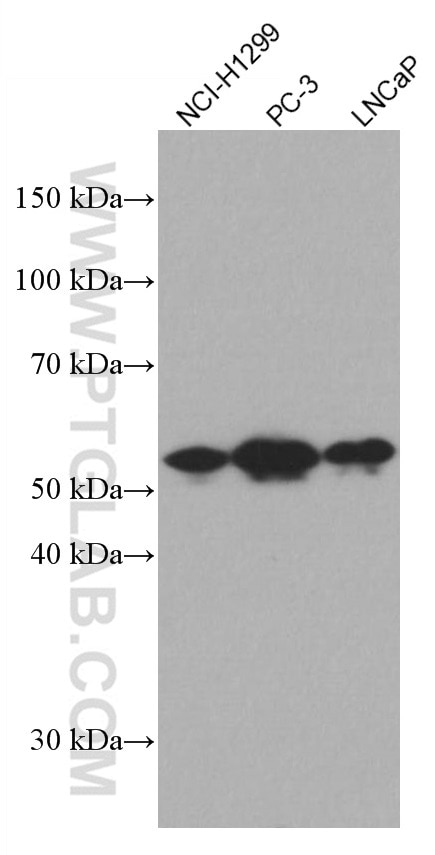
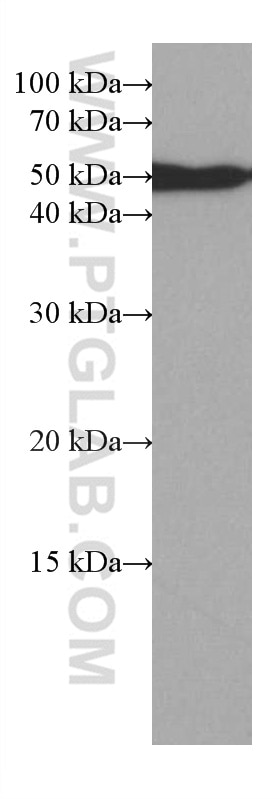
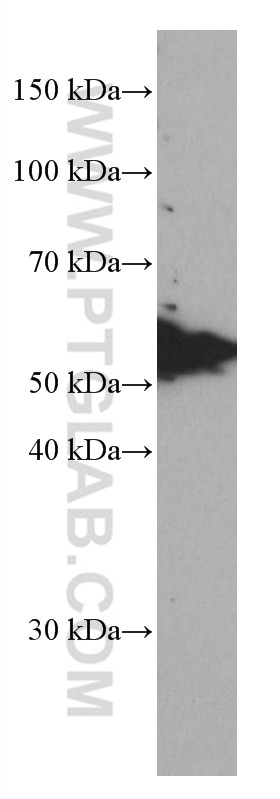
| Observed Molecular Weight | 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC023599 |
| Gene Symbol | TFG |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10342 |
| RRID | AB_2882243 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q92734 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Protein TFG (TRK-fused gene protein) plays a role in regulating phosphotyrosine-specific phosphatase-1 activity. Mutations in TFG may have important clinical relevance for current therapeutic strategies to treat metastatic melanoma. Defects in TFG are a cause of thyroid papillary carcinoma (TPC), a common tumor of the thyroid that typically arises as an irregular, solid or cystic mass from otherwise normal thyroid tissue. Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with proximal dominant involvement (HMSN-P) is an autosomal-dominant neurodegenerative disorder characterized by widespread fasciculations, proximal-predominant muscle weakness, and atrophy followed by distal sensory involvement. Recent genetic investigation indicates that formation of TFG-containing cytoplasmic inclusions and concomitant mislocalization of TAR DNA-binding protein 43 kDa (TDP-43) underlie motor neuron degeneration in HMSN-P. Pathological overlap of proteinopathies involving TFG and TDP-43 highlights a new pathway leading to motor neuron degeneration.