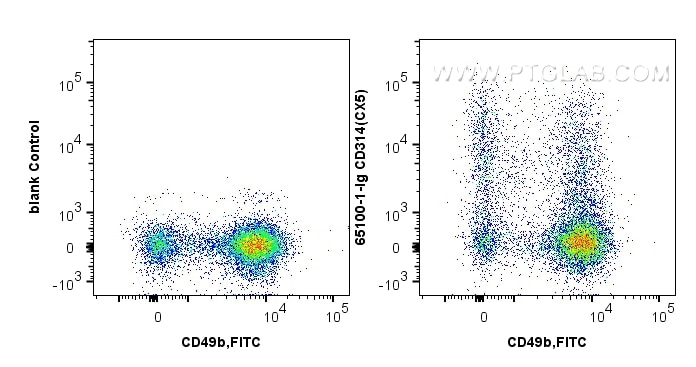
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | C57 mouse splenic NK cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
65100-1-Ig targets CD314/NKG2D in FC applications and shows reactivity with Mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rat / IgG1, kappa |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Purified Mouse NKG2D protein Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily K, member 1 |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC057147 |
| Gene Symbol | CD314 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 27007 |
| RRID | AB_3084899 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O54709 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
CD314, also known as NKG2D or Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily K member 1 (KLRK1), is a type II lectin-like transmembrane stimulatory receptor (PMID: 8436421). In mice, CD314 is expressed on NK cells, activated CD8(+) T cells and macrophages, and subsets of TCR gamma delta (+) and NK1.1 (+) T cells (PMID: 12150888). Various subfamilies of MHC class I-related glycoproteins have been identified as the ligands for mouse CD314, including RAET1A, RAET1B, RAET1C, RAET1D, RAET1E, H60 and MULT1 (PMID: 31720075).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for CD314/NKG2D antibody 65100-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |