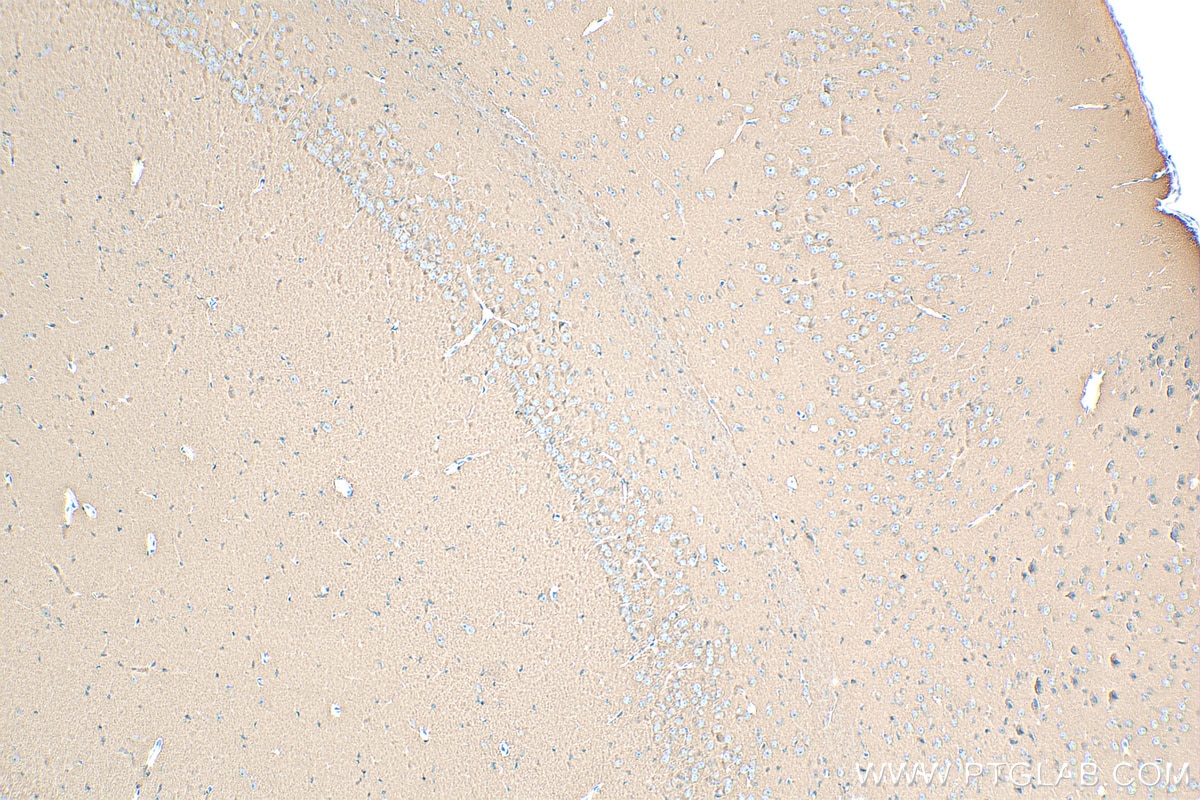
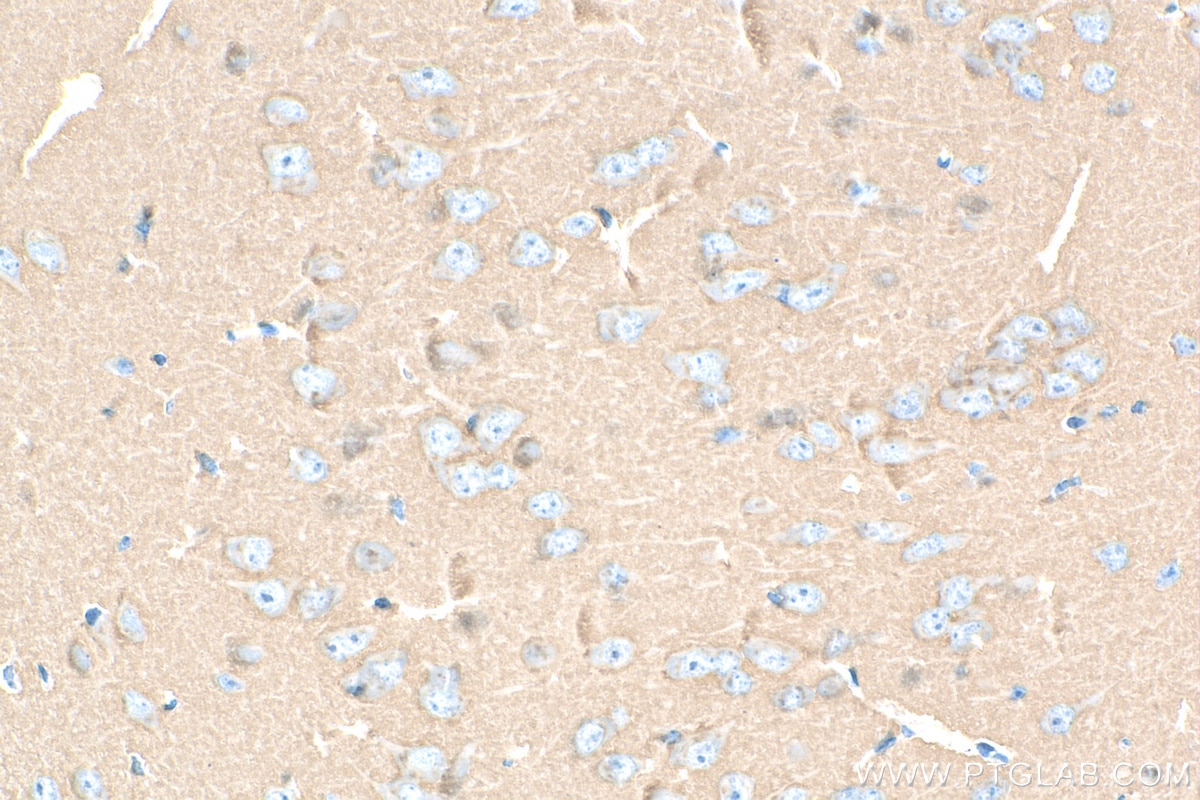
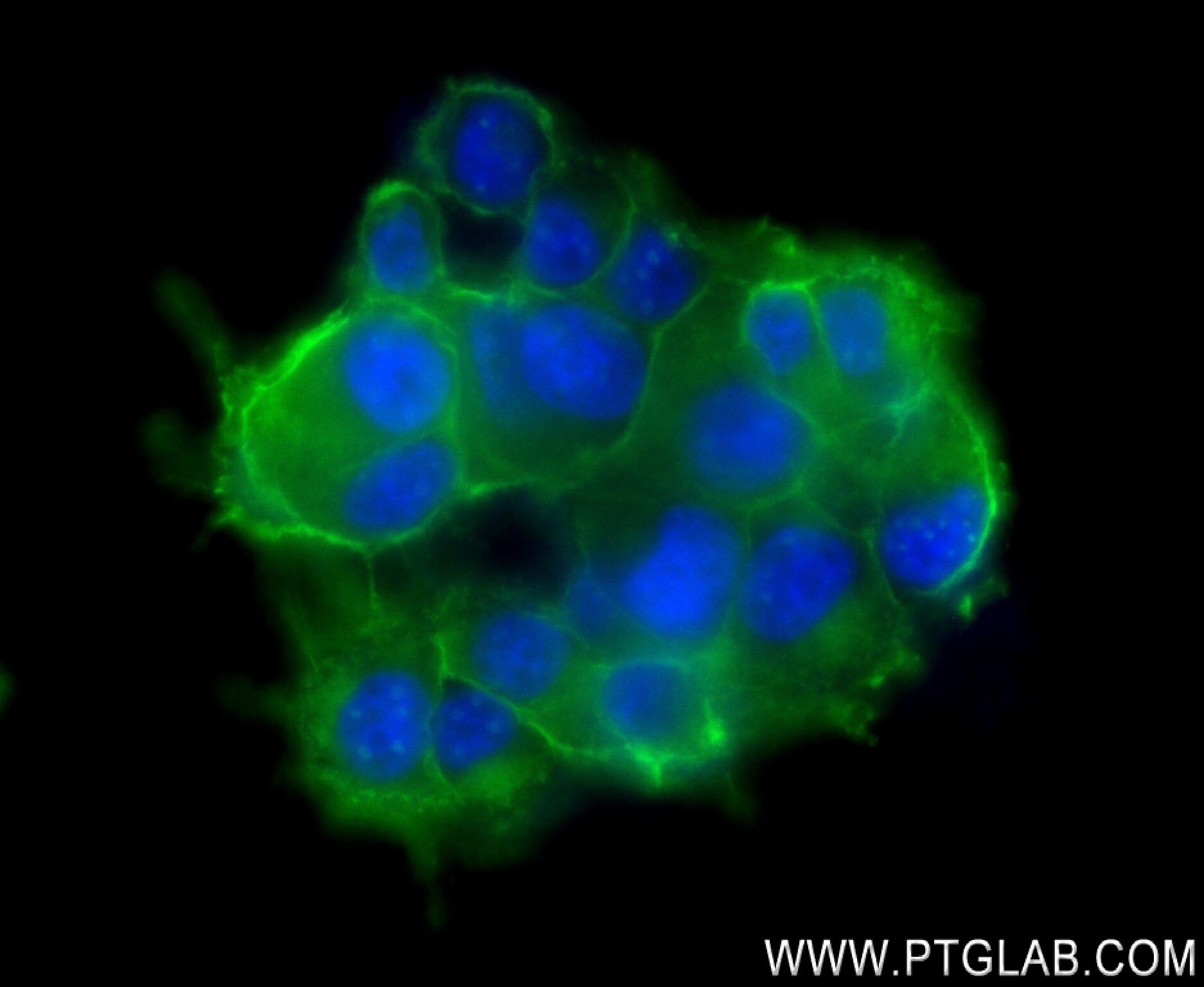
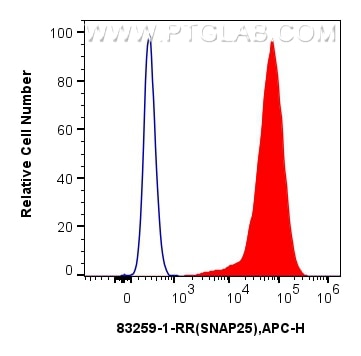
Product Information
83259-1-PBS targets SNAP25 as part of a matched antibody pair:
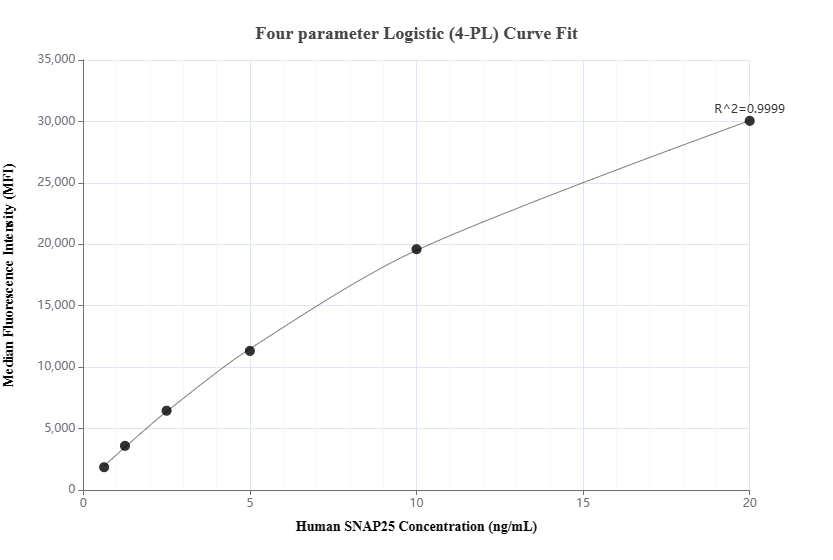
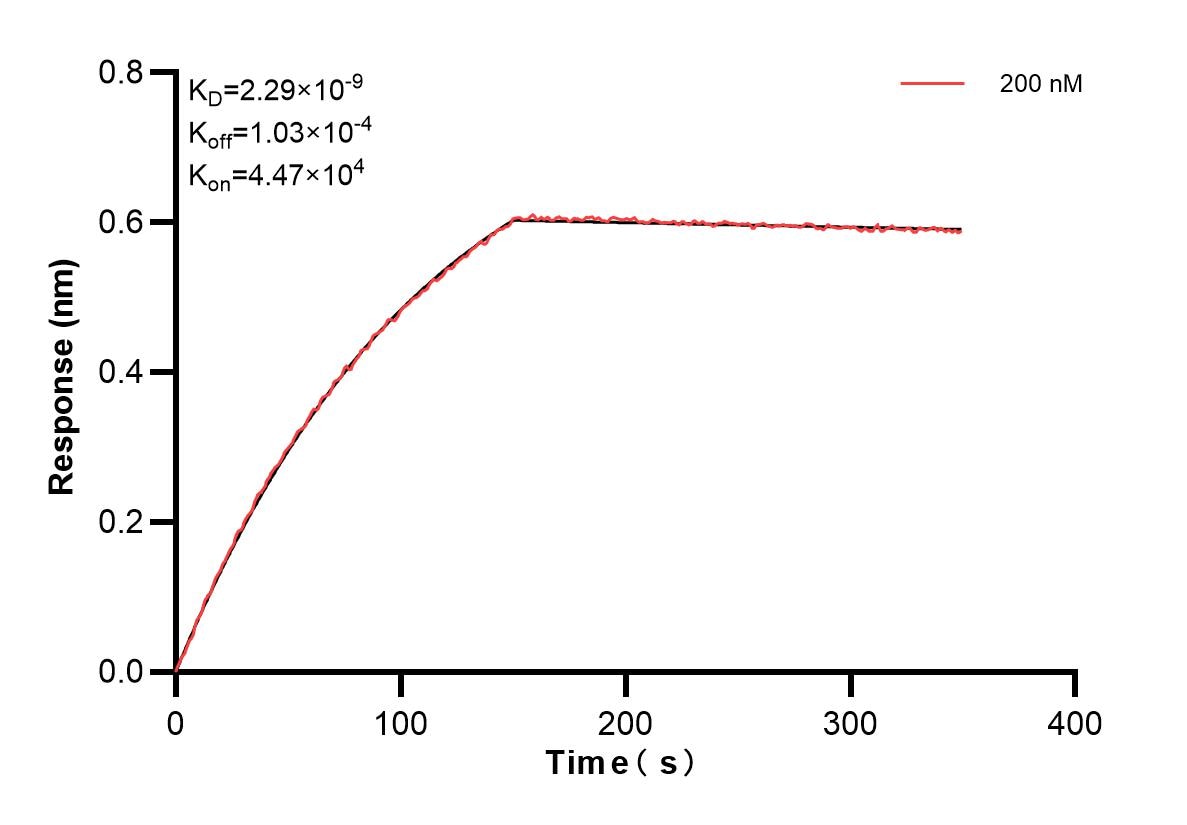
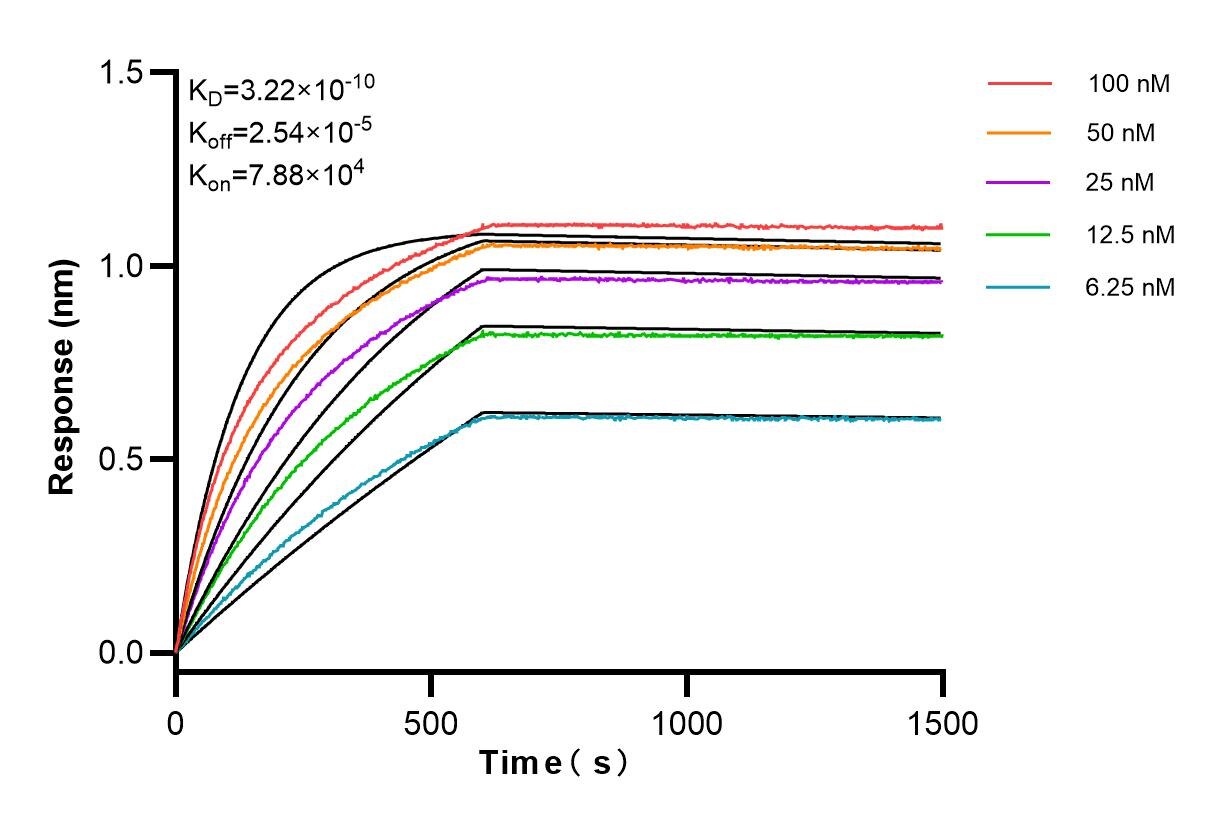
MP00196-1: 83259-3-PBS capture and 83259-1-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation. Created using Proteintech’s proprietary in-house recombinant technology. Recombinant production enables unrivalled batch-to-batch consistency, easy scale-up, and future security of supply.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | SNAP25 fusion protein Ag6695 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 23 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC010647 |
| Gene Symbol | SNAP25 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6616 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P60880 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
The synaptosomal associated protein of 25 kD (SNAP-25) was first identified as a major synaptic protein by Wilson and colleagues. The protein interacts with syntaxin and synaptobrevin through its N-terminal and C-terminal -helical domains. Its palmitoylation domain is located in the middle of the molecule that contains four cysteine residues. Mutation of the cysteines abolishes palmitoylation and membrane binding. Several elegant studies using synaptosome preparations and permeabilized PC12 cells have suggested that SNAP-25 may act in the late post-docking steps of exocytosis. By limited proteolysis and in vitro binding assay, it is proposed that the two helix domains act independently and contribute equally to form the SNARE complex with syntaxin and synaptobrevin. It seems that a major regulatory element is located in the C-terminus of SNAP-25. Removing a 9 amino acid sequence of SNAP-25 inhibited neurosecretion in chromaffin cells. In addition, it has been shown that inhibition of neurosecretion by AX type E can be rescued by a SNAP-25 C-terminal peptide, probably by initiating the formation of a fusion competent SNARE complex.