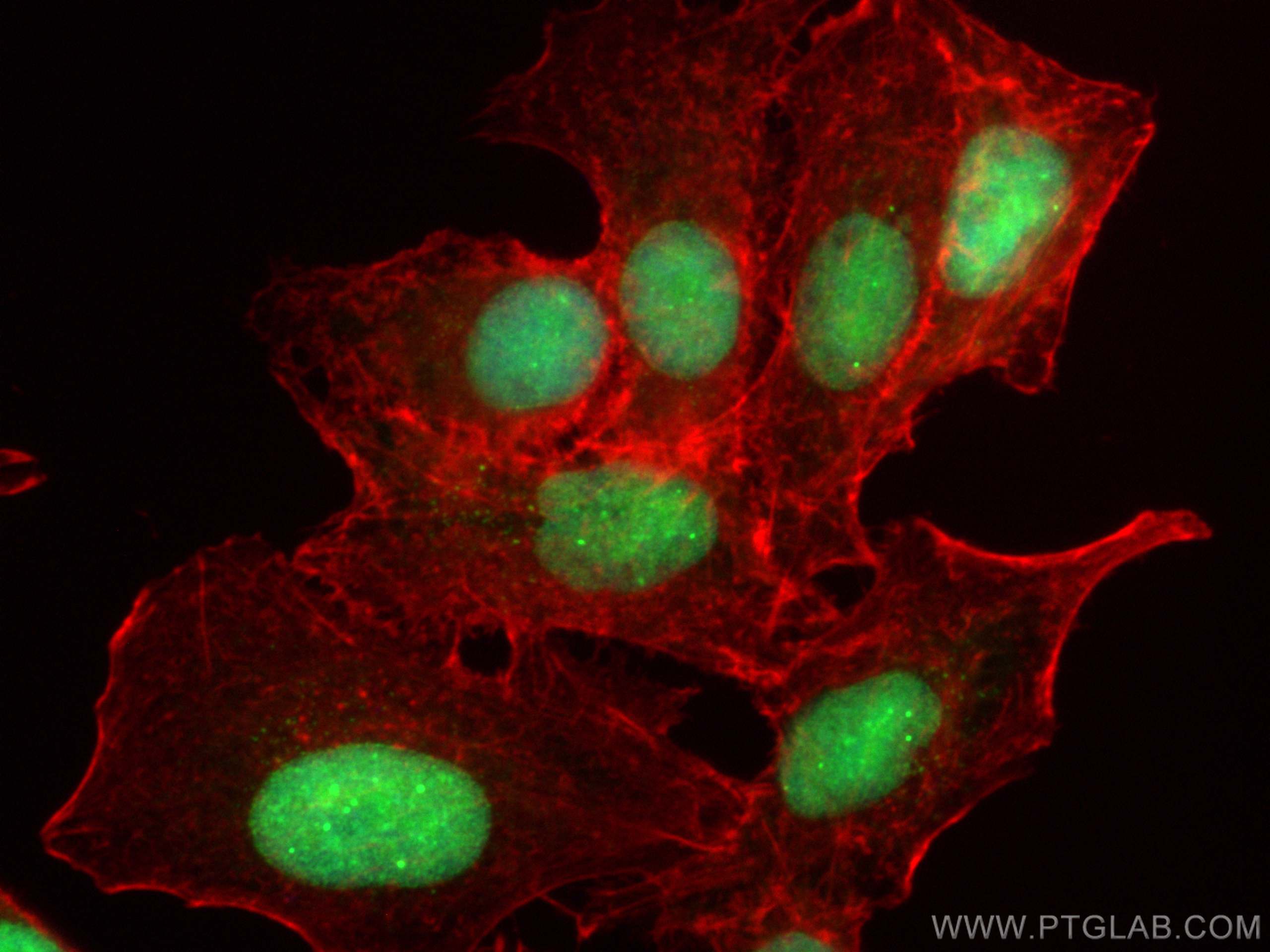
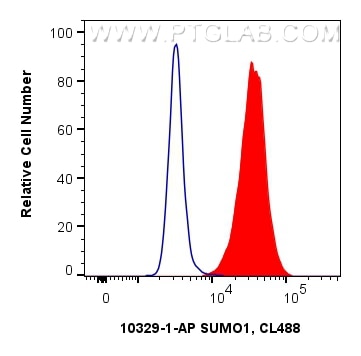
Product Information
10329-1-PBS targets SUMO1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | SUMO1 fusion protein Ag0414 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | SMT3 suppressor of mif two 3 homolog 1 (S. cerevisiae) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 12 kDa |
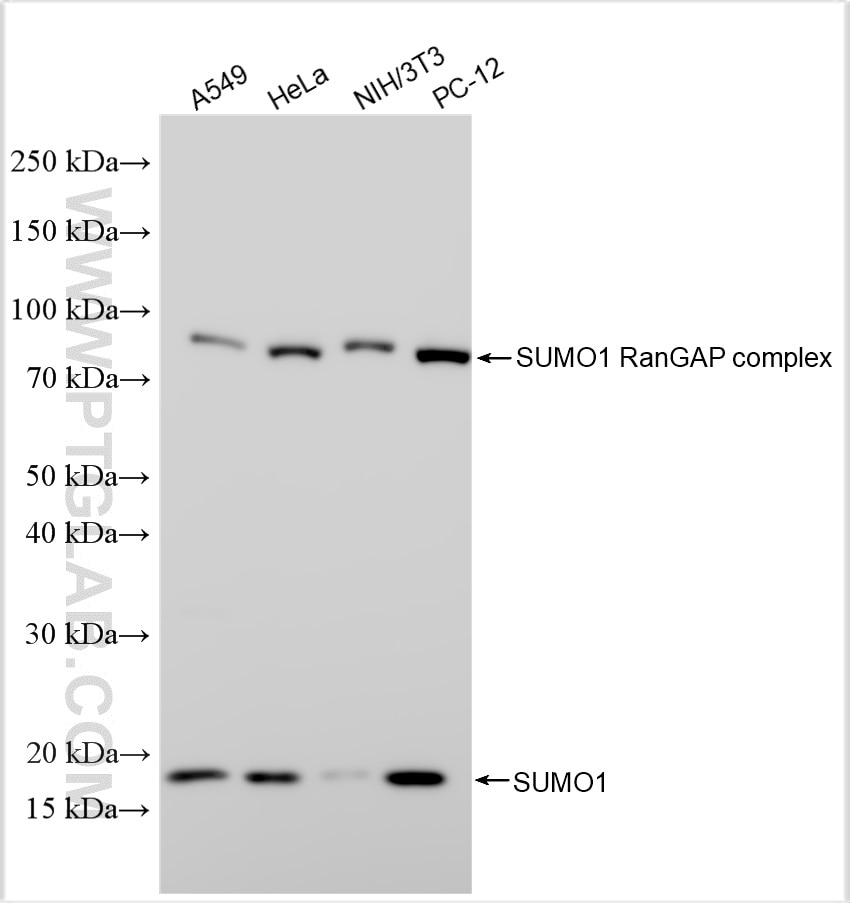
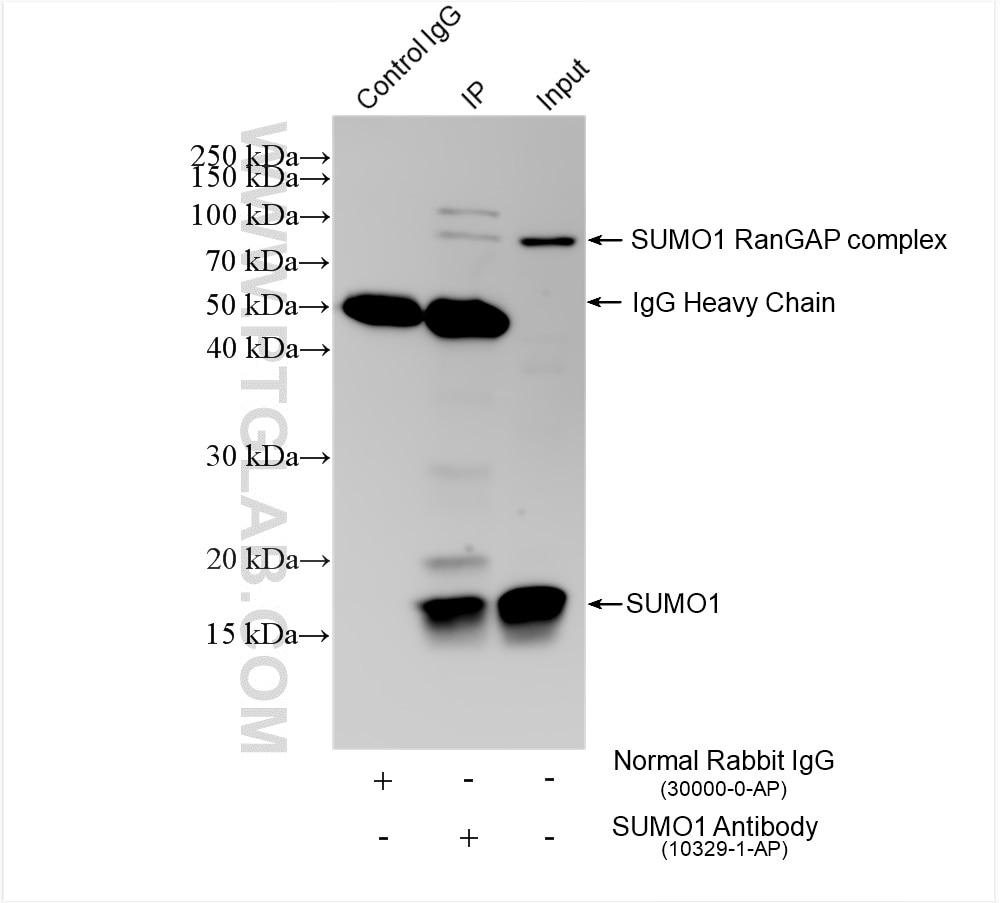
| Observed Molecular Weight | 12~18 kDa, 80-90 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC006462 |
