Tested Applications
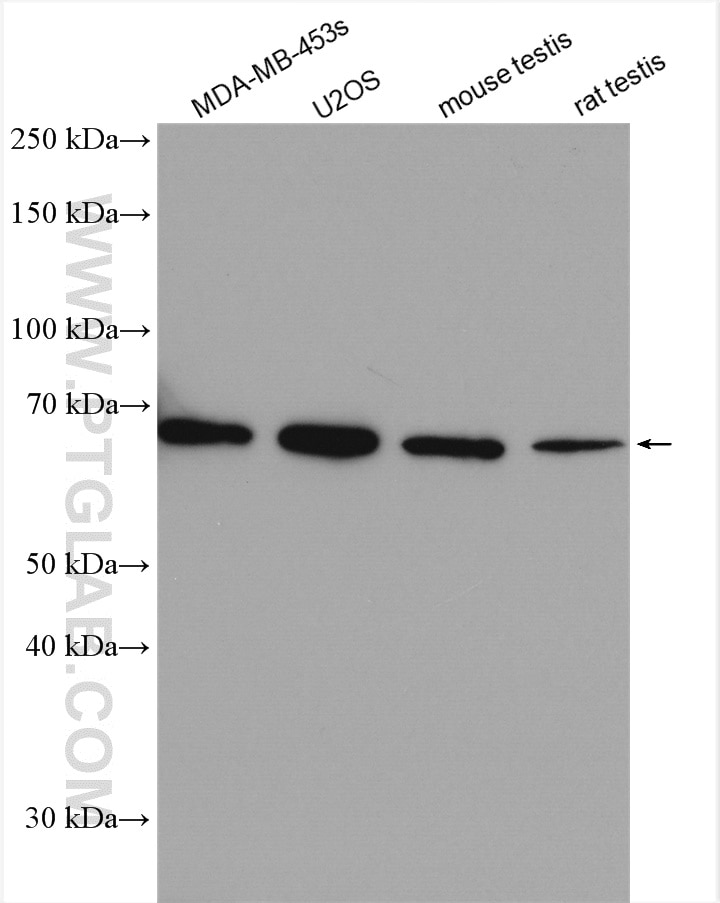
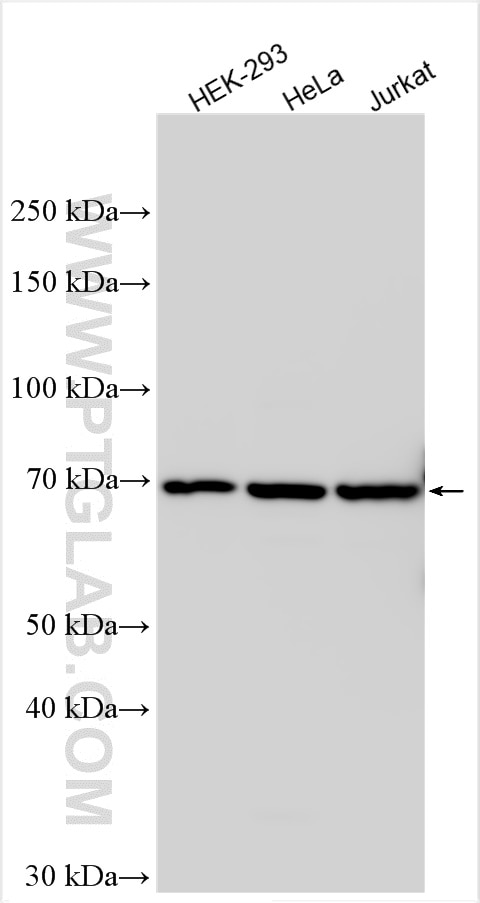
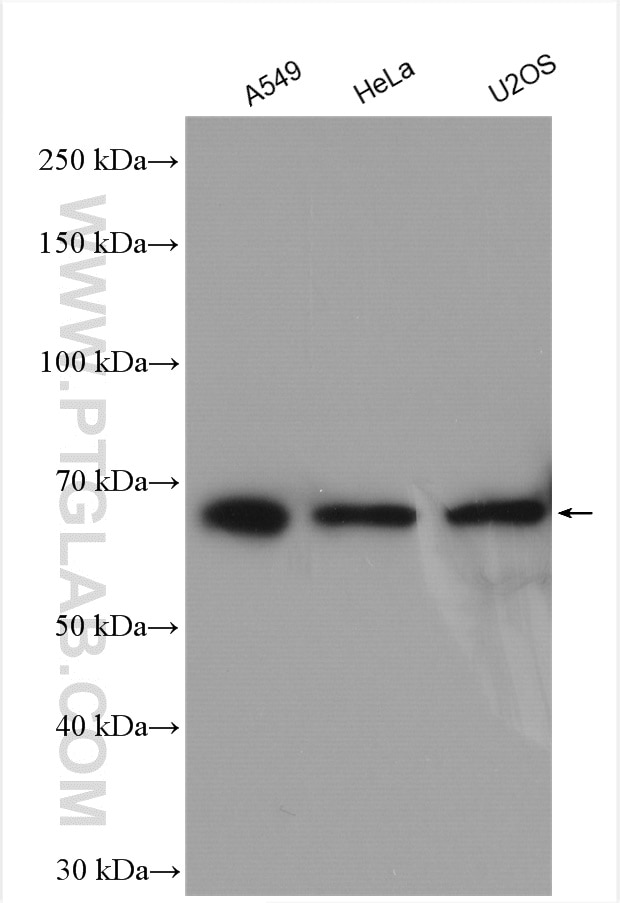
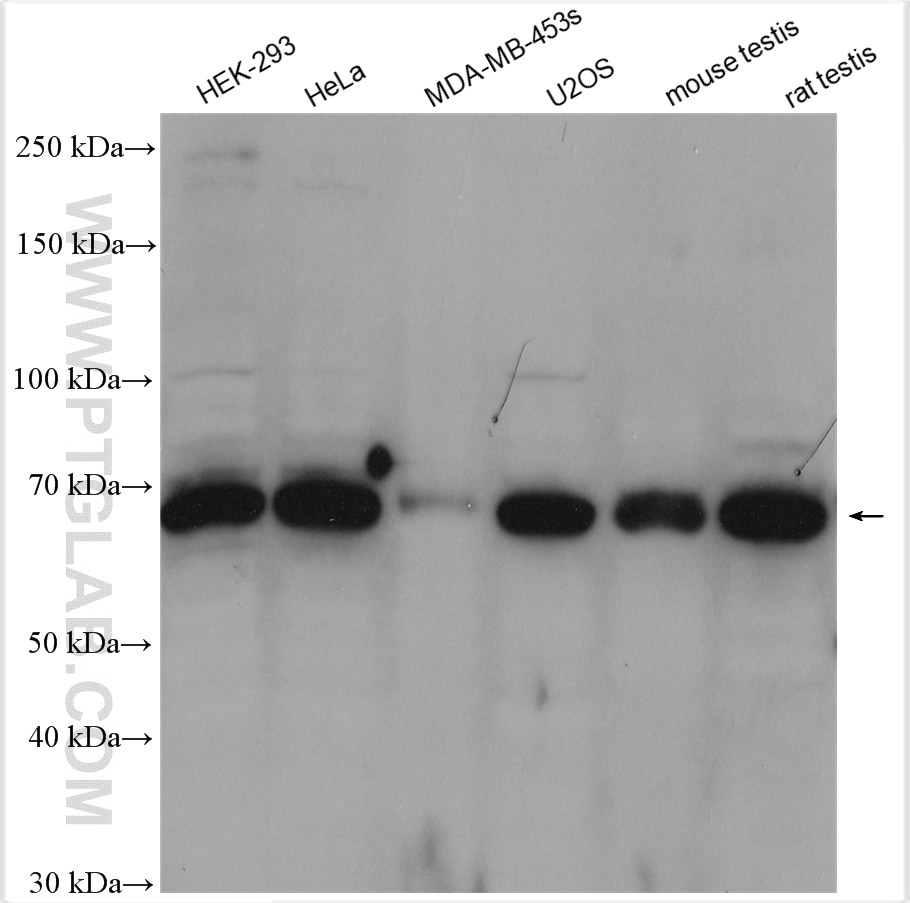
| Positive WB detected in | HEK-293 cells, A549 cells, HeLa cells, MDA-MB-453s cells, U2OS cells, Jurkat cells, mouse testis tissue, rat testis tissue |
| Positive IHC detected in | rat stomach tissue, mouse kidney tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
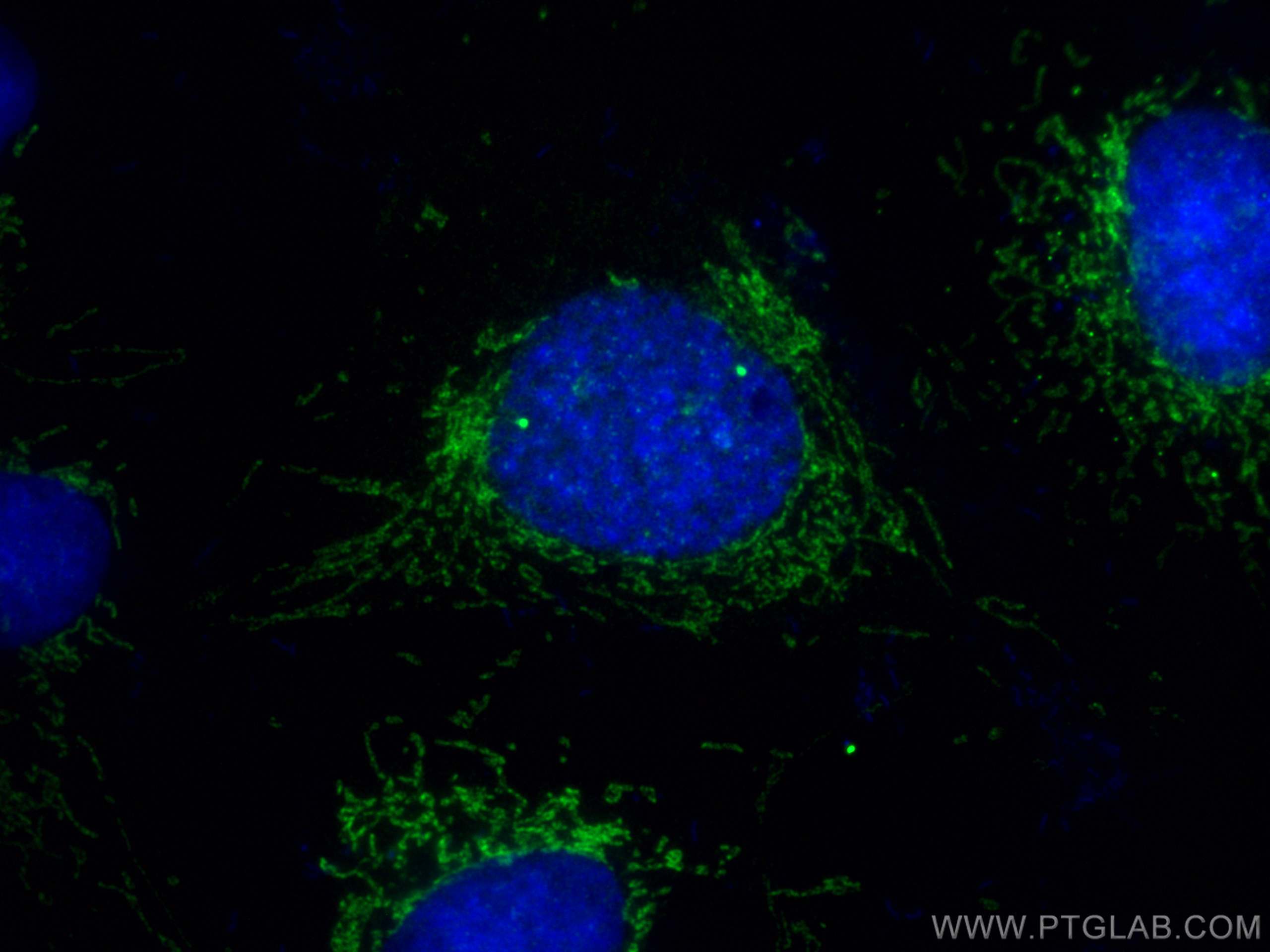
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | U2OS cells |
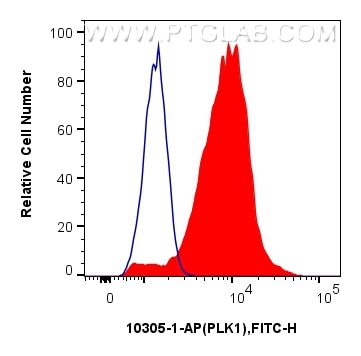
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | Ramos cells |
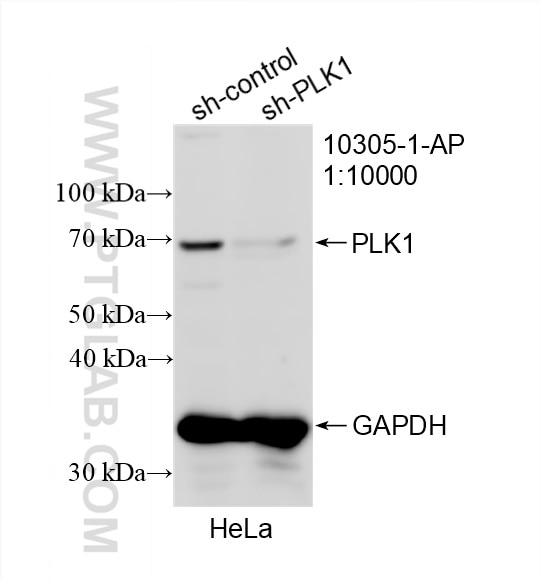
PLK1 expression is low or nonexistent in normal tissues, but high in tumor tissues.
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 5 publications below |
| WB | See 39 publications below |
| IHC | See 13 publications below |
| IF | See 8 publications below |
| IP | See 4 publications below |
| CoIP | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
