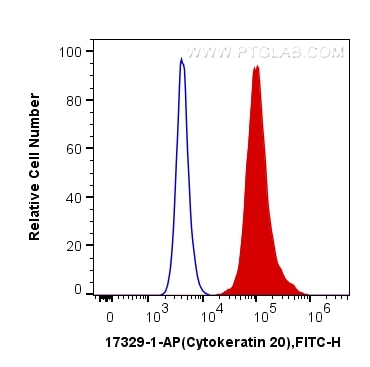
Tested Applications
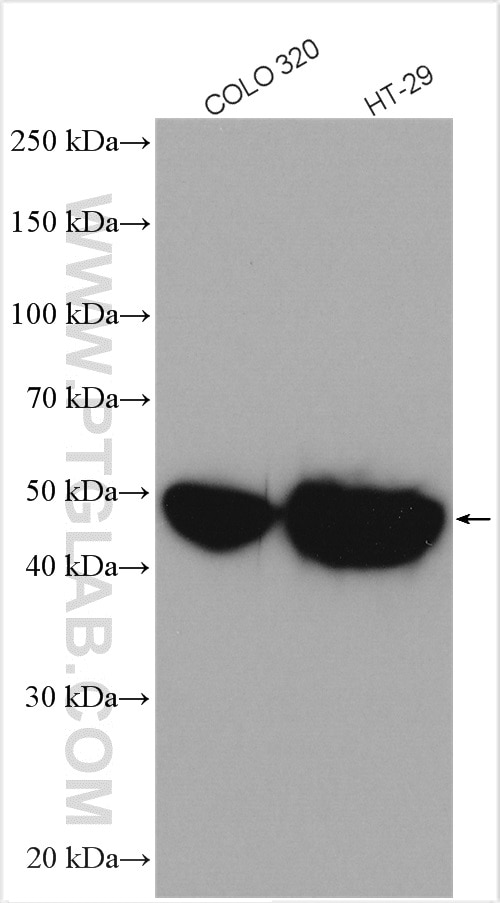
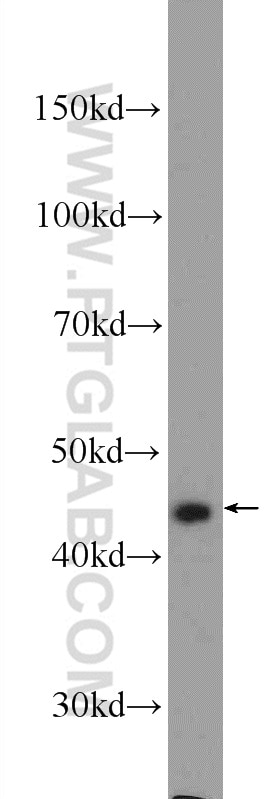
| Positive WB detected in | COLO 320 cells, HeLa cells, HT-29 cells |
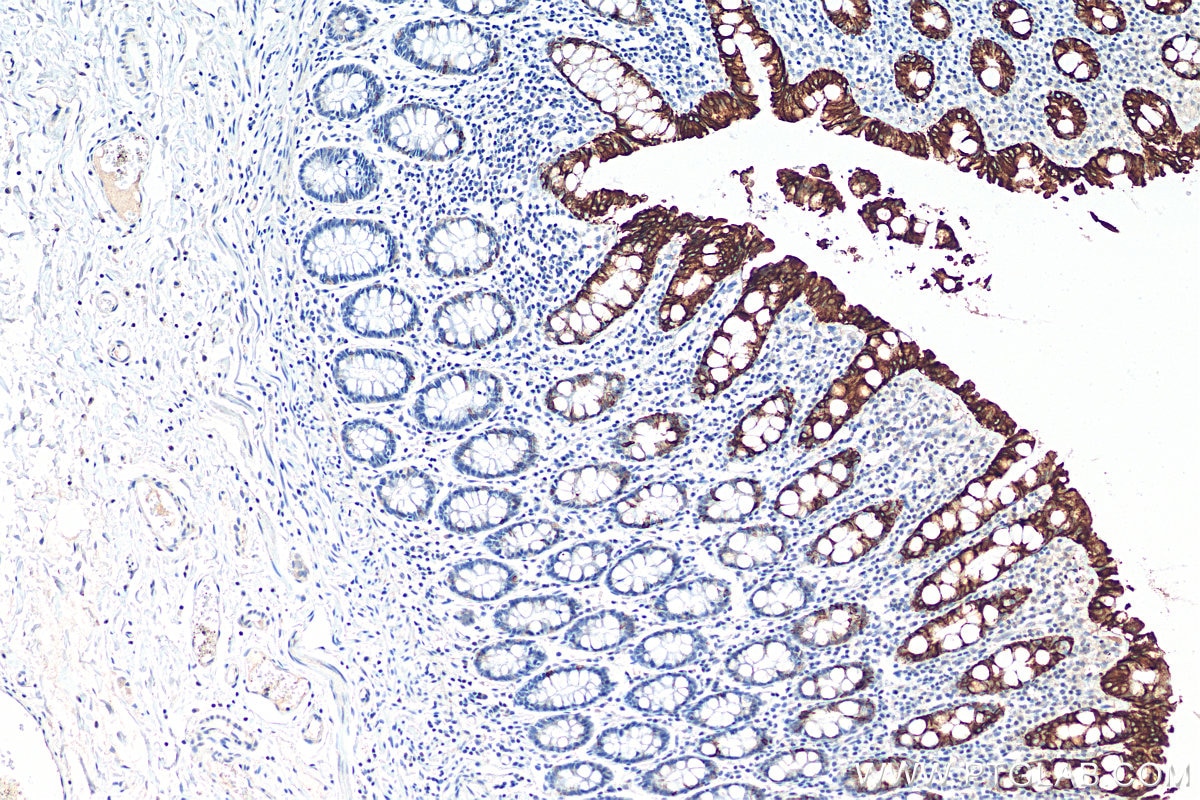
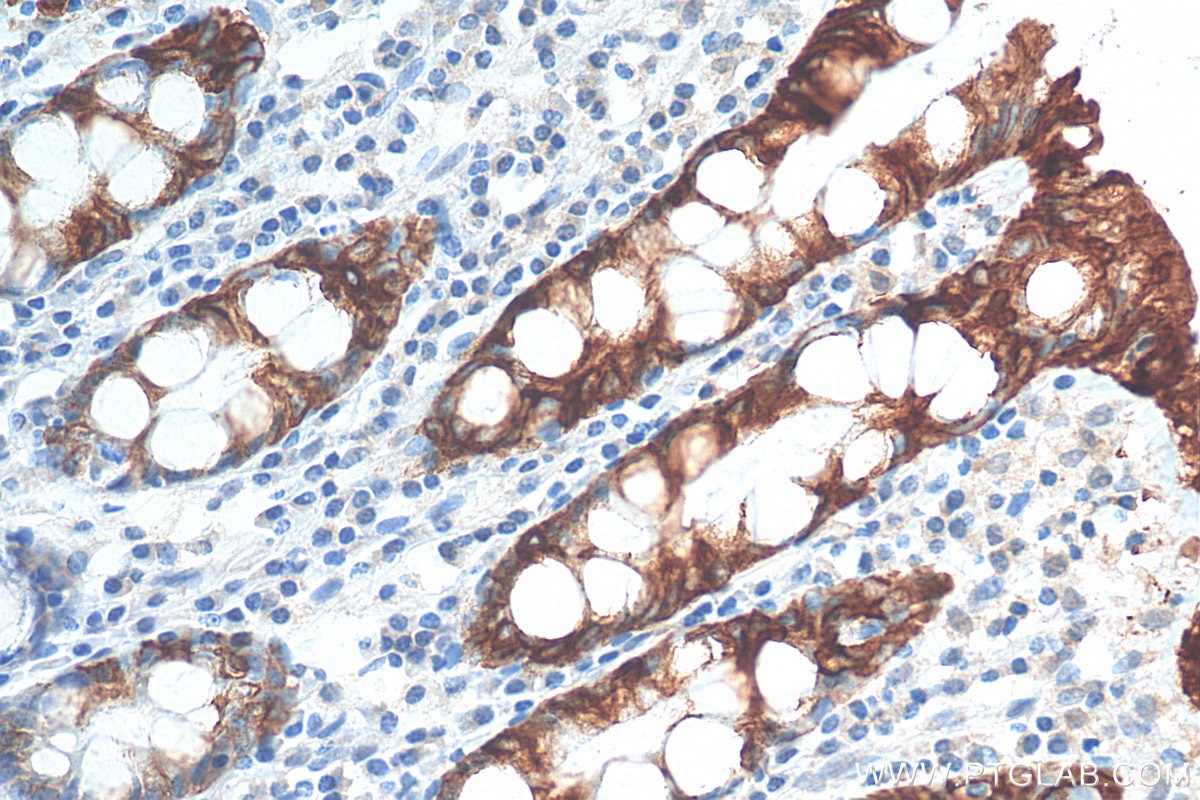
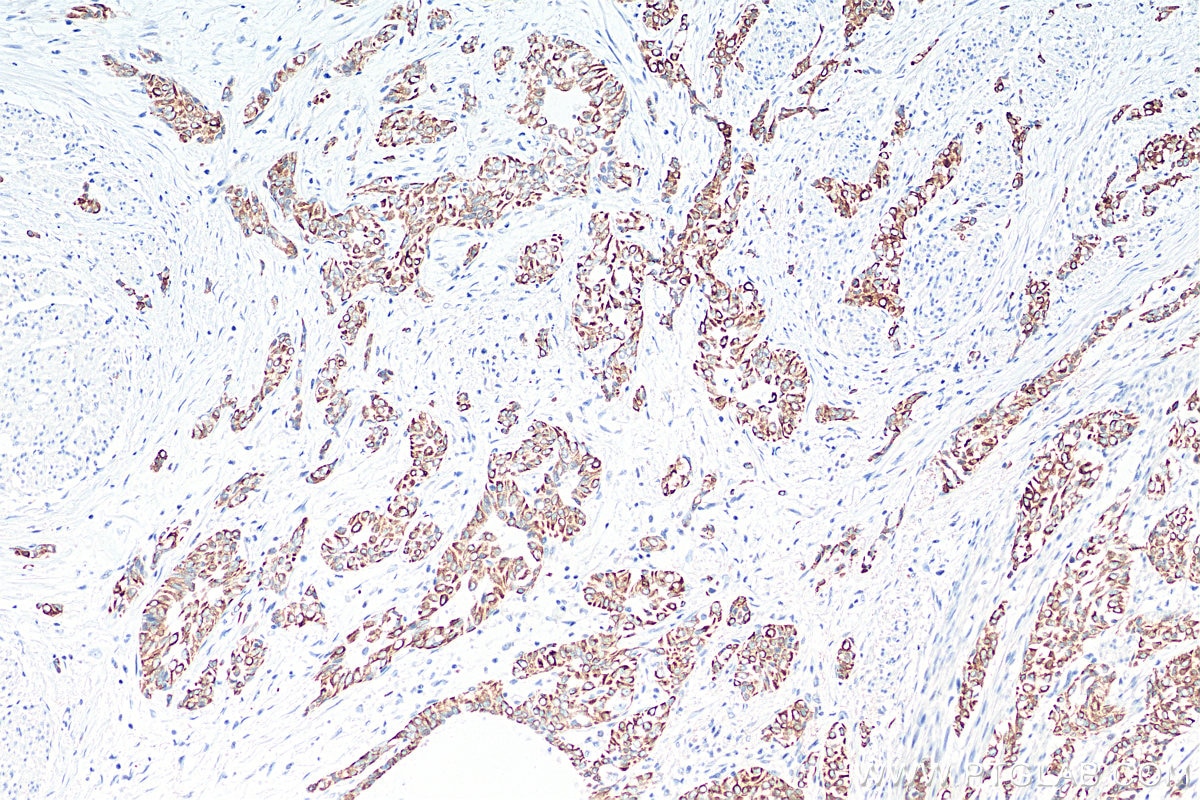
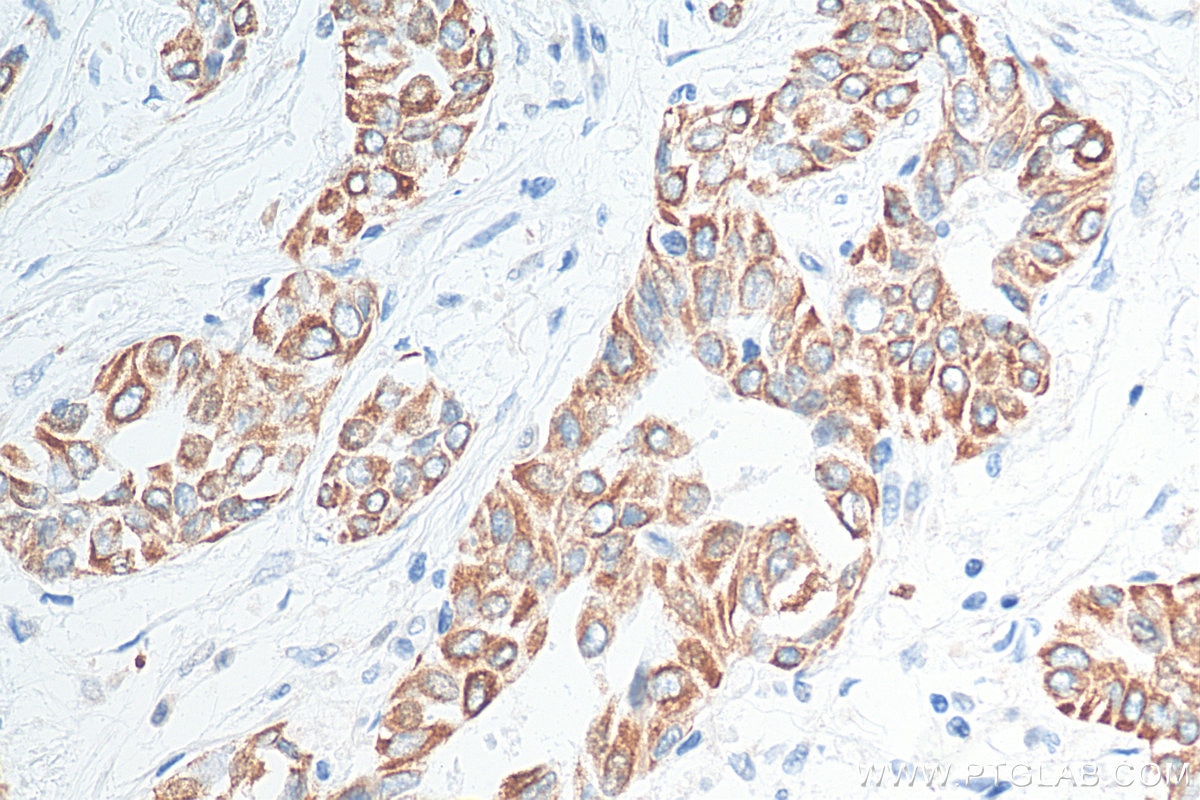
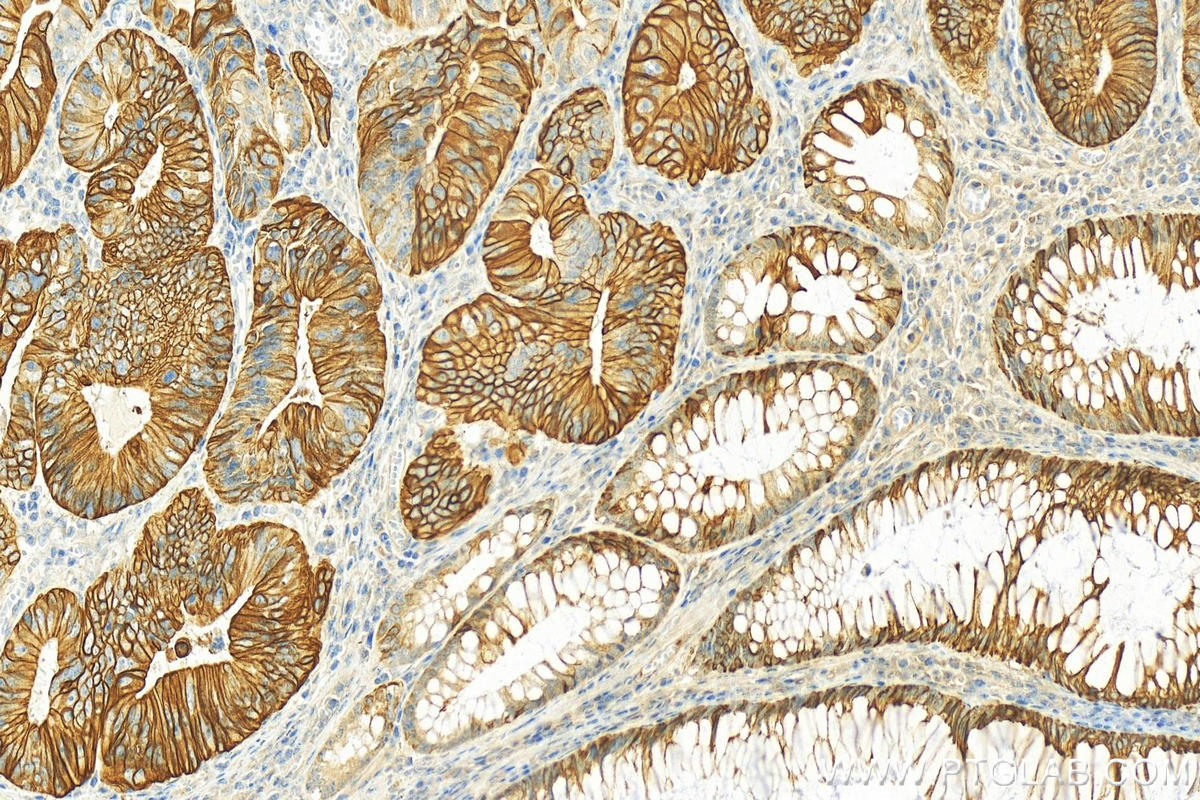
