Product Information
66545-1-PBS targets STAT1 as part of a matched antibody pair:
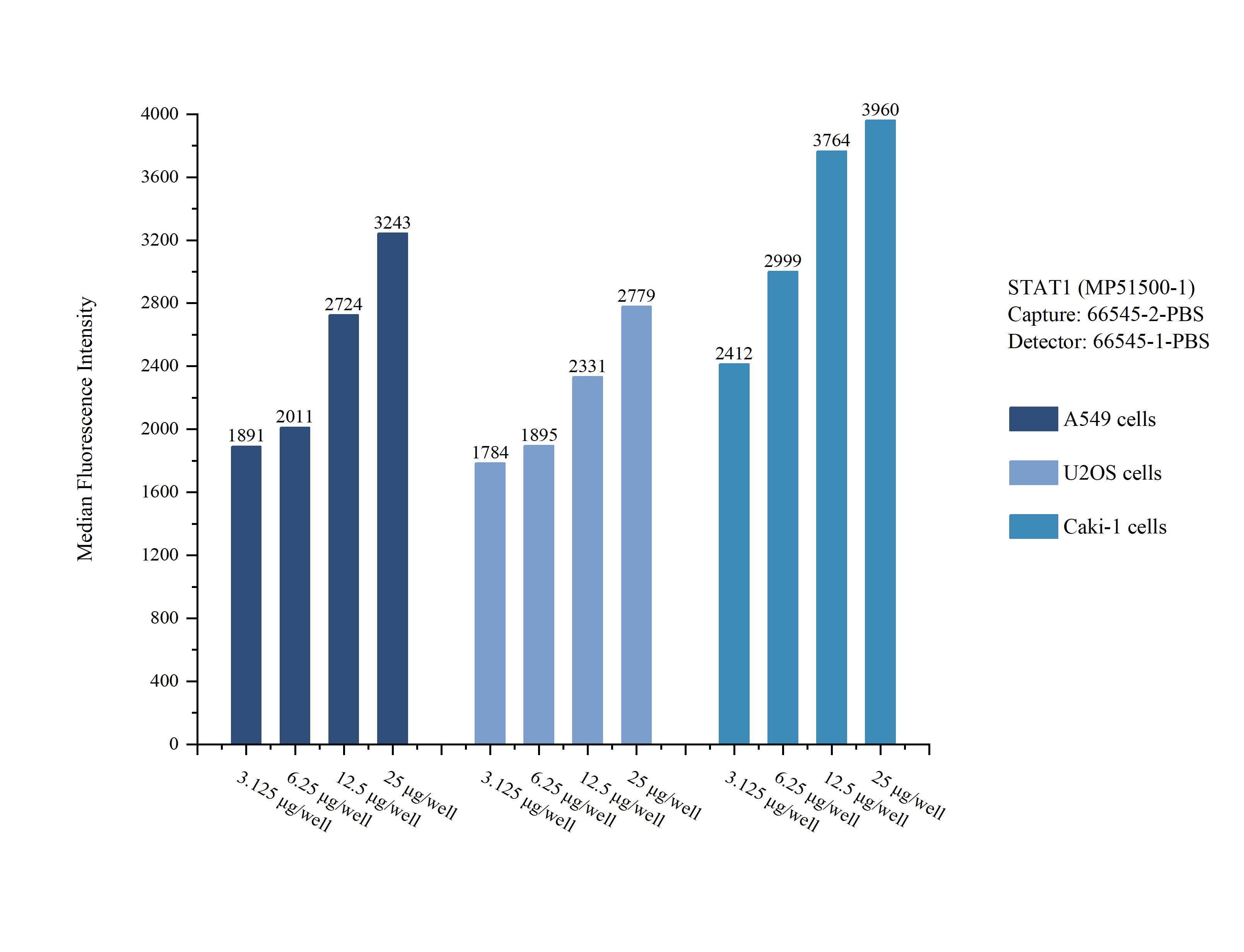
MP51500-1: 66545-2-PBS capture and 66545-1-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
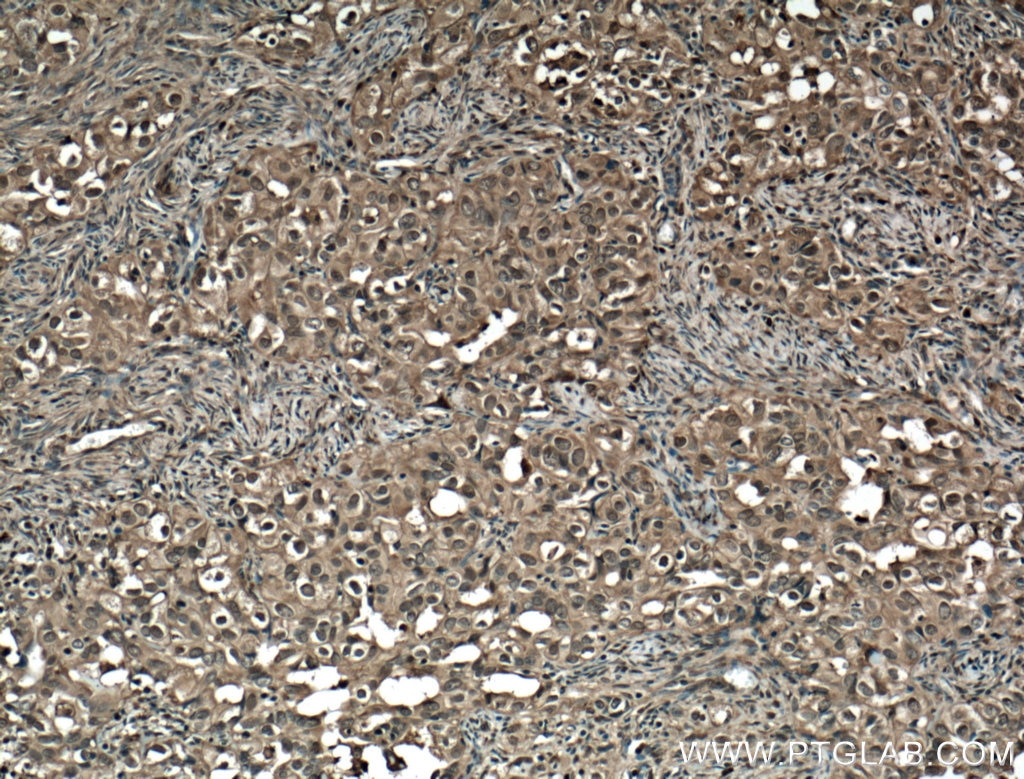
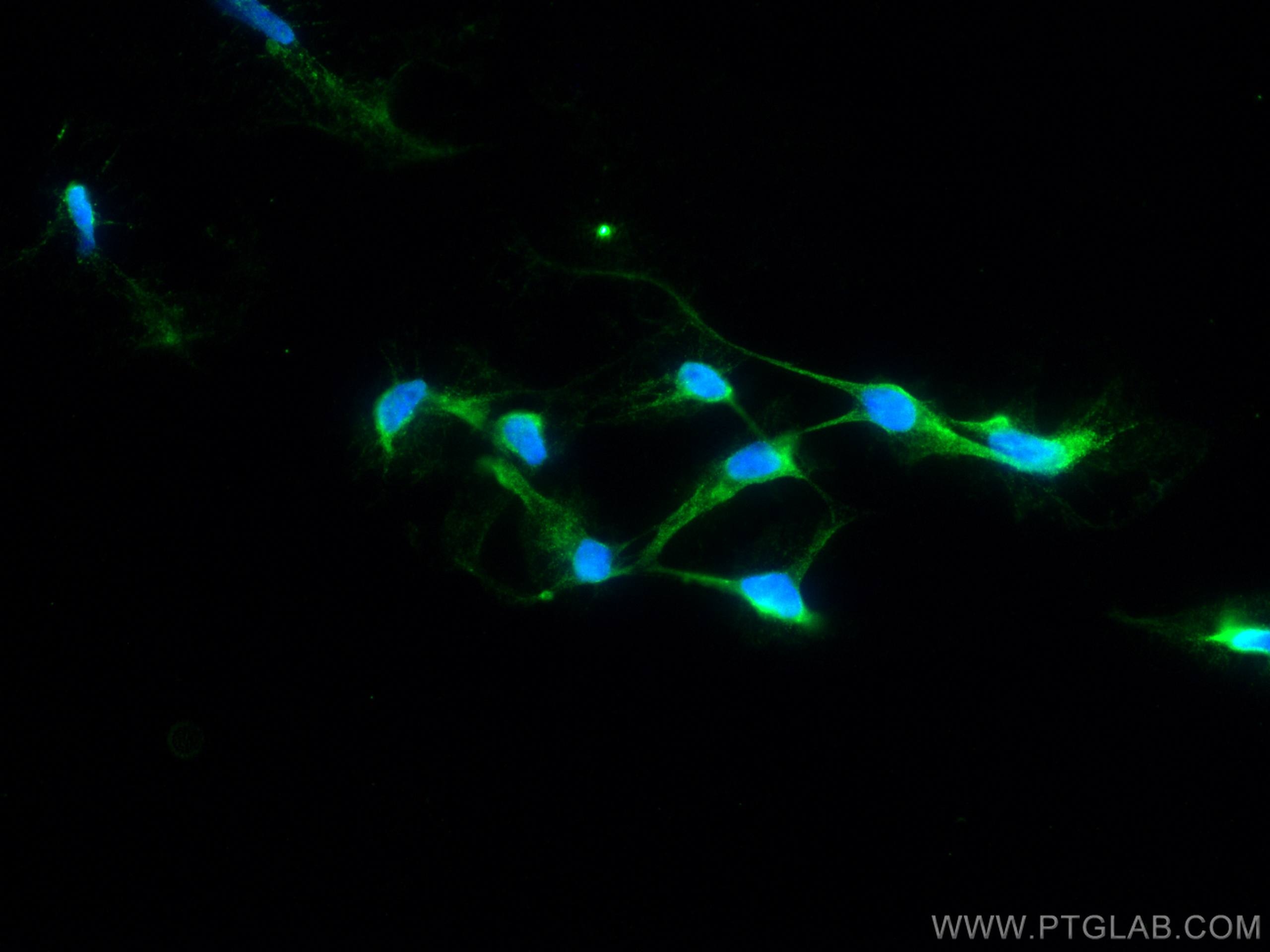
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag0199 