10305-1-AP targets PLK1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag0284 Product name: Recombinant human PLK1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 415-603 aa of BC002369 Sequence: VDYSDKYGLGYQLCDNSVGVLFNDSTRLILYNDGDSLQYIERDGTESYLTVSSHPNSLMKKITLLKYFRNYMSEHLLKAGANITPREGDELARLPYLRTWFRTRSAIILHLSNGSVQINFFQDHTKLILCPLMAAVTYIDEKRDFRTYRLSLLEEYGCCKELASRLRYARTMVDKLLSSRSASNRLKAS Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | polo-like kinase 1 (Drosophila) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 68 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 68 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC002369 |
| Gene Symbol | PLK1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5347 |
| RRID | AB_2877731 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P53350 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
PLK1(Polo-like kinase 1), also named as PLK and STPK13, belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, Ser/Thr protein kinase family and CDC5/Polo subfamily. PLK1 is a Serine/threonine-protein kinase that performs several important functions throughout M phase of the cell cycle, including the regulation of centrosome maturation and spindle assembly, the removal of cohesins from chromosome arms, the inactivation of APC/C inhibitors, and the regulation of mitotic exit and cytokinesis.The localization of Polo changes during the cell cycle. In interphase, Polo shows a mostly diffuse cytoplasmic localization. Polo becomes concentrated on centrosomes from early prophase and appears on centromeres or kinetochores from late prophase, before nuclear envelope breakdown (NEB). After anaphase onset, Polo relocalizes to the central spindle and remains enriched at the midbody ring in late stages of cytokinesis (PMID: 29167465).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for PLK1 antibody 10305-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for PLK1 antibody 10305-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for PLK1 antibody 10305-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Struct Mol Biol Aurora kinase A-mediated phosphorylation triggers structural alteration of Rab1A to enhance ER complexity during mitosis | ||
J Clin Invest PLK1 inhibition dampens NLRP3 inflammasome-elicited response in inflammatory disease models | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Targeting CBX3 with a Dual BET/PLK1 Inhibitor Enhances the Antitumor Efficacy of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Prostate Cancer
| ||
Sci Adv Cascade dynamic assembly/disassembly of DNA nanoframework enabling the controlled delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 system | ||
Nat Commun Hyperactivation of HER2-SHCBP1-PLK1 axis promotes tumor cell mitosis and impairs trastuzumab sensitivity to gastric cancer. | ||
Biomaterials Biocompatible PEGylated Gold nanorods function As cytokinesis inhibitors to suppress angiogenesis. |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Prakash (Verified Customer) (10-28-2025) | very good in western blot
|
FH Daniel (Verified Customer) (02-24-2025) | Antibody works really well for IP and Western blot.
|