Tested Applications
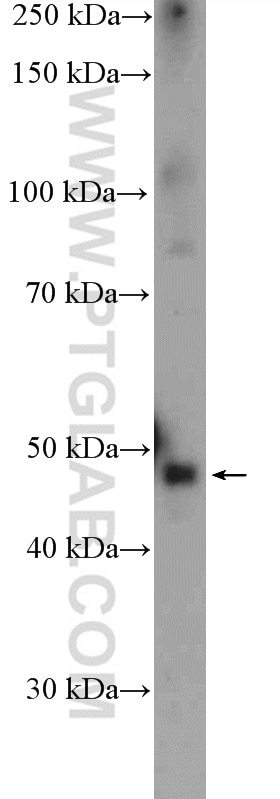
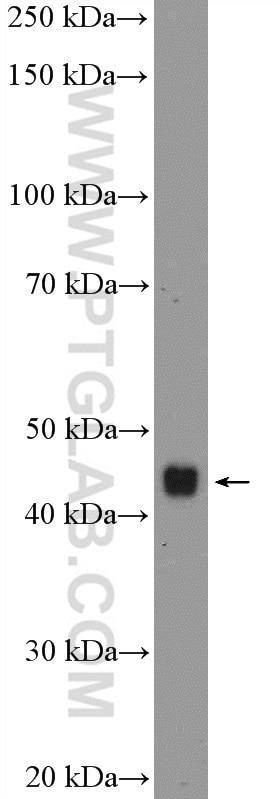
| Positive WB detected in | mouse brain tissue, mouse cerebellum tissue |
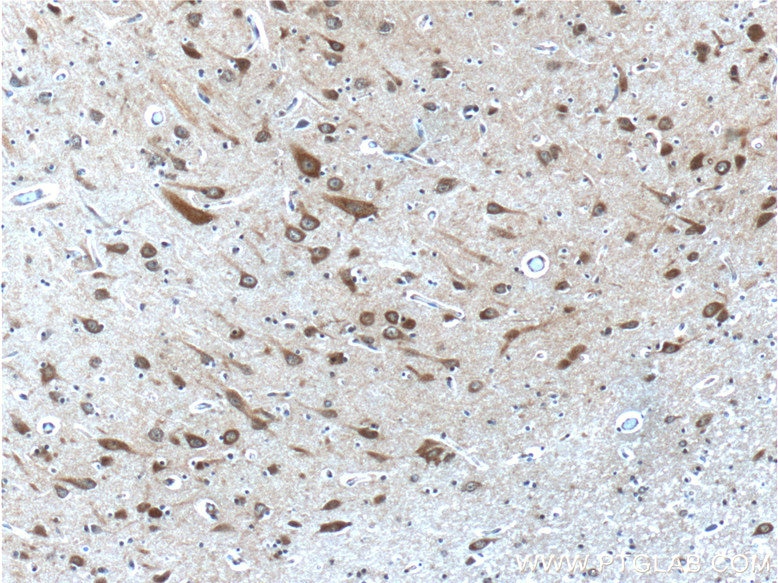
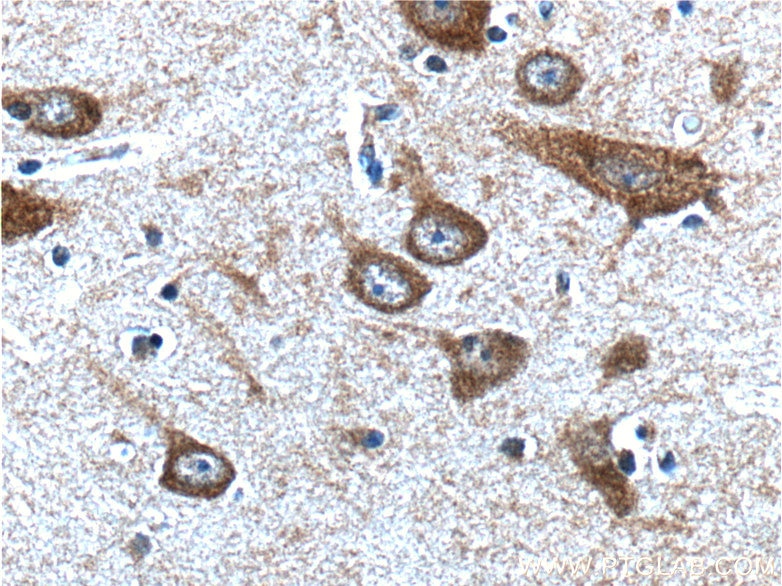
| Positive IHC detected in | human brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
24761-1-AP targets PTGER3 in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag21542 Product name: Recombinant human PTGER3 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET30a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-100 aa of BC024229 Sequence: MKETRGYGGDAPFCTRLNHSYTGMWAPERSAEARGNLTRPPGSGEDCGSVSVAFPITMLLTGFVGNALAMLLVSRSYRRRESKRKKSFLLCIGWLALTDL Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | prostaglandin E receptor 3 (subtype EP3) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 43 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 40-48 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC024229 |
| Gene Symbol | PTGER3 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5733 |
| RRID | AB_2879710 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P43115 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
PTGER3 (Prostaglandin E Receptor 3), also known as EP3, is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Activates pathways involved in proliferation, migration, and apoptosis, often via cross-talk with PI3K-AKT and MAPK cascades (PMID: 38566528). High PTGER3 levels drive tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, and cisplatin resistance via the Ras-MAPK/Erk-ETS1-ELK1/CFTR1 axis (PMID: 30655206).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for PTGER3 antibody 24761-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for PTGER3 antibody 24761-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab m6A mRNA methylation in brown fat regulates systemic insulin sensitivity via an inter-organ prostaglandin signaling axis independent of UCP1 | ||
Dev Cell Chromatin remodeling of prostaglandin signaling in smooth muscle enables mouse embryo passage through the female reproductive tract |