Tested Applications
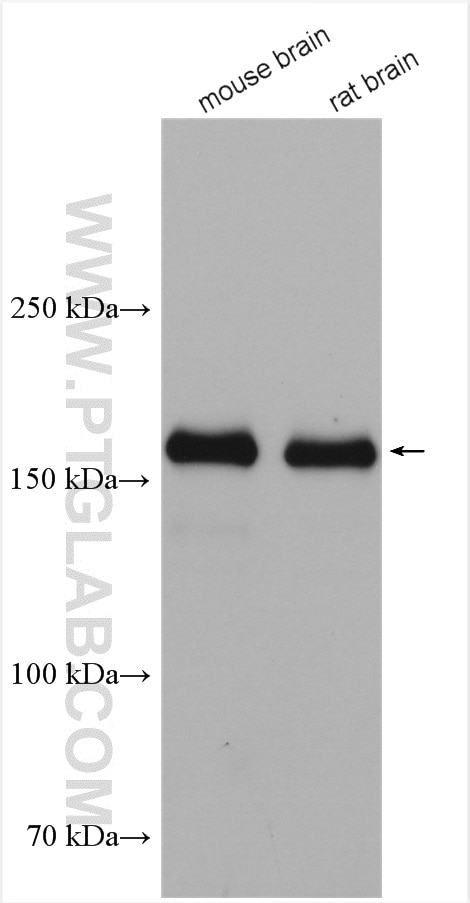
| Positive WB detected in | mouse brain tissue, rat brain tissue |
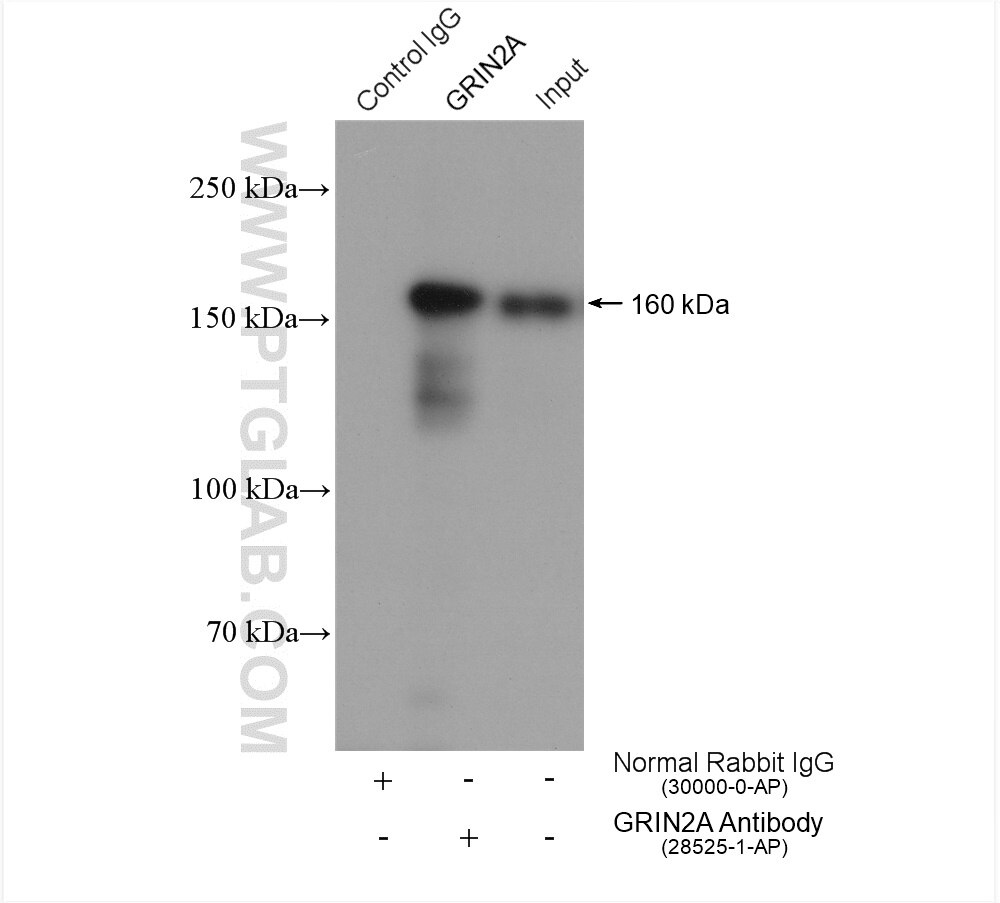
| Positive IP detected in | rat brain tissue |
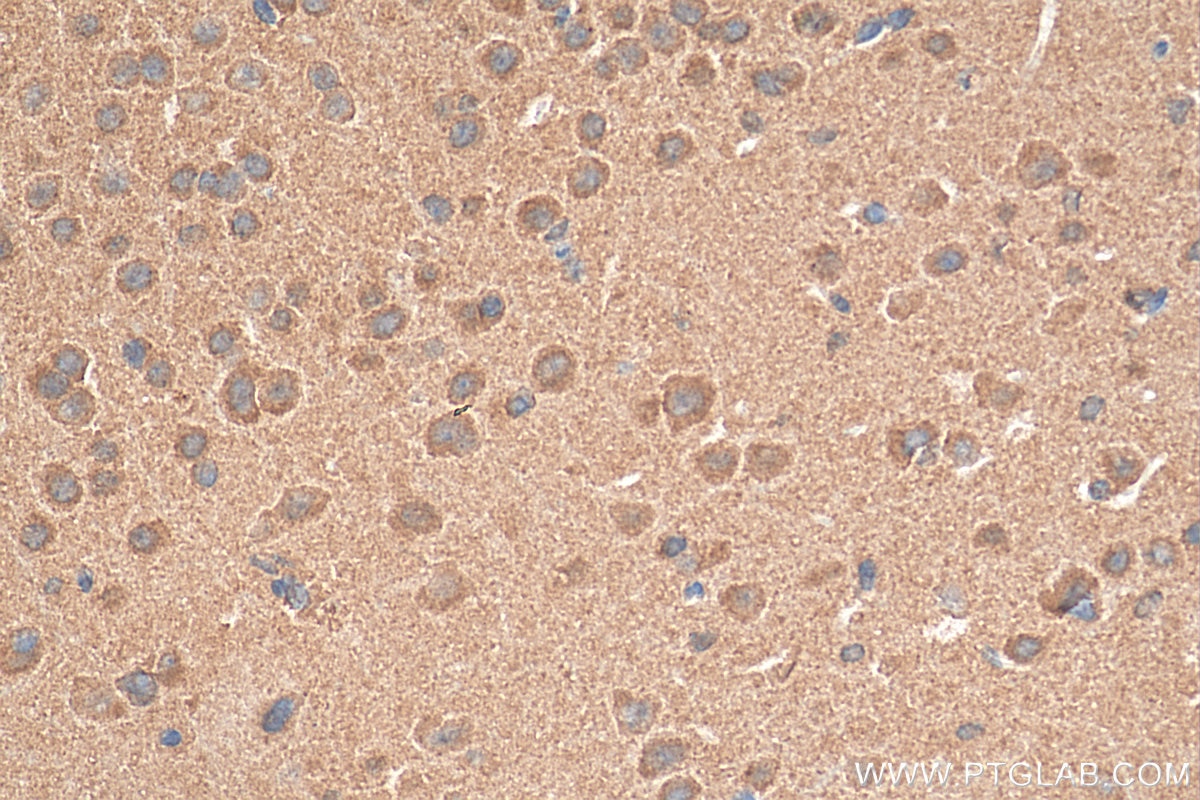
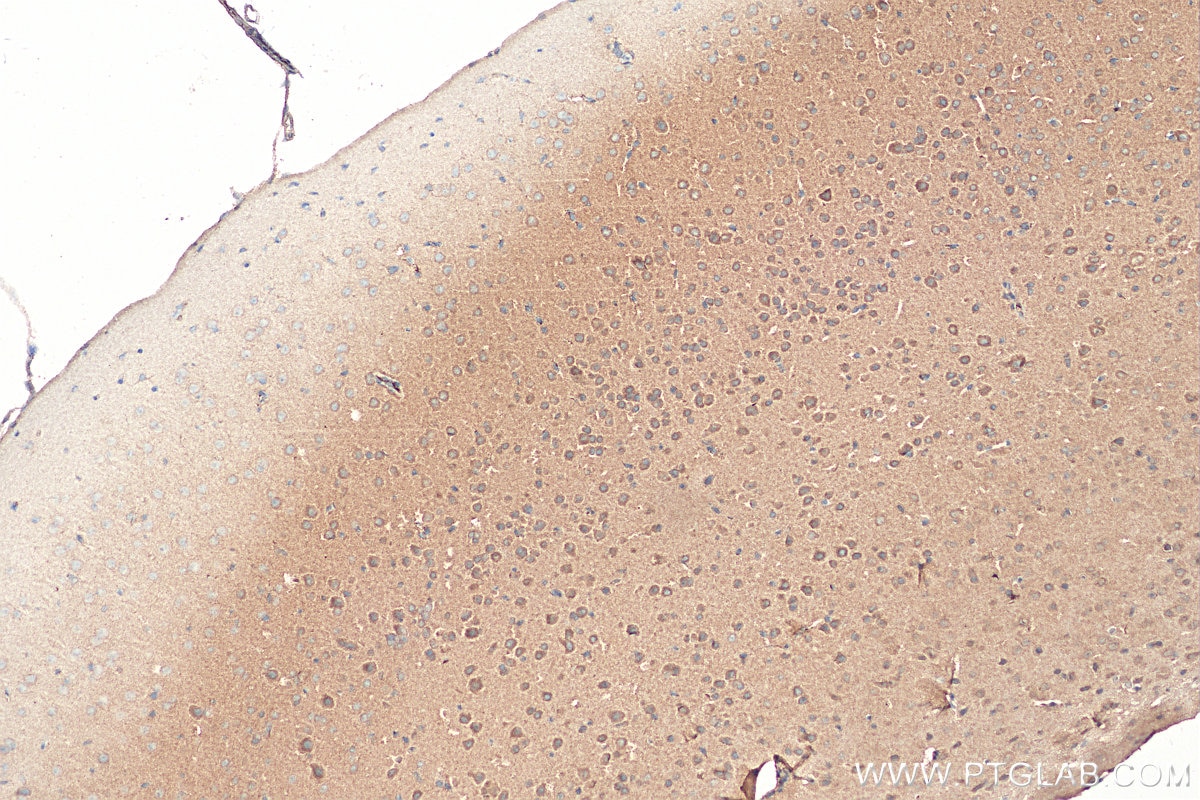
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 10 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
28525-1-AP targets NMDAR2A/GRIN2A in WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | NMDAR2A/GRIN2A fusion protein Ag29101 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2A |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 165 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 160-180 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_000833 |
| Gene Symbol | GRIN2A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2903 |
| RRID | AB_2881163 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q12879 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
