Tested Applications
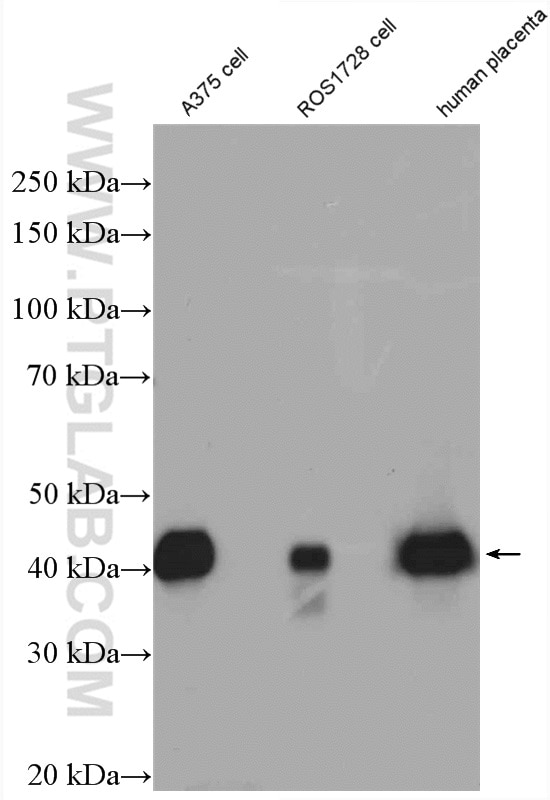
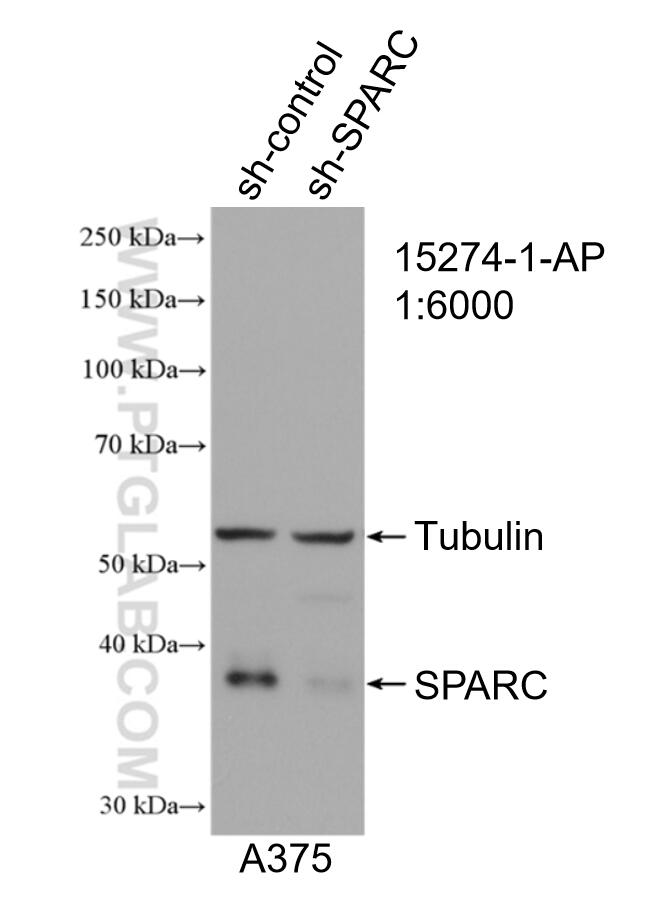
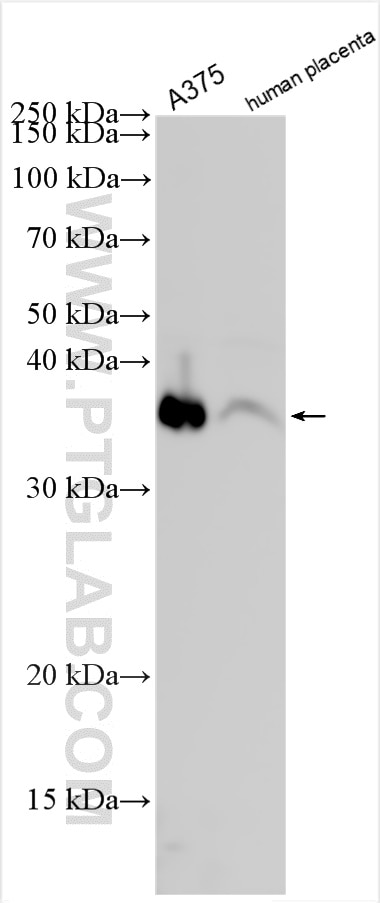
| Positive WB detected in | A375 cells, human testis tissue, ROS1728 cells, human placenta tissue |
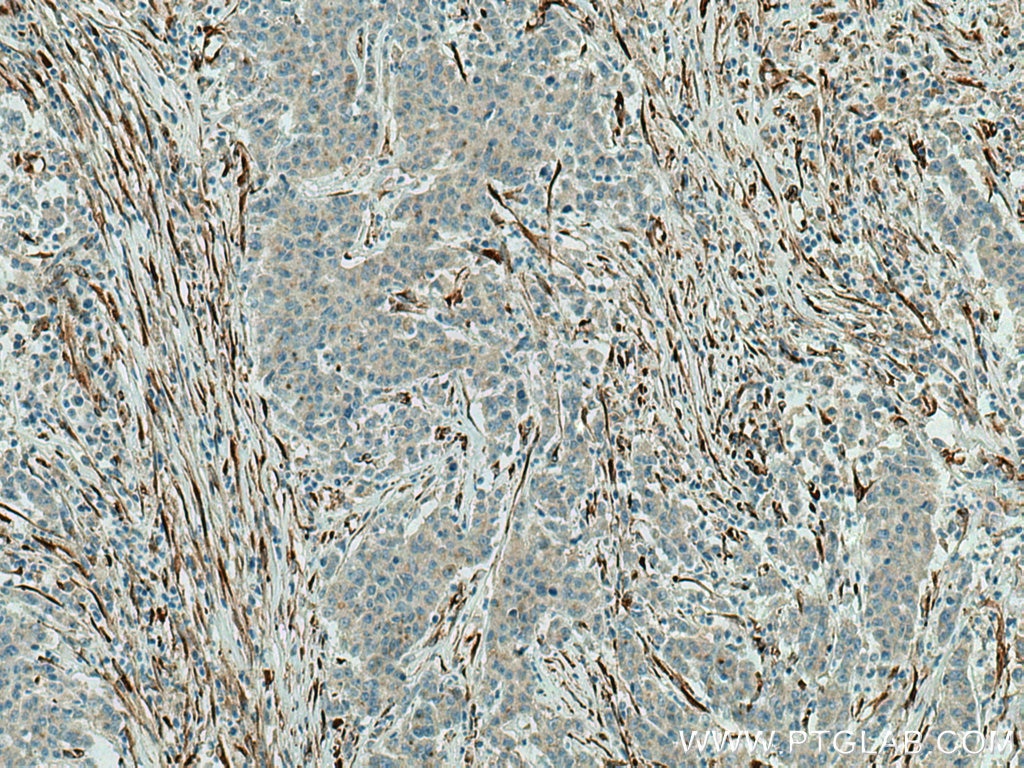
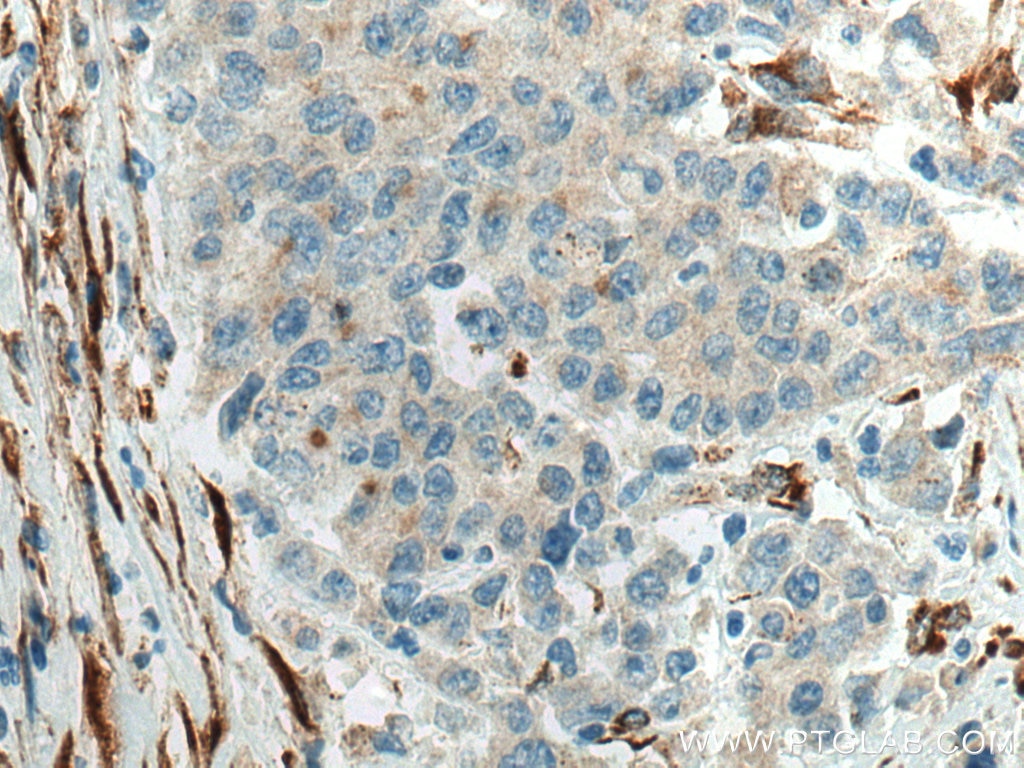
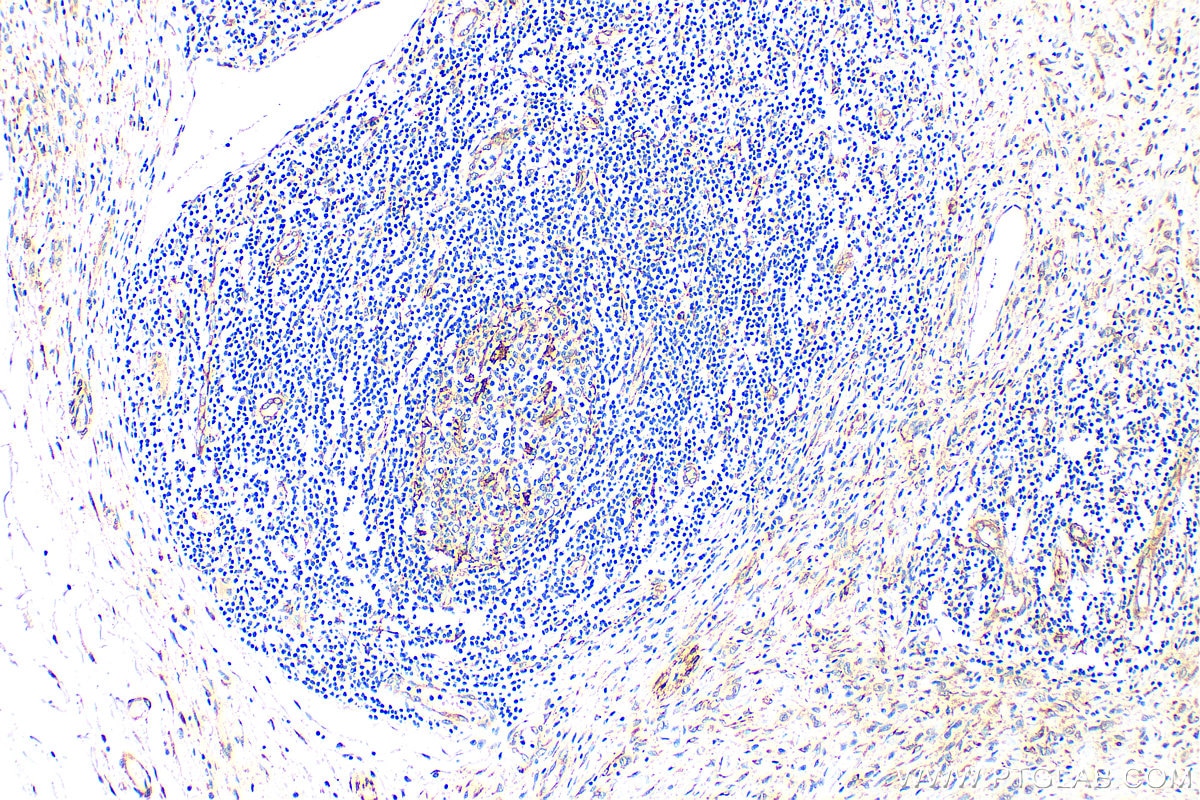
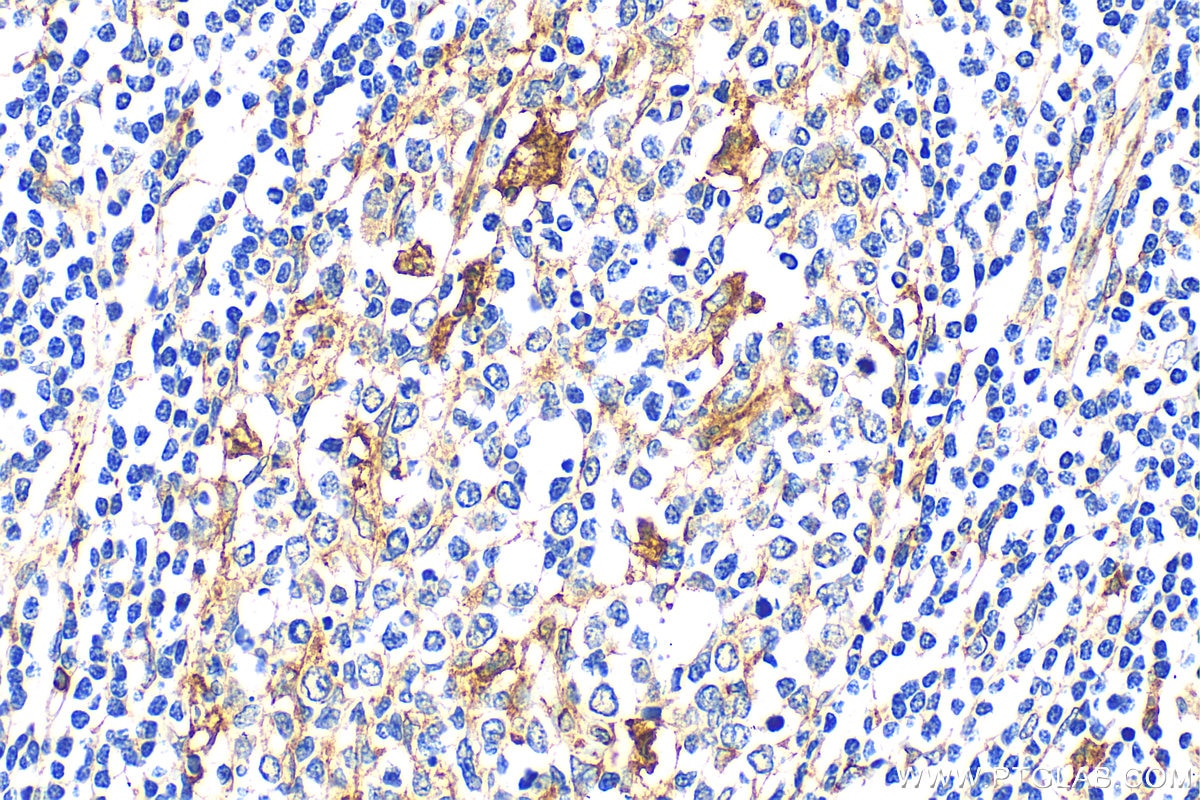
| Positive IHC detected in | human stomach cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 35 publications below |
| IHC | See 12 publications below |
| IF | See 11 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