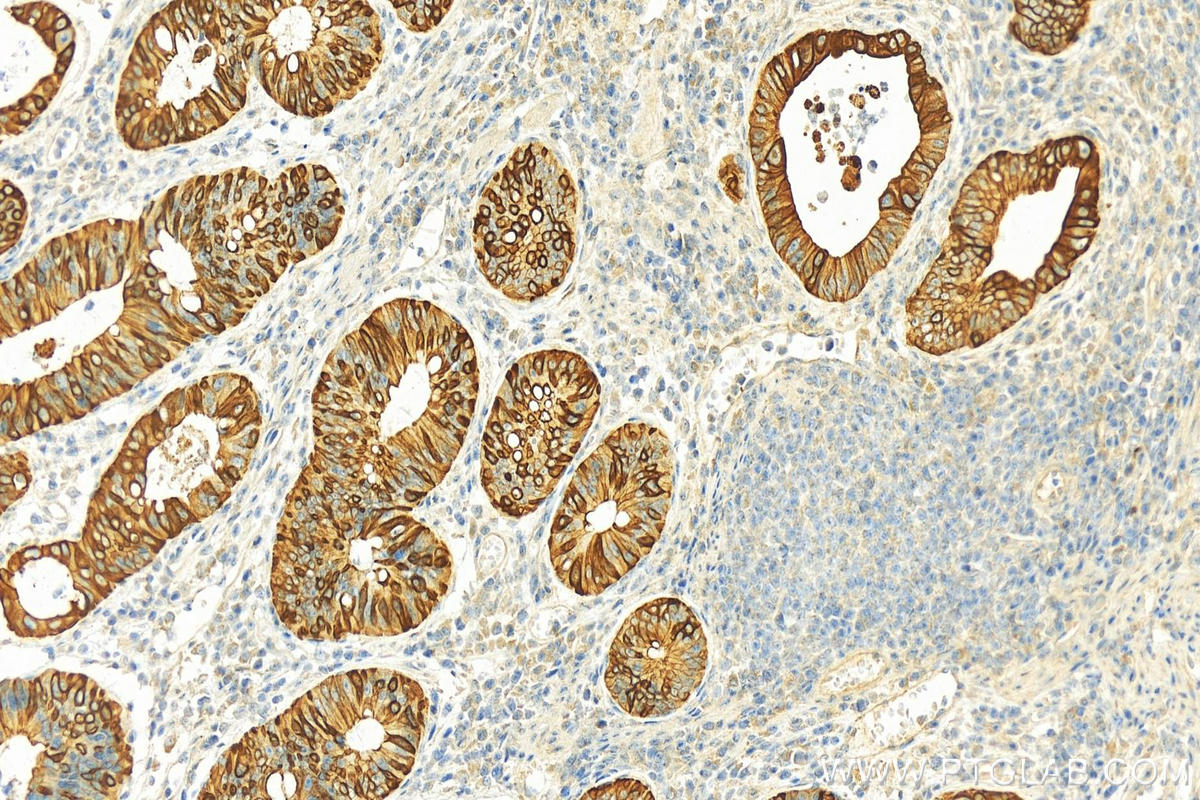
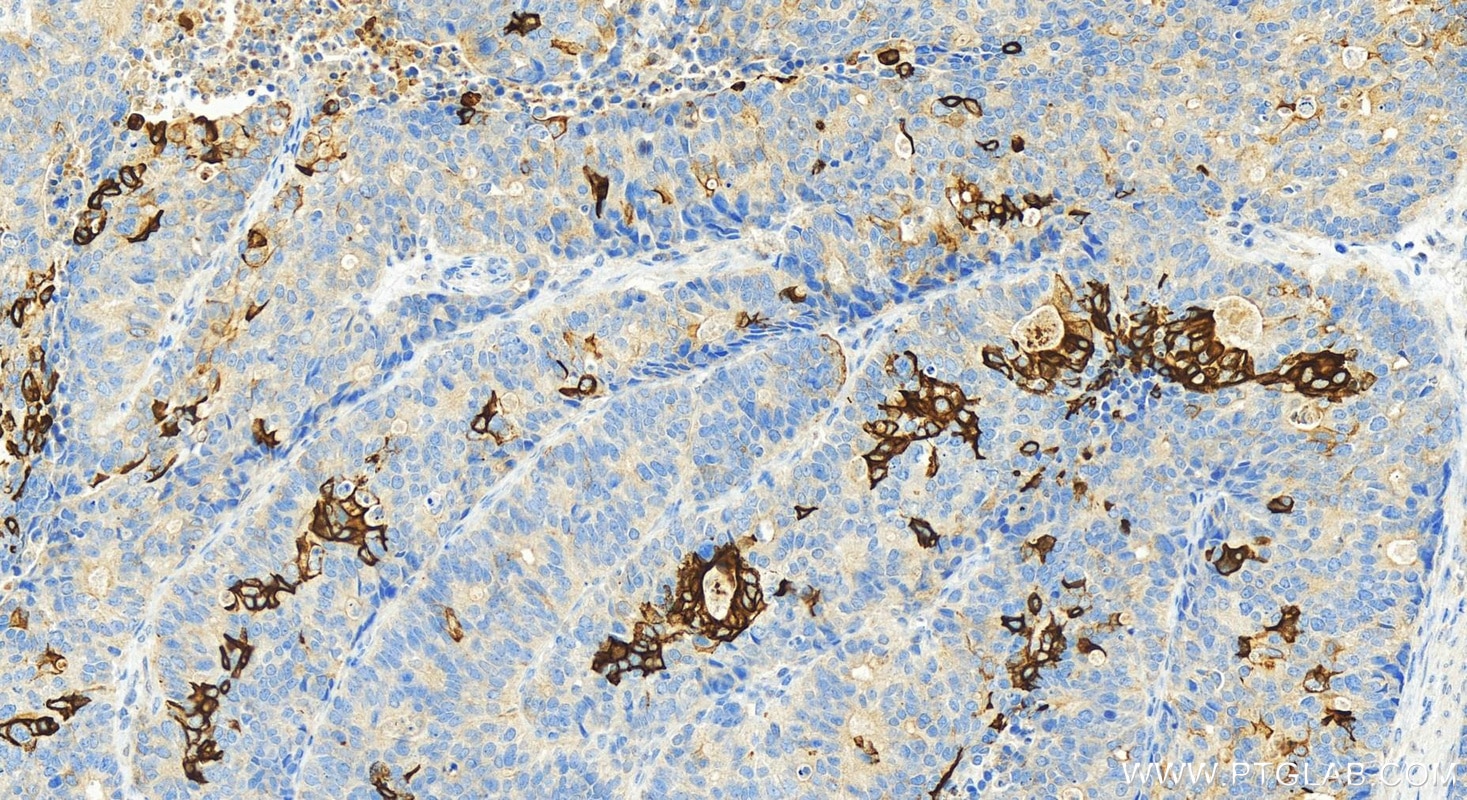
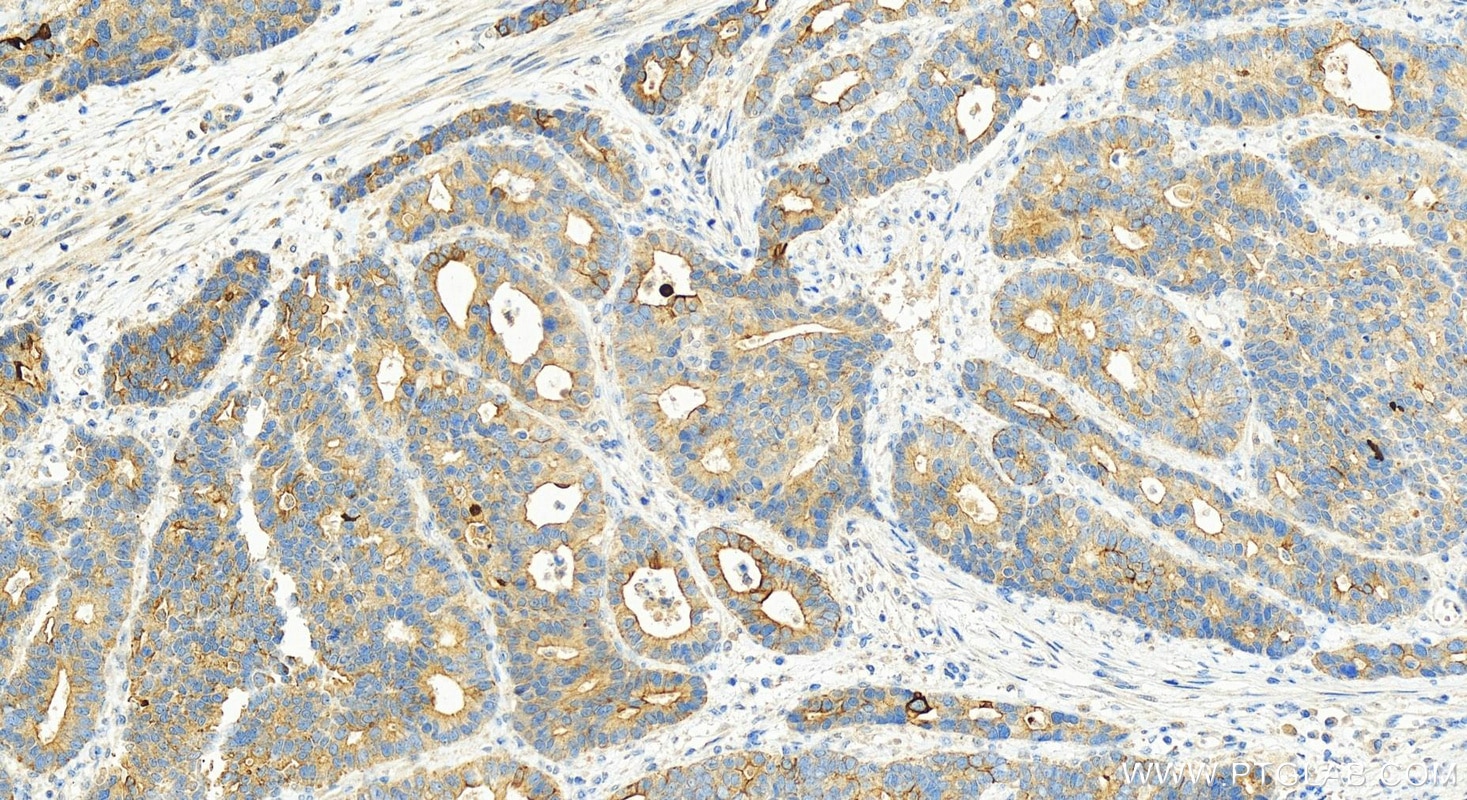
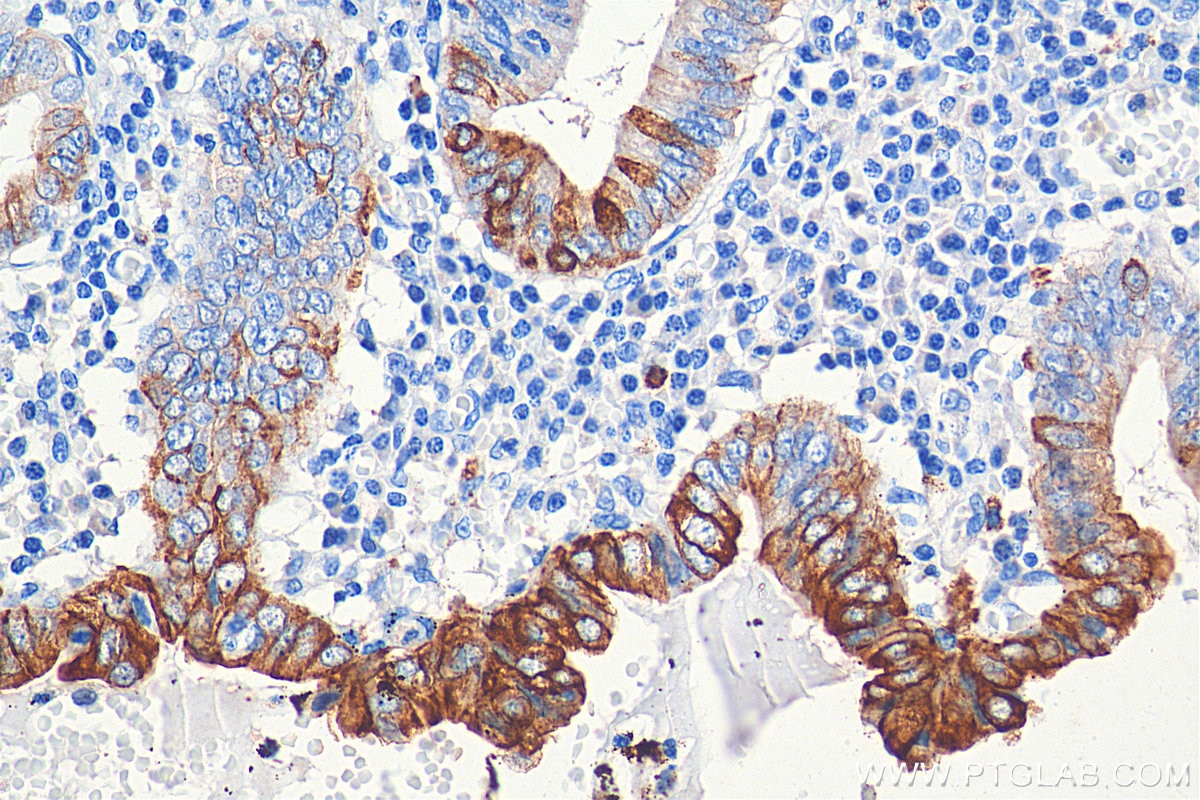
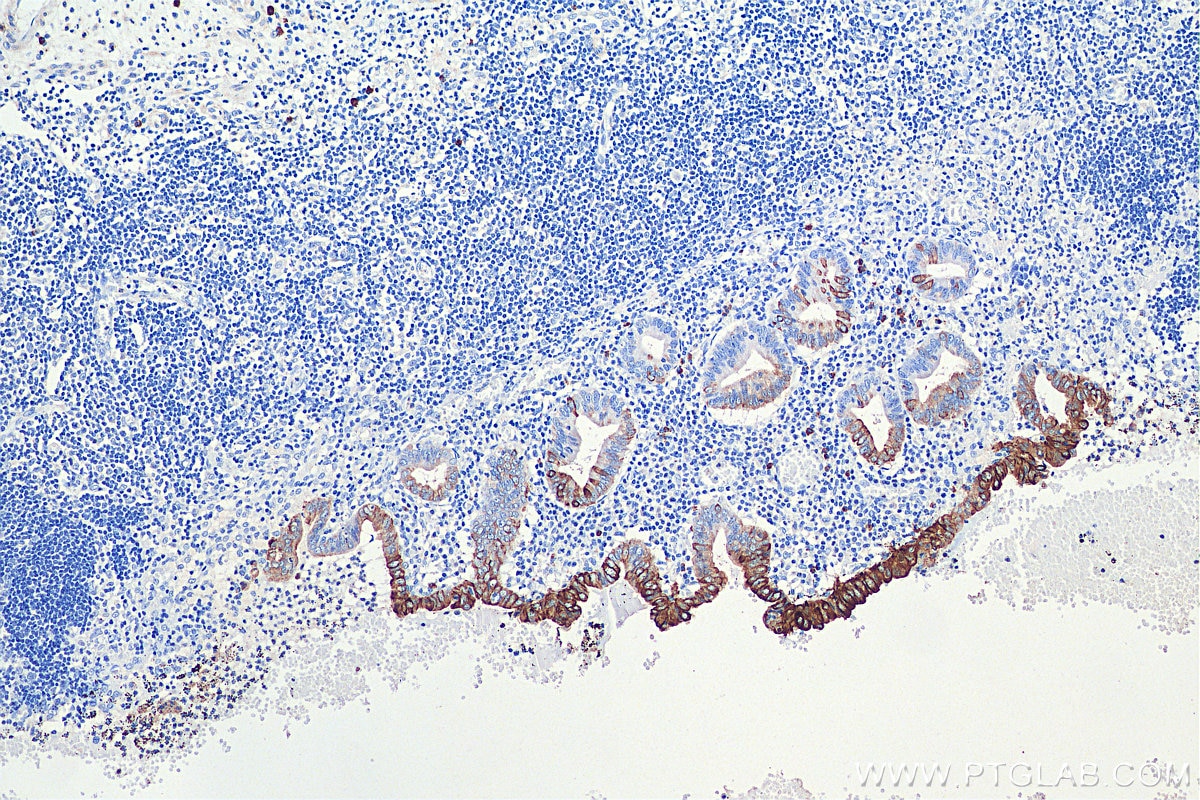
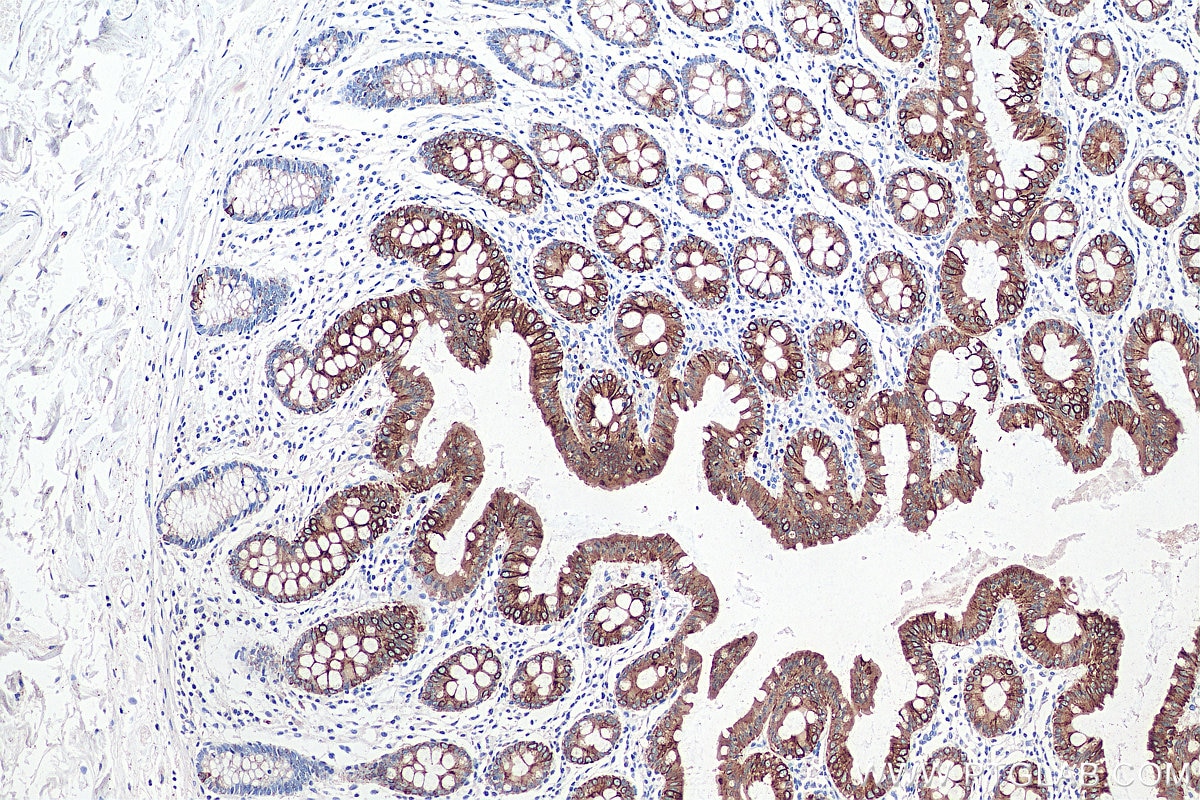
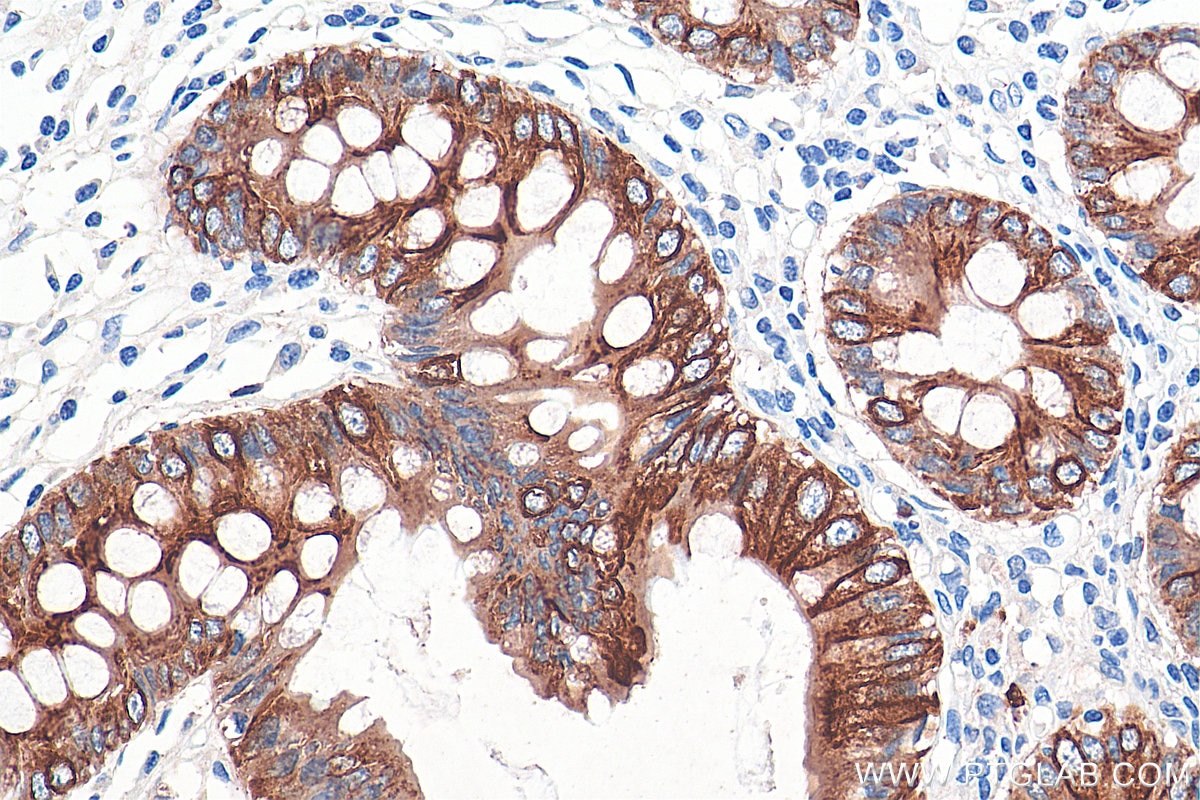
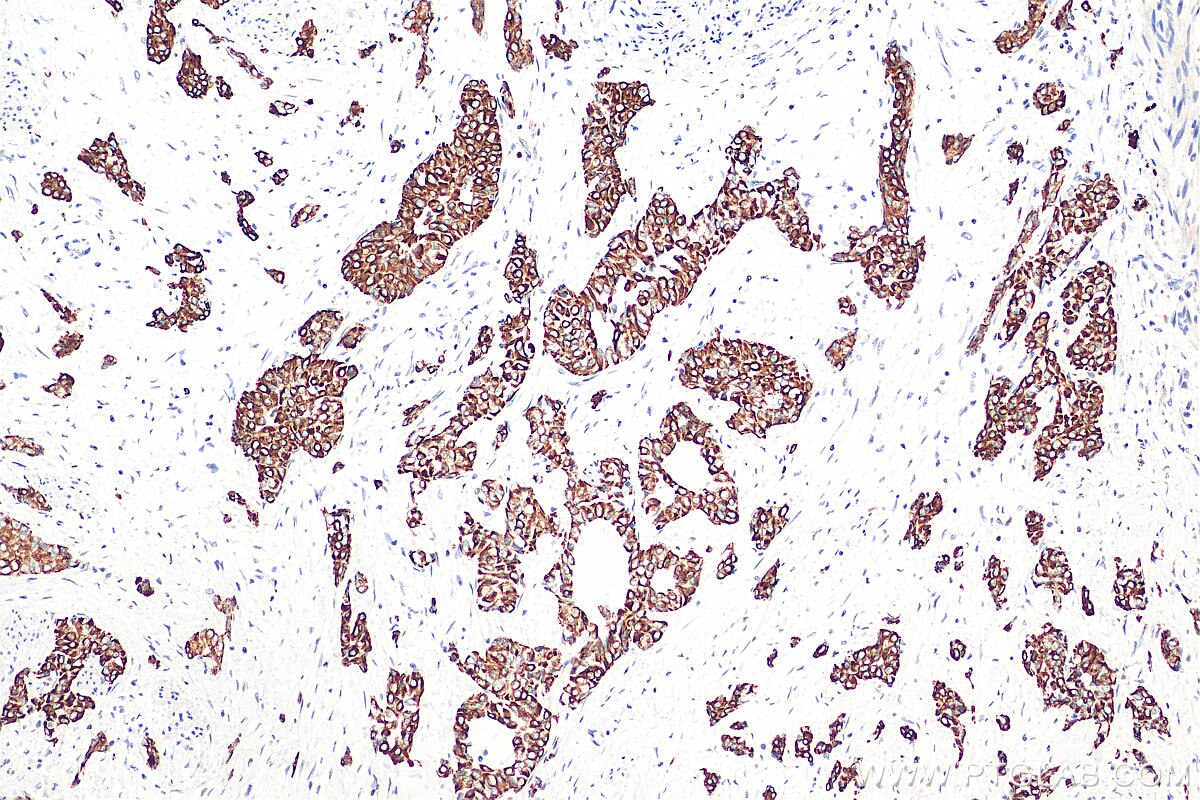