GRIN2A (glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 2A), also known as NMDAR2A. And its molecular weight is 165 kDa. GRIN2A is located in cell projection, dendritic spine, cell membrane, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrae, cytolamic vesicle membrane, which is expressed in many tissues, highest expression in brain and heart. This gene encodes a member of the glutamate-gated ion channel protein family. The encoded protein is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit. NMDA receptors are both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent, and are involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning. These receptors are permeable to calcium ions, and activation results in a calcium influx into post-synaptic cells, which results in the activation of several signaling cascades. Disruption of this gene is associated with focal epilepsy and speech disorder with or without cognitive disability. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NMDAR2A/GRIN2A antibody 28525-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for NMDAR2A/GRIN2A antibody 28525-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for NMDAR2A/GRIN2A antibody 28525-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Adv Sci (Weinh) Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing Reveals that Decorin Expression in the Amygdala Regulates Perineuronal Nets Expression and Fear Conditioning Response after Traumatic Brain Injury. | ||
Transl Psychiatry Reduction of p11 in dorsal raphe nucleus serotonergic neurons mediates depression-like behaviors | ||
J Affect Disord Dysregulation of striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor-mediated by hypocretin induces depressive behaviors in rats | ||
J Neurosci Cortex-specific Tmem169 Deficiency Induces Defects in Cortical Neuron Development and Autism-like Behaviors in Mice | ||
Andrology Catch-up fat in male adults induces low testosterone and consequently promotes metabolic abnormalities and cognitive impairment. | ||
Psychiatry Res The role of reelin in the pathological mechanism of depression from clinical to rodents |