15274-1-AP targets SPARC in WB, IHC, IF, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, pig samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, deer, sika deer |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag7390 Product name: Recombinant human SPARC protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-303 aa of BC004974 Sequence: MRAWIFFLLCLAGRALAAPQQEALPDETEVVEETVAEVTEVSVGANPVQVEVGEFDDGAEETEEEVVAENPCQNHHCKHGKVCELDENNTPMCVCQDPTSCPAPIGEFEKVCSNDNKTFDSSCHFFATKCTLEGTKKGHKLHLDYIGPCKYIPPCLDSELTEFPLRMRDWLKNVLVTLYERDEDNNLLTEKQKLRVKKIHENEKRLEAGDHPVELLARDFEKNYNMYIFPVHWQFGQLDQHPIDGYLSHTELAPLRAPLIPMEHCTTRFFETCDLDNDKYIALDEWAGCFGIKQKDIDKDLVI Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | secreted protein, acidic, cysteine-rich (osteonectin) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 35 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 35-43 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC004974 |
| Gene Symbol | SPARC |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6678 |
| RRID | AB_2194961 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P09486 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Secreted Protein Acidic And Cysteine Rich (SPARC), also known as osteonectin or basement-membrane protein 40 (BM-40), is a secreted protein essential in the calcification of bone.
What is the molecular weight of SPARC?
The calculated molecular mass of SPARC is 35 kDa. SPARC is a glycoprotein consisting of 303 amino acids in the cytoplasm and 286 amino acids after the signal sequence is cleaved in secretion.
Where is SPARC expressed?
Osteoblasts secrete SPARC during bone formation, with high levels found in immature bone compared to mature bone that is in homeostasis (PMID: 2440898). SPARC is also secreted in adult mineralized tissues that have high turnover, such as osteoid and dentin, by cells other than osteoblasts. This includes bone marrow progenitor cells and hypertrophic chondrocytes but also endothelial cells and fibroblasts.
Though previously described as being exclusively expressed in mineralized tissue, it is now understood that SPARC is more widely expressed and is associated with high levels of collagen deposition, found in the extracellular matrix (ECM) of a number of tissues.