Product name: Recombinant human STAT1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 2-230 aa of BC002704 Sequence: SQWYELQQLDSKFLEQVHQLYDDSFPMEIRQYLAQWLEKQDWEHAANDVSFATIRFHDLLSQLDDQYSRFSLENNFLLQHNIRKSKRNLQDNFQEDPIQMSMIIYSCLKEERKILENAQRFNQAQSGNIQSTVMLDKQKELDSKVRNVKDKVMCIEHEIKSLEDLQDEYDFKCKTLQNREHETNGVAKSDQKQEQLLLKKMYLMLDNKRKEVVHKIIELLNVTELTQNA Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kDa |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 83 kDa |
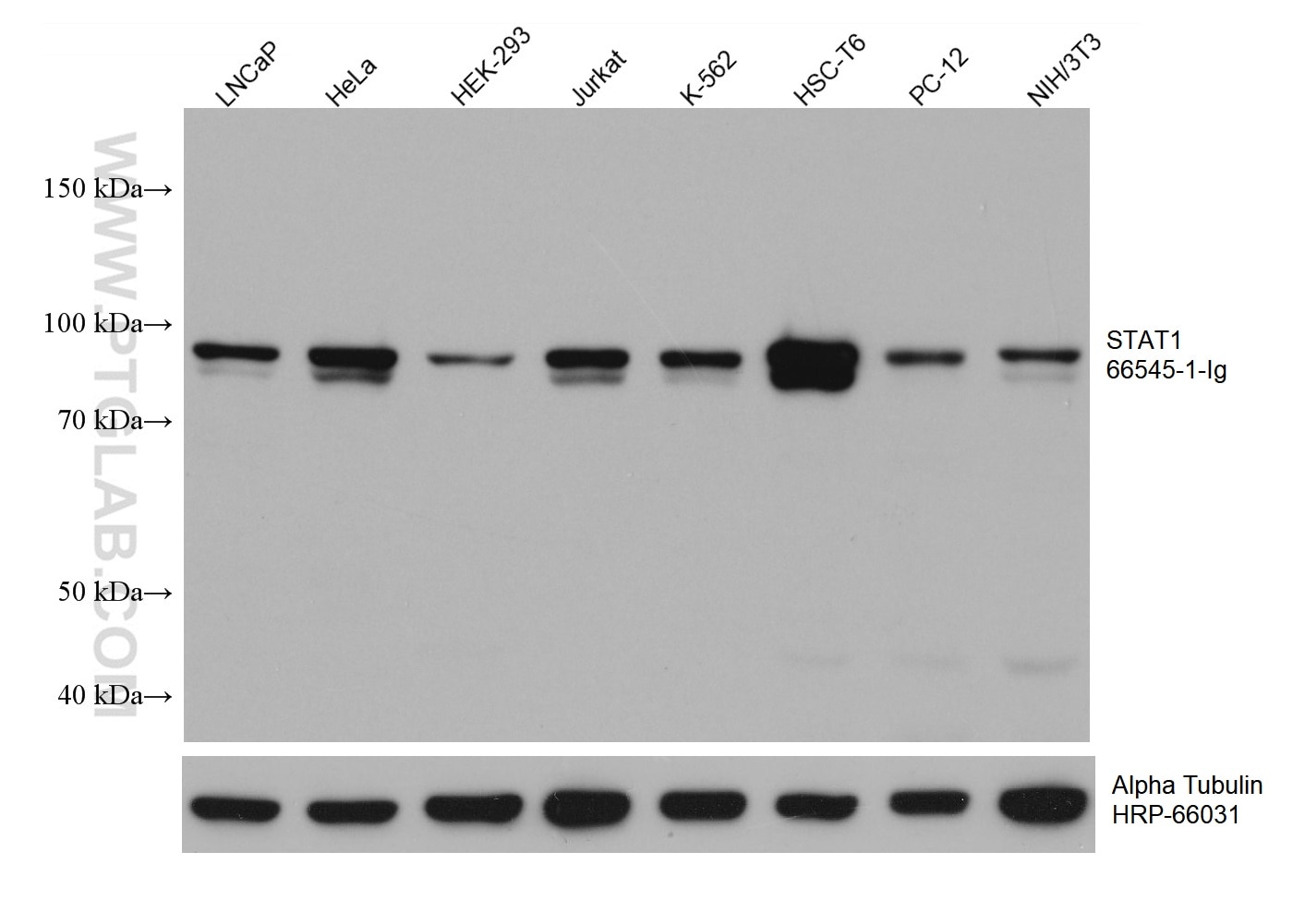
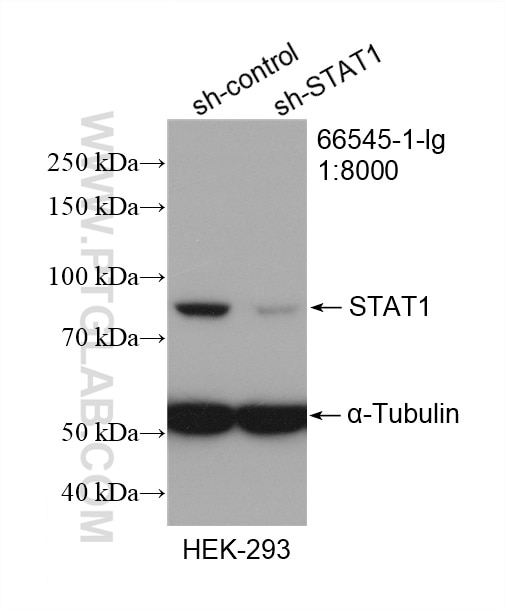
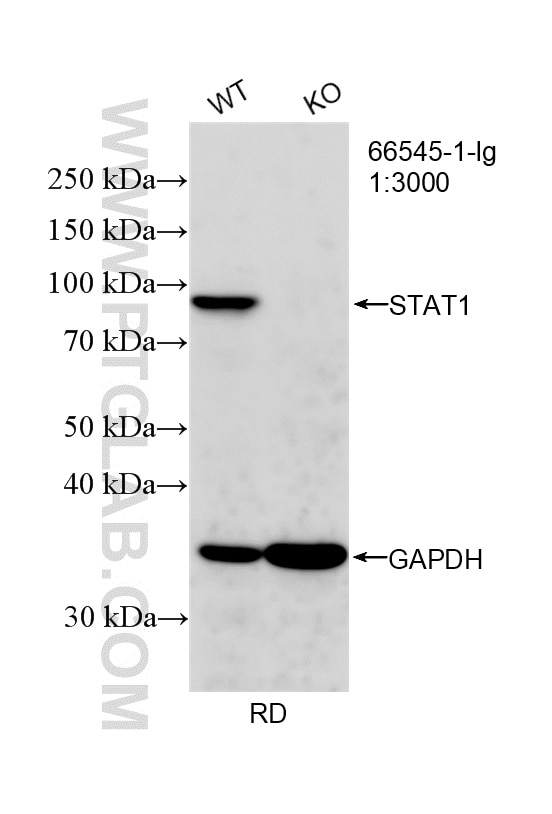
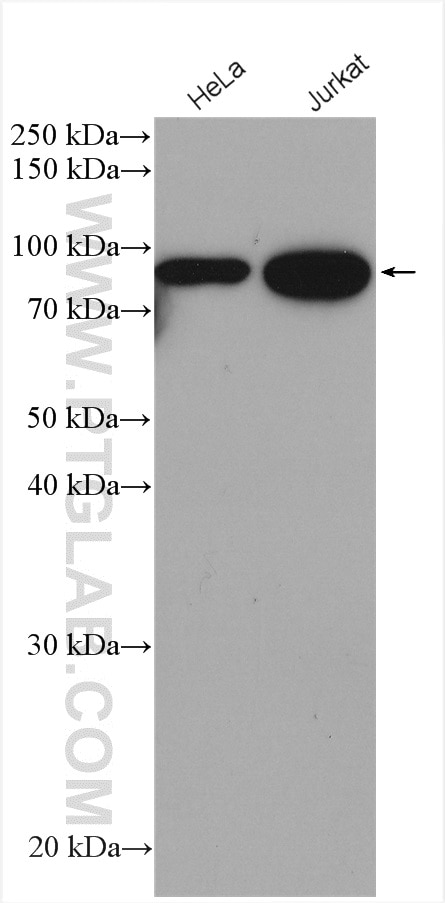
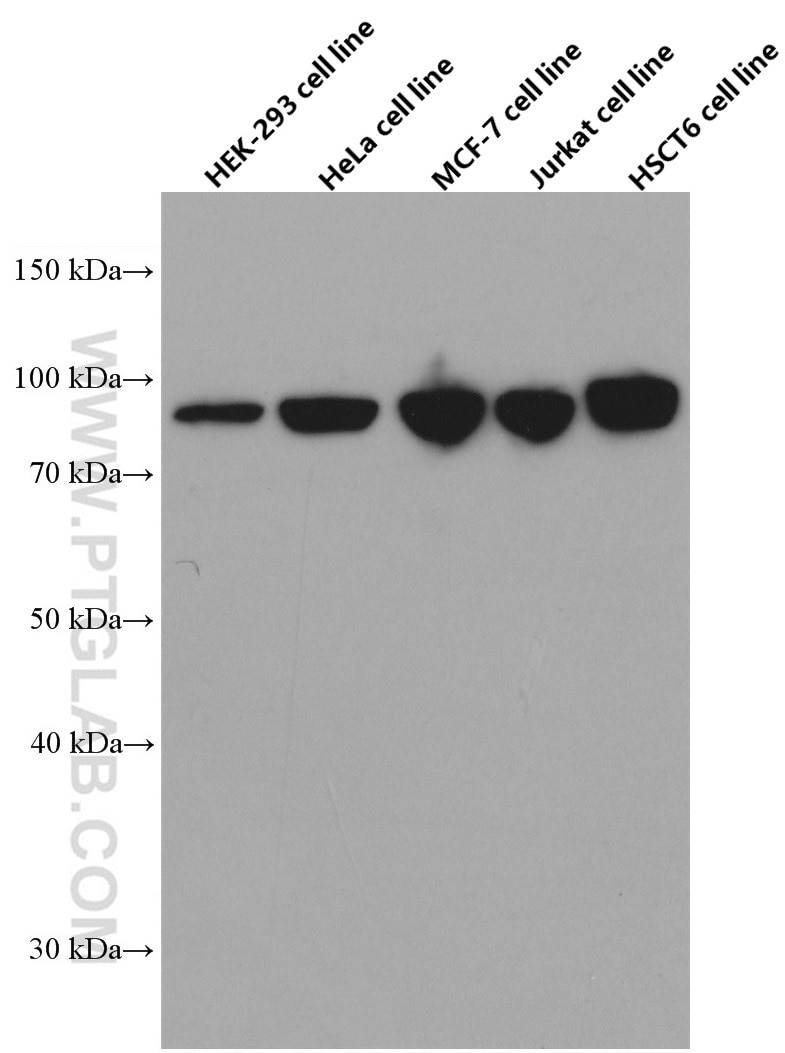
| Observed Molecular Weight | 84 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC002704 |
| Gene Symbol | STAT1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6772 |
| RRID | AB_2881907 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P42224 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
What is the molecular weight of STAT1? Are there any isoforms of STAT1? Is STAT1 post-translationally modified?
The molecular weight of STAT1 is 91 kDa for full-length STAT1α and 84 kDa for STAT1β, which is devoid of the C-terminal activation domain (PMID: 1502203). Phosphorylation of STAT1 regulates STAT1 activity. Phosphorylation of Tyr701 by Janus kinases (JAKs) triggers STAT1 homo- and hetero-dimerization with other STAT family members and also causes nuclear translocation, while phosphorylation of Ser727 is needed for full activation (PMID: 10851062). STAT1β lacks Ser727 and has therefore been considered to be inactive or acting in a dominant negative manner to STAT1α, although it has been further shown to be capable of transcription activation in vivo (PMID: 24710278).
What is the subcellular localization of STAT1?
