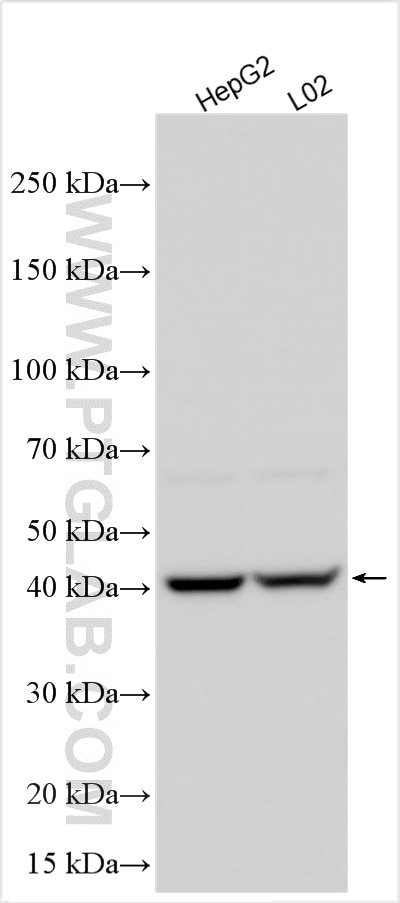
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | HepG2 cells, L02 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
16576-1-AP targets NAAA in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | NAAA fusion protein Ag9861 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | N-acylethanolamine acid amidase |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 359 aa, 40 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 40 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC011854 |
| Gene Symbol | NAAA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 27163 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q02083 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
NAAA (N-acylethanolamine acid amidase), also named ASAHL and PLT, is a novel lysosomal hydrolase structurally and functionally similar to acid ceramidase and is mainly involved in the hydrolysis of fatty amides. NAAA is mainly responsible for the degradation of bioactive fatty amides, such as palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), and is involved in lipid metabolism and fatty acid metabolism processes (PMID: 32191459; PMID: 17712833).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NAAA antibody 16576-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |