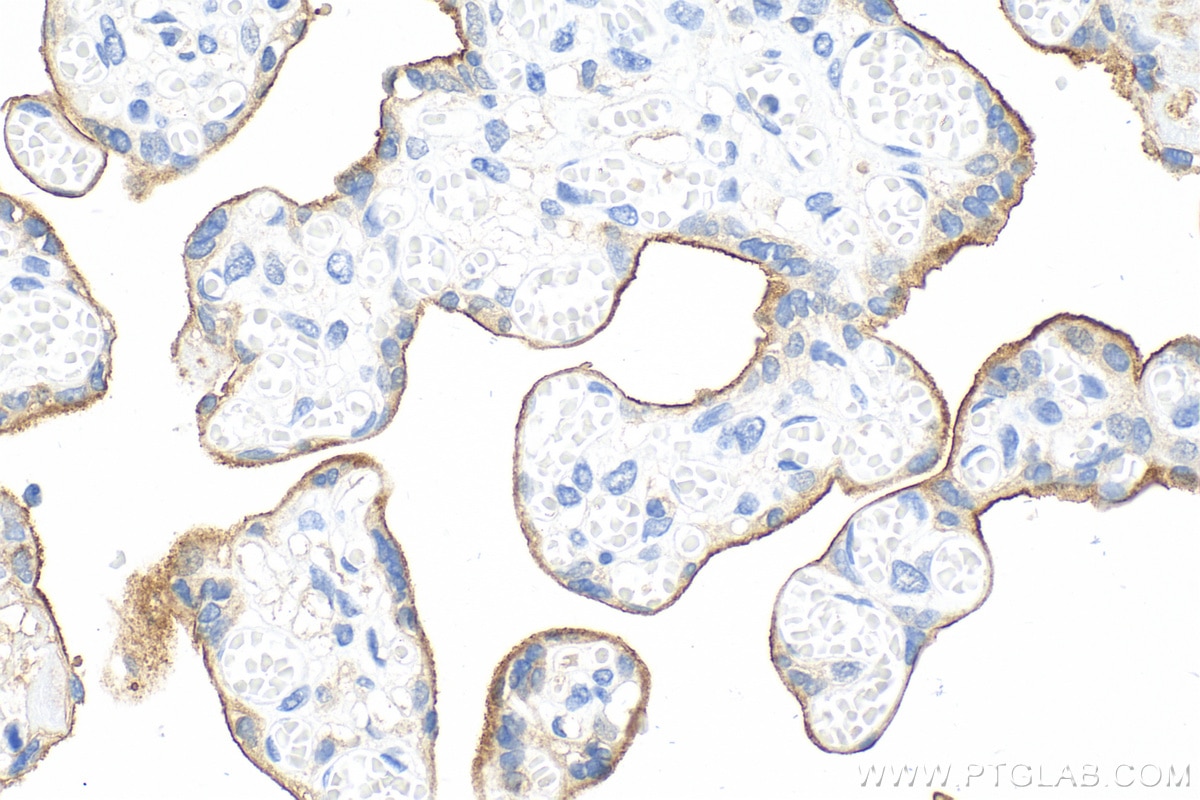
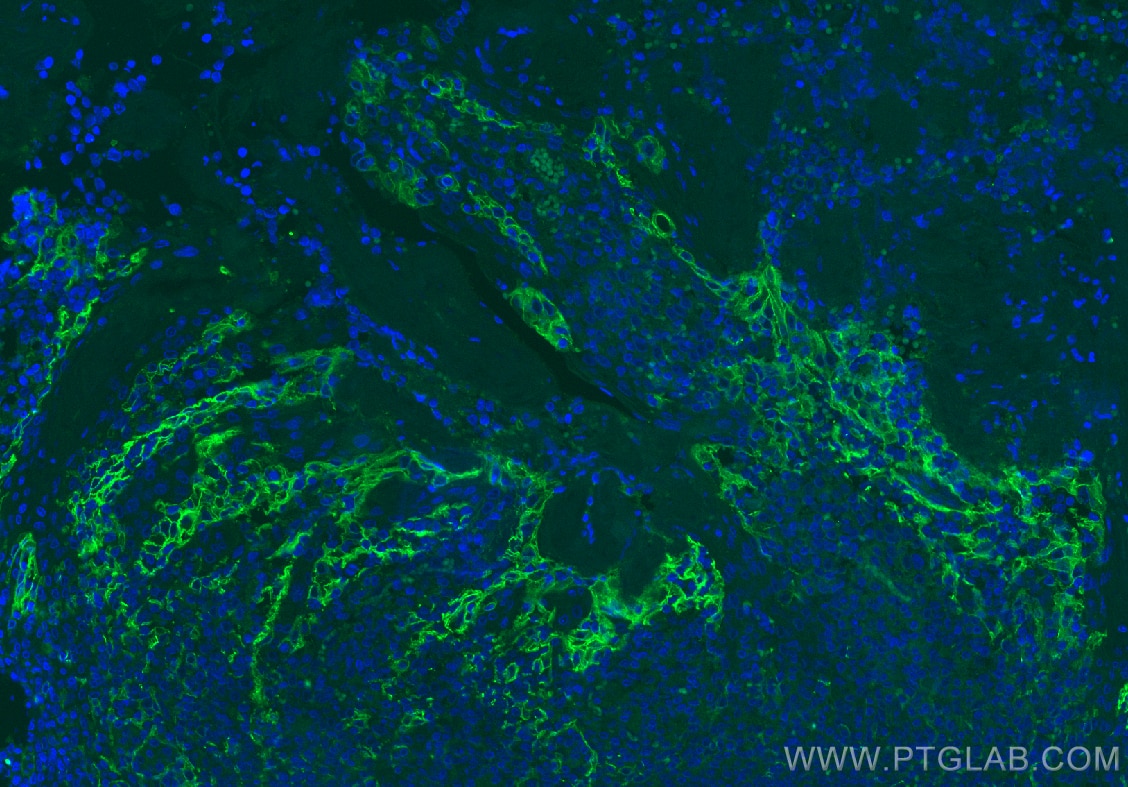
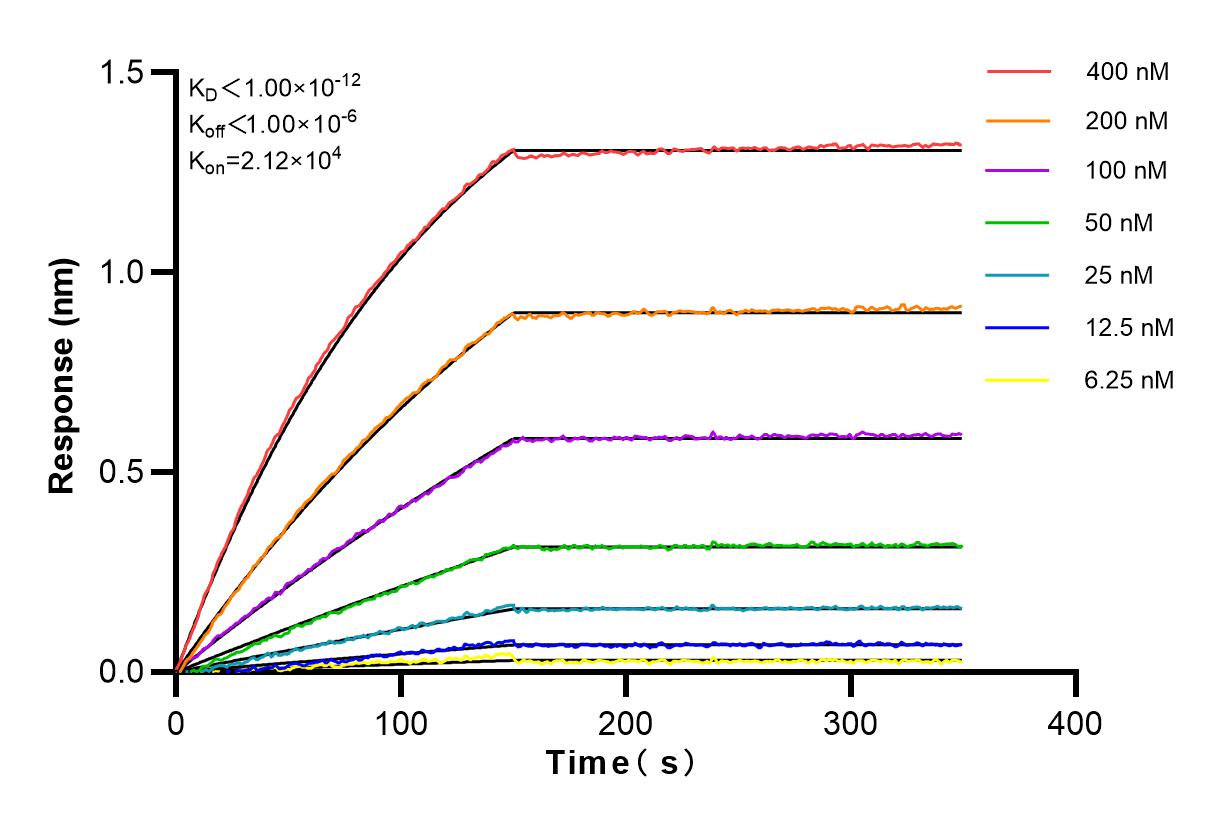
Product Information
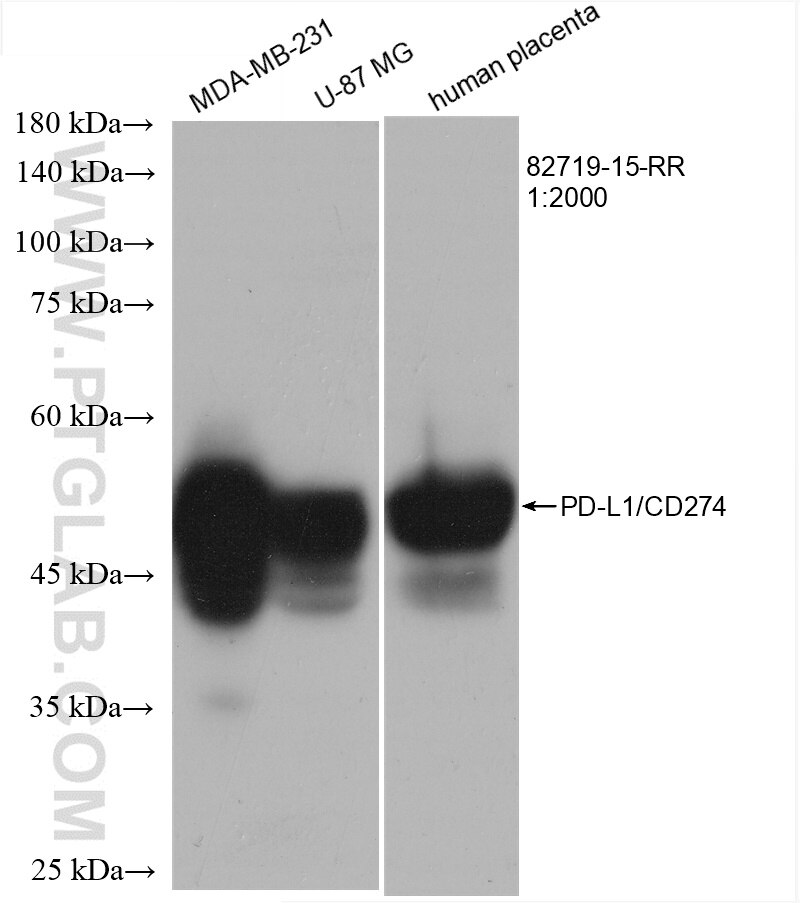
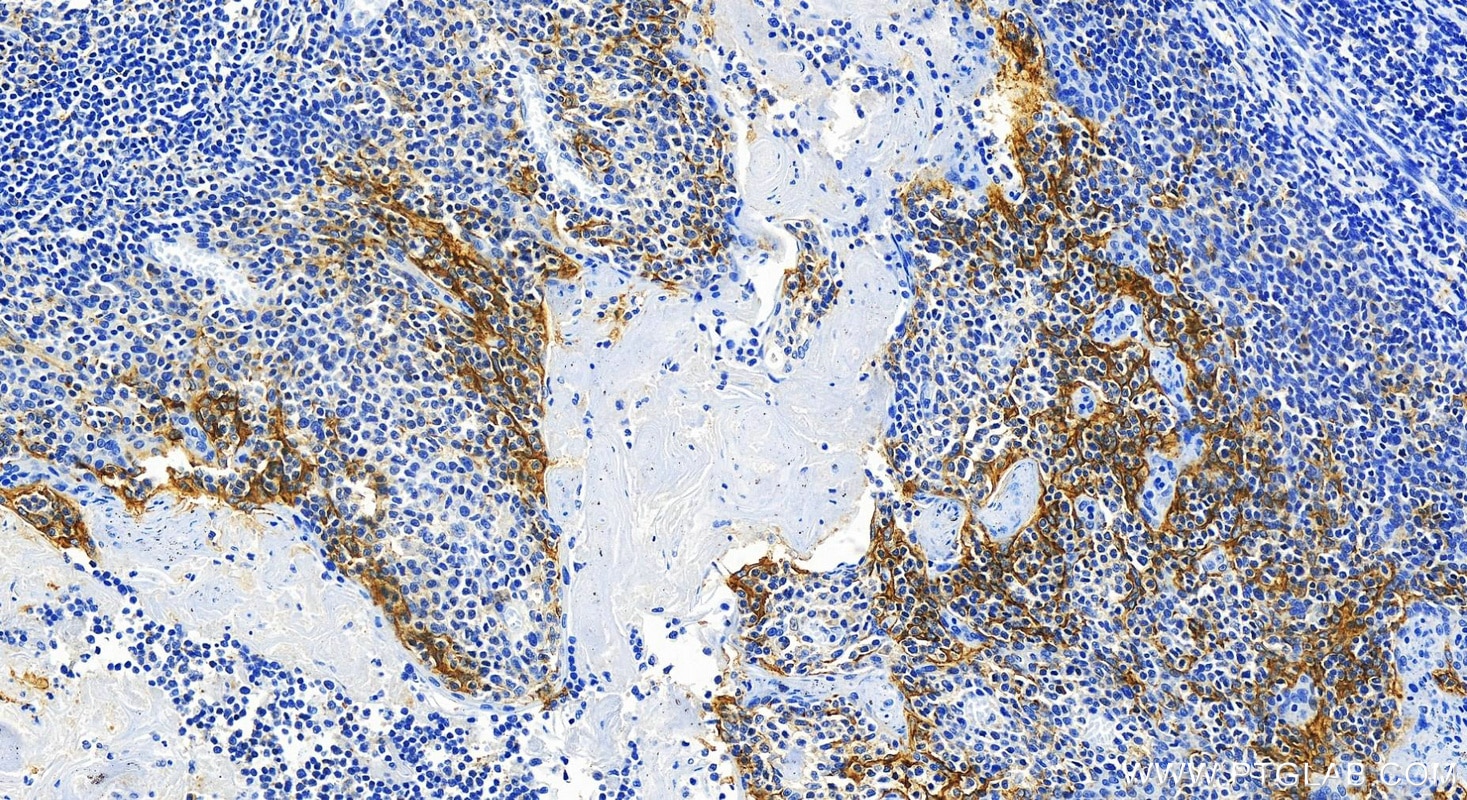
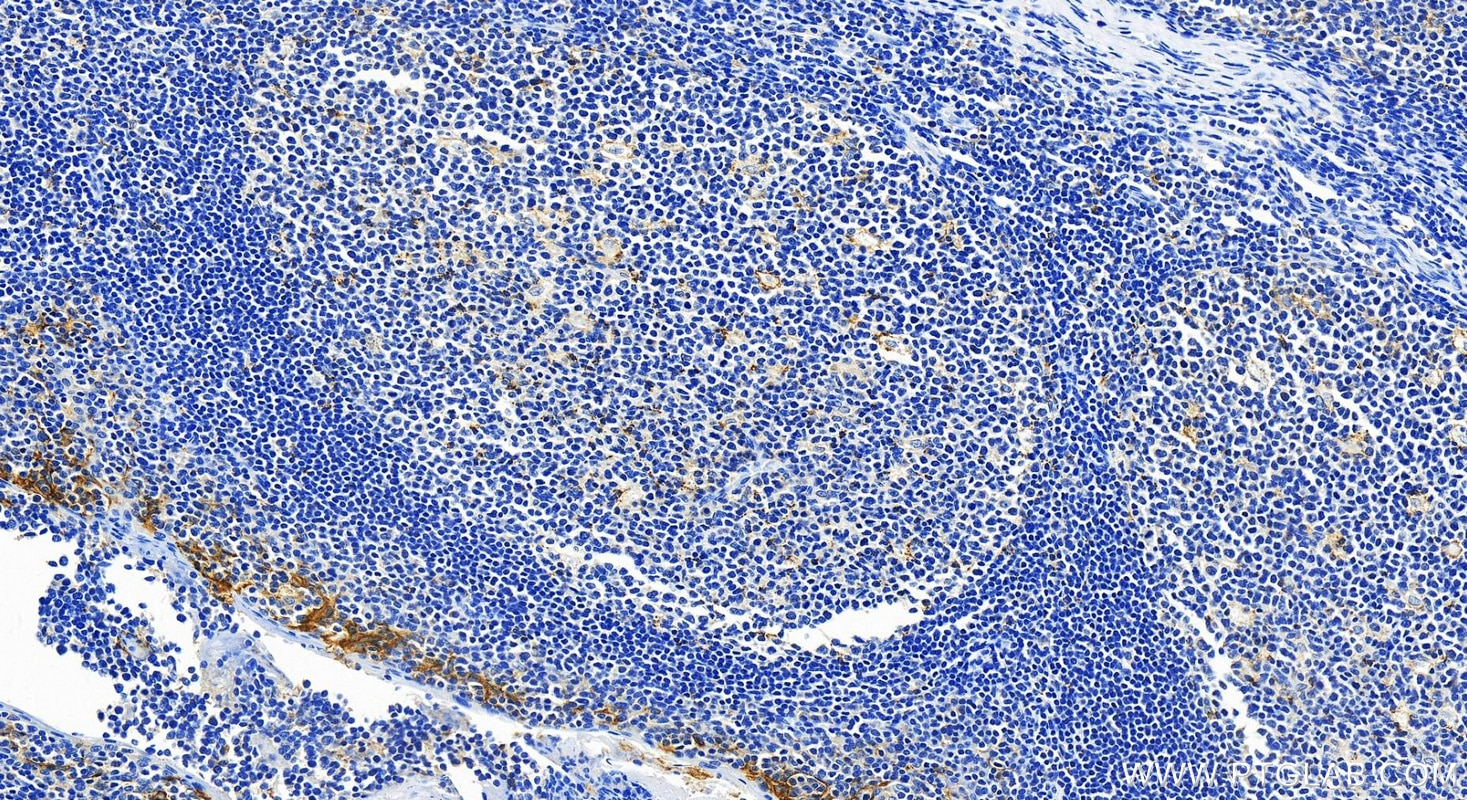
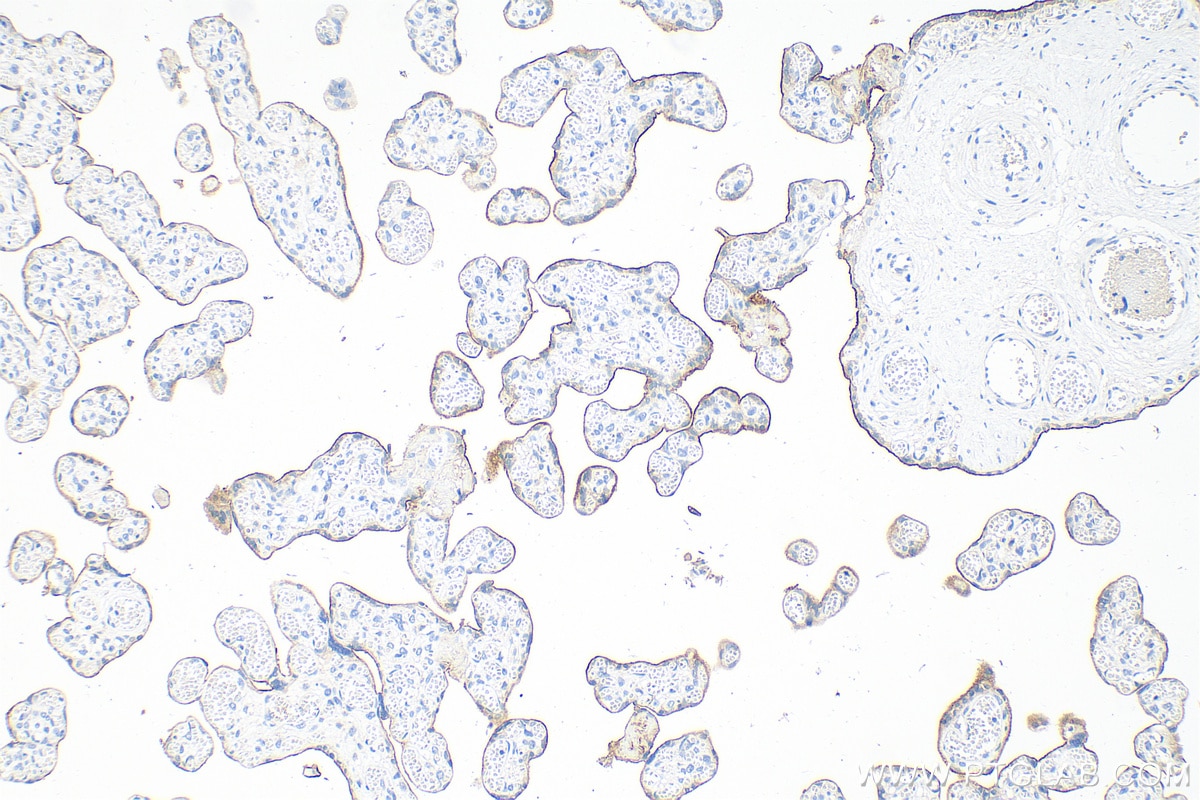
82719-15-PBS targets PD-L1/CD274 in WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | PD-L1/CD274 fusion protein Ag12432 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | CD274 molecule |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 