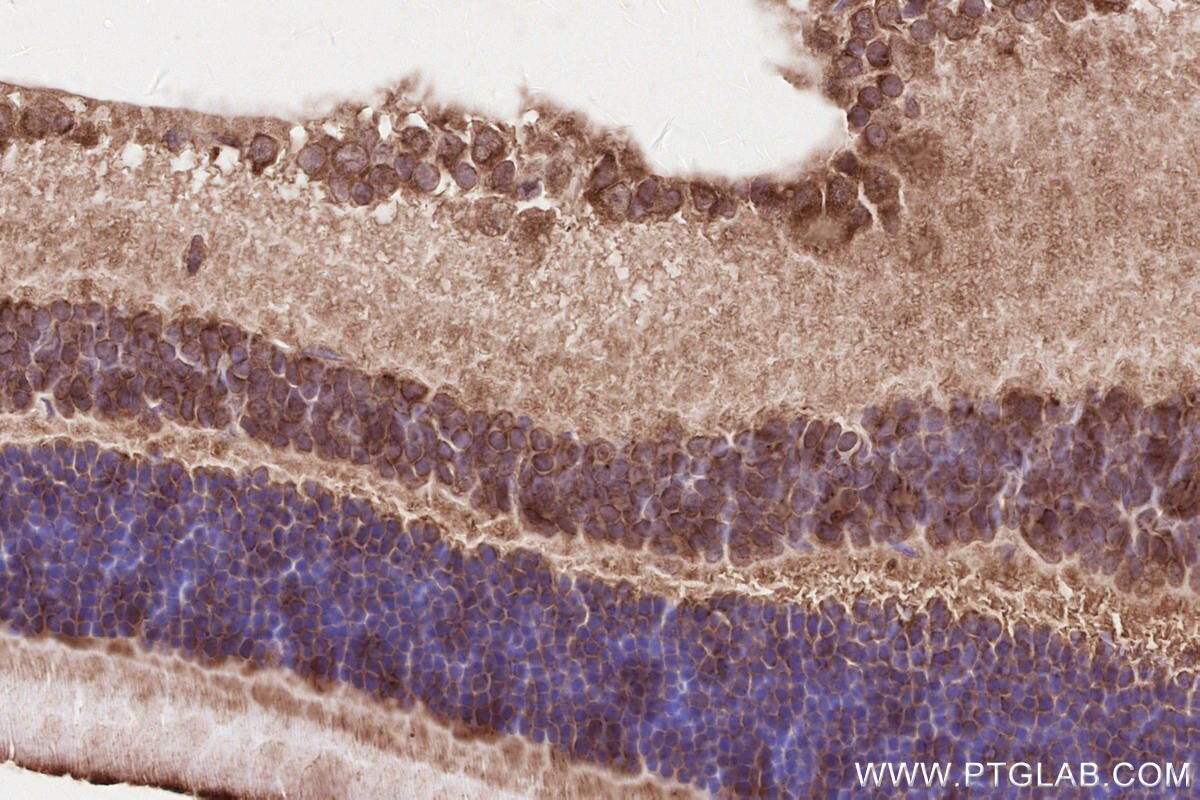
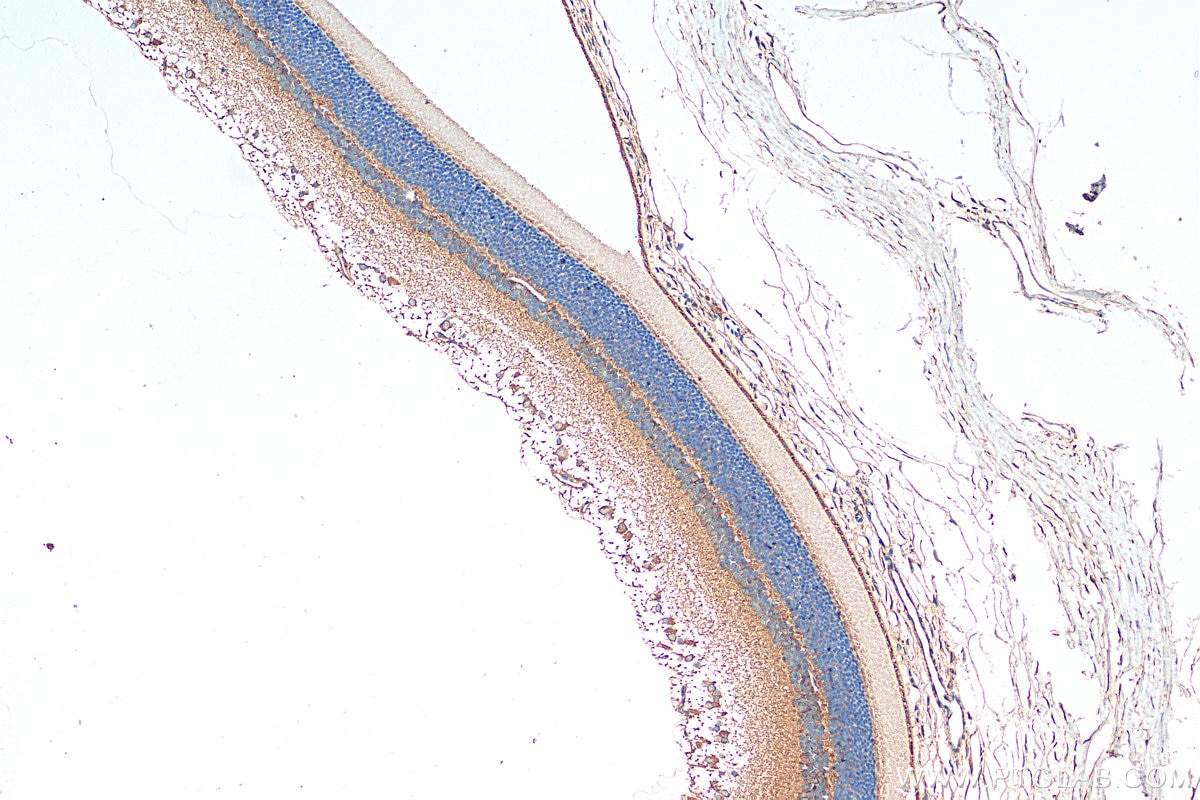
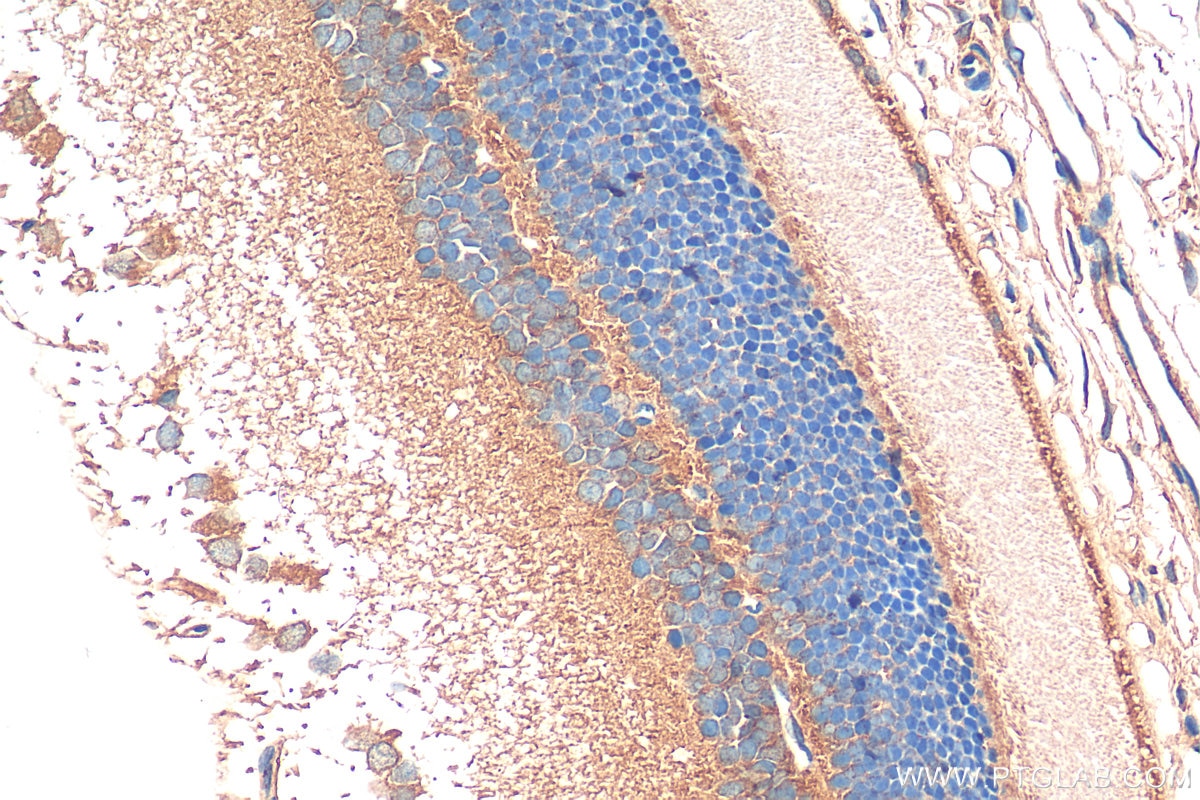
Product Information
14855-1-PBS targets RD3 in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | RD3 fusion protein Ag6641 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | retinal degeneration 3 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 22.7 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 23 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC065541 |
| Gene Symbol | RD3 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 343035 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q7Z3Z2 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
RD3, or Retinal Degeneration 3, plays a critical role in regulating guanylate cyclase (GC) signaling and photoreceptor cell survival (PMID: 30559291). RD3 is highly conserved across vertebrates, with the human protein sharing high sequence identity with other primates and varying degrees of identity with other species (PMID: 29030614). The main functions of RD3 include inhibiting photoreceptor-specific guanylate cyclase activity and promoting the accumulation of retinal membrane guanylyl cyclase (RetGC) in the photoreceptor outer segment (PMID: 30559291). RD3 is essential for the normal expression of RetGC in photoreceptor cells and blocks RetGC catalytic activity. Mutations in the RD3 gene can lead to Leber congenital amaurosis type 12, which results in retinal degeneration. RD3 is also involved in the trafficking of RetGC from the endoplasmic reticulum to the photoreceptor outer segments, which is crucial for maintaining the normal function and survival of photoreceptors (PMID: 34537244).