What is the function of SPARC?
SPARC contains both a collagen-binding domain and a hydroxyapatite (HA) binding region, so is thought to enhance mineralization by binding both collagen and HA crystals, causing the release of calcium ions (PMID: 26851678).
SPARC can bind to a number of different ECM proteins, particularly collagen, and may even influence the assembly of these proteins (PMID: 19798598). It is known to regulate interactions between cells and the ECM, meaning it plays a role in many important processes such as cell migration and proliferation.
What diseases are associated with SPARC?
Overexpression of SPARC has been identified in a number of different types of cancers (PMID: 18849185), although its role may vary. For example, in neuroblastomas SPARC acts as a suppressor but in gliomas, it causes greater invasion of the tumor. Mutations in SPARC can also lead to Osteogenesis Imperfecta, also known as brittle bone disease (PMID: 26027498).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for SPARC antibody 15274-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for SPARC antibody 15274-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces Evidence for Delivery of Abraxane via a Denatured-Albumin Transport System. | ||
Theranostics A 9-kDa matricellular SPARC fragment released by cathepsin D exhibits pro-tumor activity in the triple-negative breast cancer microenvironment. | ||
Int J Cancer Tissue-resident CXCR4+ macrophage as a poor prognosis signature promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression | ||
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Víctor (Verified Customer) (11-03-2025) | The antibody appears to be quite specific and worked very well
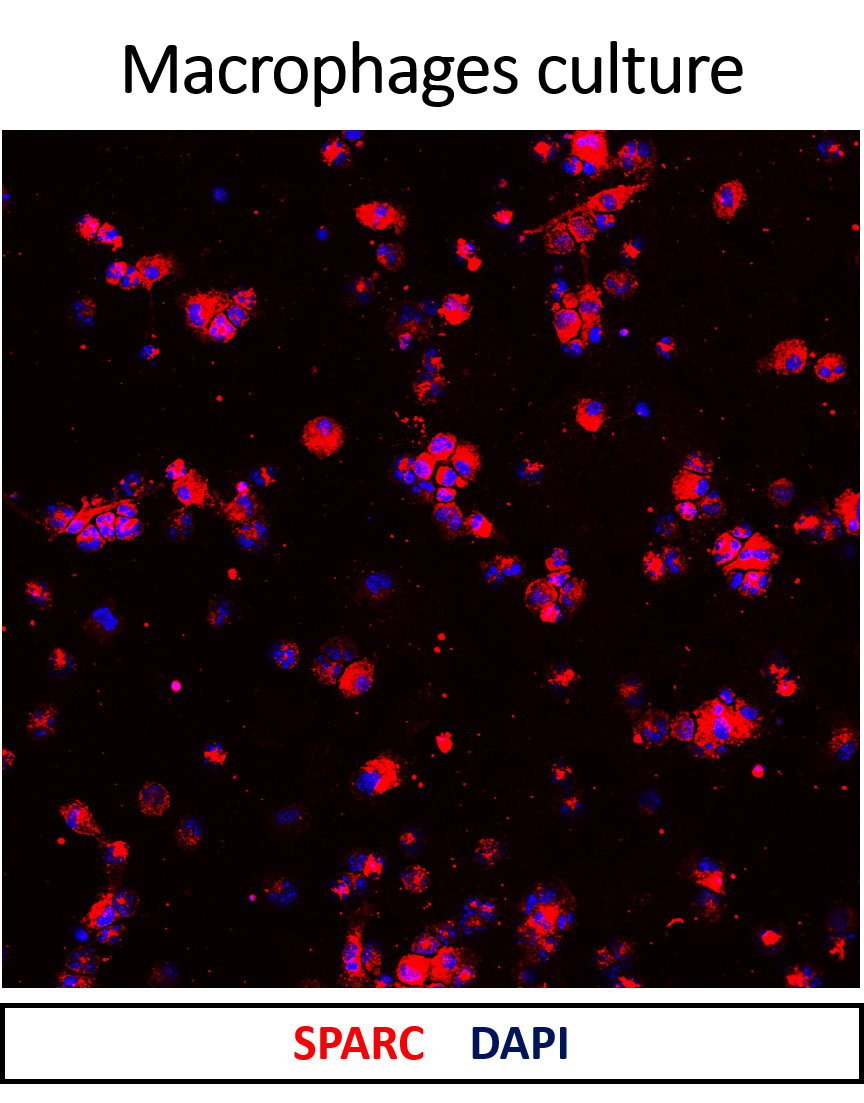 |
FH Susanne (Verified Customer) (11-19-2024) | works in human and mouse dermal fibroblasts
 |