290 aa, 33 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 50 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC074984 |
| Gene Symbol | PD-L1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 29126 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9NZQ7 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
PD-L1, also known as CD274 or B7H1, stands for programmed cell death ligand 1. It is a type I transmembrane protein that is thought to repress immune responses by binding to its receptor (PD1), thus inhibiting T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. It contains V-like and C-like immunoglobulin domains. PD-L1 expression is regulated by various cytokines, such as TNF-α or LPS (ISSN: 1848-7718). Increased expression of this protein in certain types of cancers, e.g., renal cell carcinoma or colon cancer, correlates with poor prognosis.
What is the molecular weight of PD-L1?
Depending on the isoform, the calculated molecular weight of the protein varies between 20 and 33 kDa (176-290 aa).
What are the isoforms of PD-L1?
According to NCBI, three different isoforms have been identified. There are significant differences in the untranslated and protein coding regions.
What is the subcellular localization and tissue specificity of PD-L1?
It is predicted to localize in the plasma membrane of various cell types, with a particularly high expression in placental trophoblast and subsets of immune cells. High levels of PD-L1 protein have also been detected in lung and colon tissues.
What is the function of PD-L1 in immune responses?
PD-L1 is critical for the induction and maintenance of immune self-tolerance during infection or inflammation in normal tissues. The interaction of PD-L1 and its receptors is responsible for preventing auto-immune phenotypes and balancing the overall immune response in situations such as pregnancy or tissue allografts. The interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1 or B7.1 starts an inhibitory signaling cascade, which results in the decreased proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells and increased survival of regulatory T-cells (PMID: 15240681).
How can PD-L1's implication in cancer be used as a drug target?
In certain tumors, high expression of PD-L1 serves as a stop-sign to inhibit the recognition of cancer cells by T-cells (PMID: 23087408). The interaction between PD-L1 and its receptors (PD1 and B7.1) is a mechanism for the tumor to evade the host immune response (PMID: 29357948). Several mAbs have been developed to target that interaction and thus prevent the inactivation of cytotoxic T-cells by the tumor (PMIDs: 23890059, 18173375).