| Gene Symbol | SUMO1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7341 |
| RRID | AB_2286872 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P63165 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 (SUMO1) belongs to the ubiquitin family and the SUMO subfamily as it contains 1 ubiquitin-like domain and is also 18% identical to ubiquitin (PMID: 9654451).
1. What is the molecular weight of SUMO1?
The molecular weight of SUMO1 is 12 kDa.
2. What is the cellular localization of SUMO1?
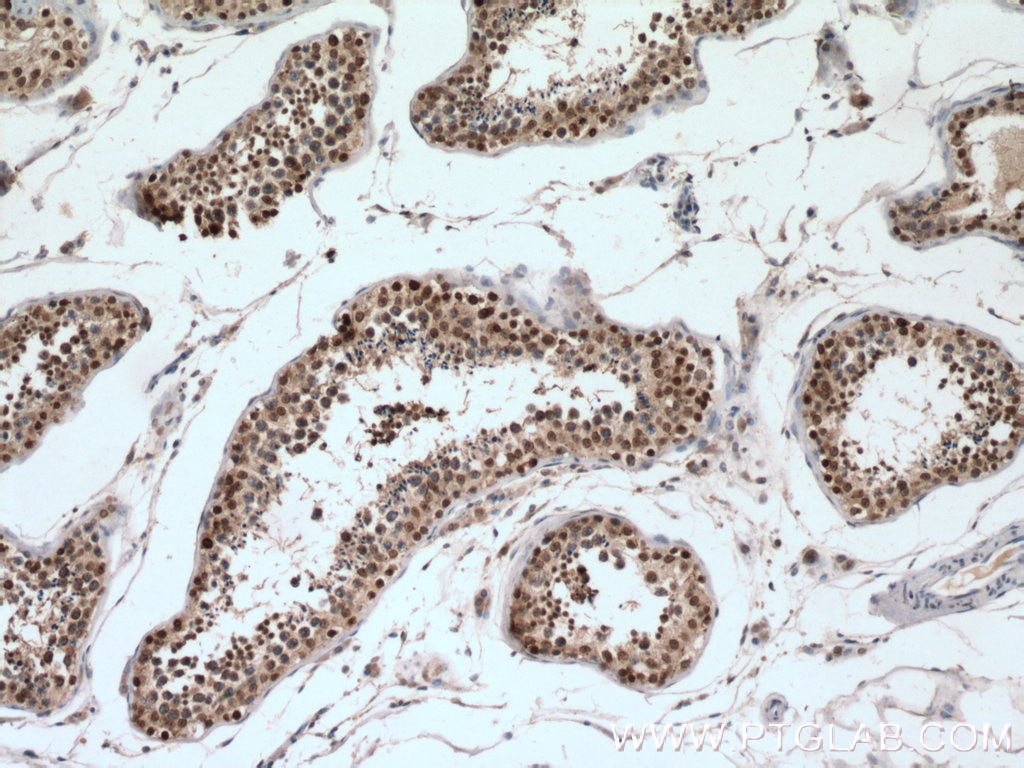
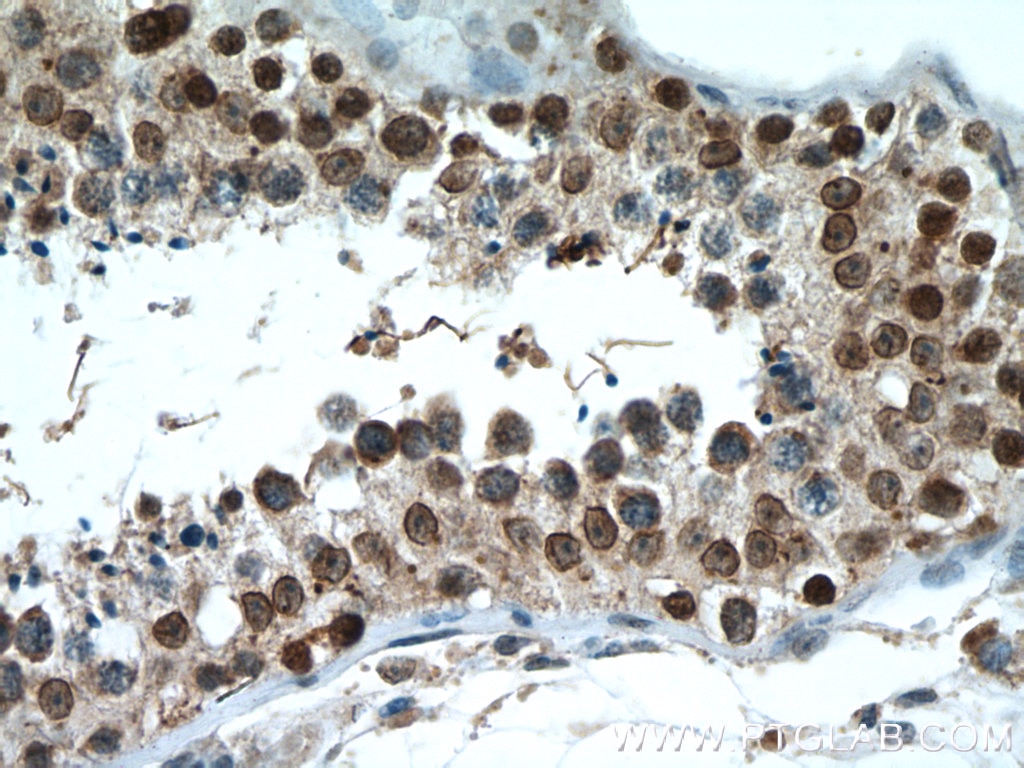
SUMO1 is located in the nuclear membrane and is recruited by BCL11A to the nuclear body (PMID: 18681895).
3. What modifications is SUMO1 subjected to?
SUMO1 function occurs after the cleavage of its precursor form by SENP1 or SENP2 (PMID: 27576863). Polymeric SUMO1 chains also undergo polyubiquitination by RNF4 (PMID: 18408734).
4. What is the function of SUMO1?
SUMO1 post-translationally modifies many proteins that have roles in an array of processes including transcriptional regulation, chromatin structure, and DNA repair. SUMO1 can covalently attach itself to protein as a monomer or a lysine-linked polymer via an isopeptide bond (PMID:11124955). This SUMO modification can regulate the localization and activity of the affected proteins.
5. What is SUMO1's involvement in disease?
Defects in SUMO1 as a result of a chromosomal translocation are associated with non-syndromic orofacial cleft type 10, or non-syndromic cleft lip, and are associated with cleft palate in two-thirds of cases (PMID: 18983974).