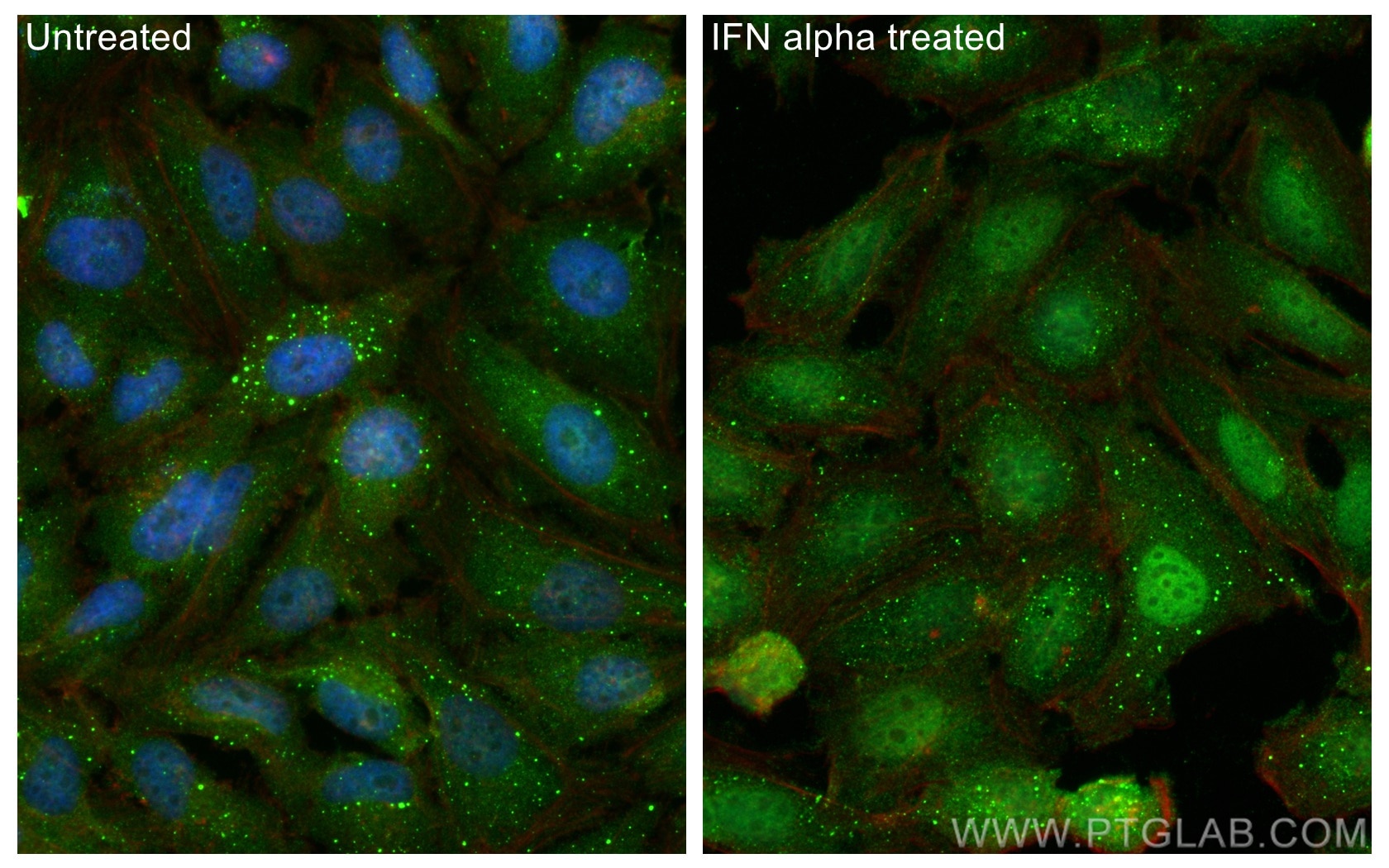
STAT1 is present in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. Translocation of STAT1 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus is required for its regulation of gene expression and is dependent on phosphorylation (see above). However, low levels of unphosphorylated STAT1, often referred to as U-STAT1, can also be found in the nucleus, where U-STAT1 regulates the stability of heterochromatin by binding to chromatin in monomeric or dimeric states (PMID: 18840523).
What is the tissue expression pattern of STAT1?
STAT1 is ubiquitously expressed.