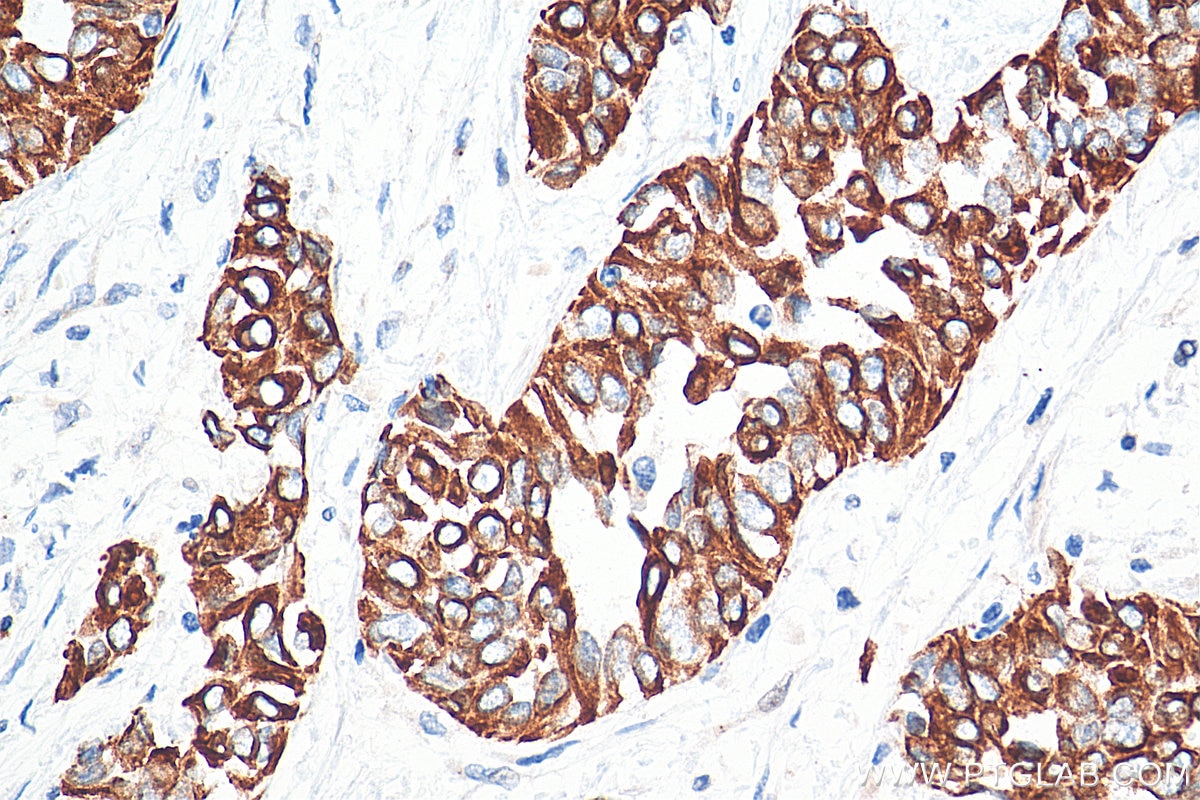
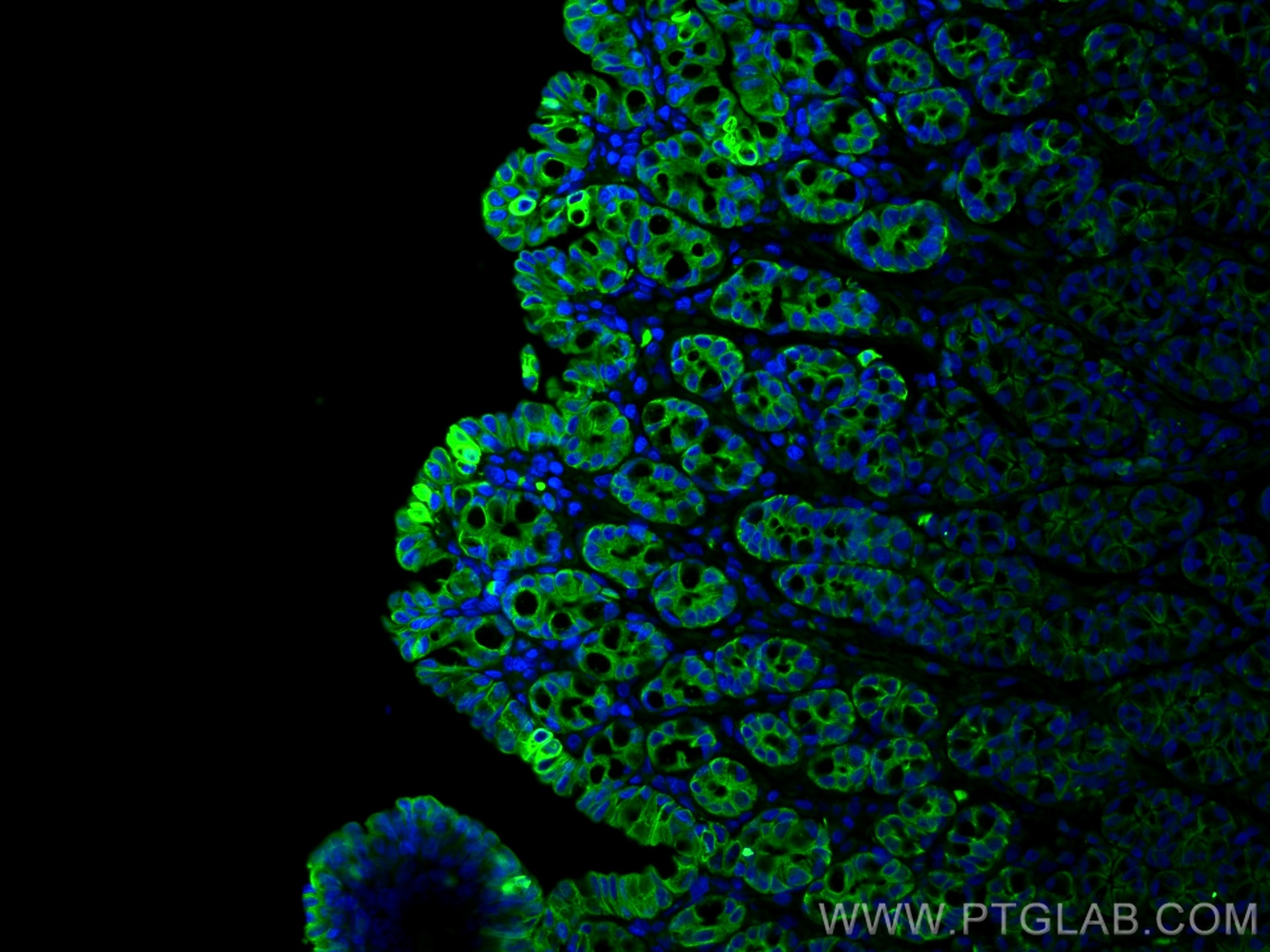
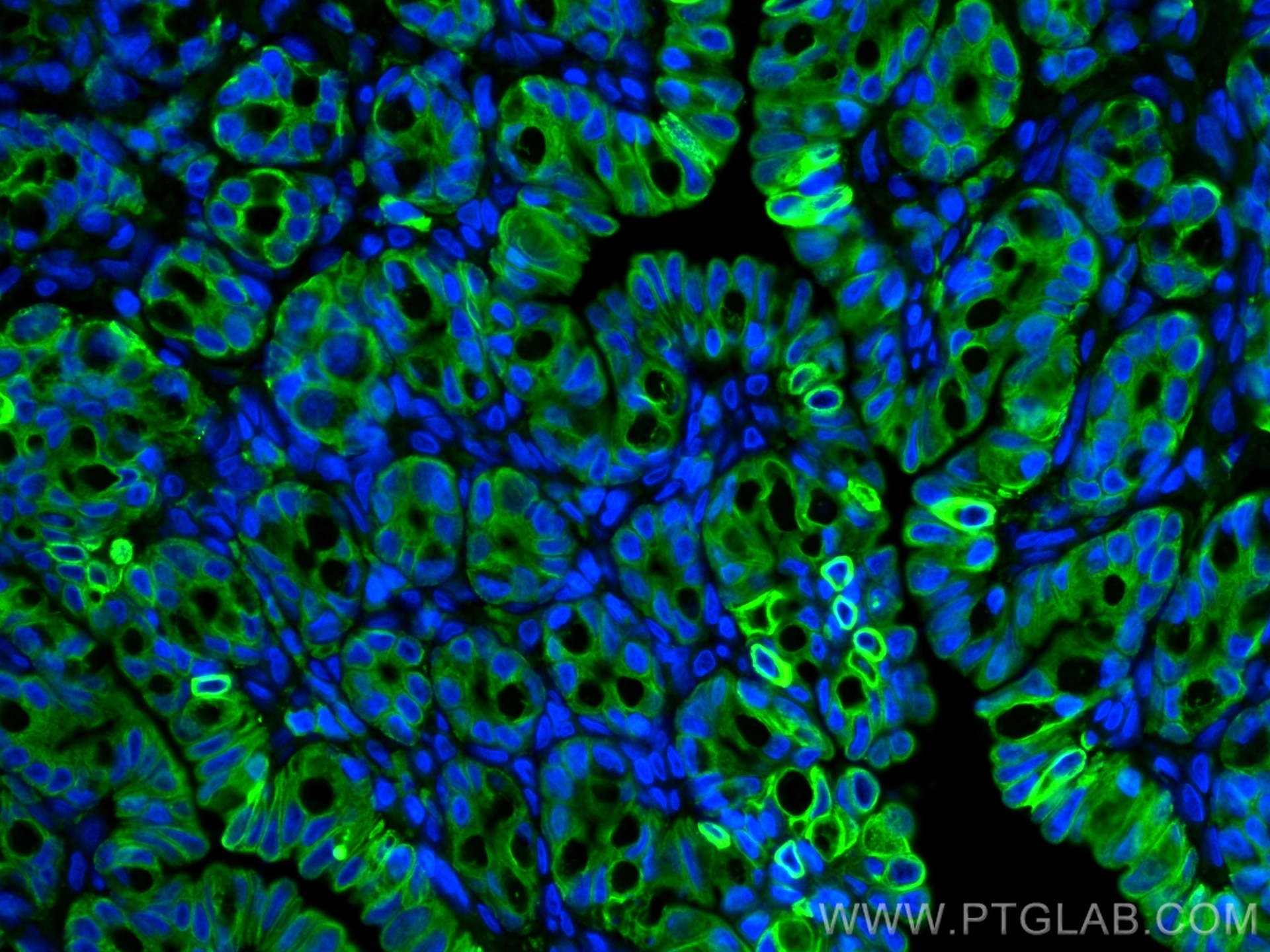
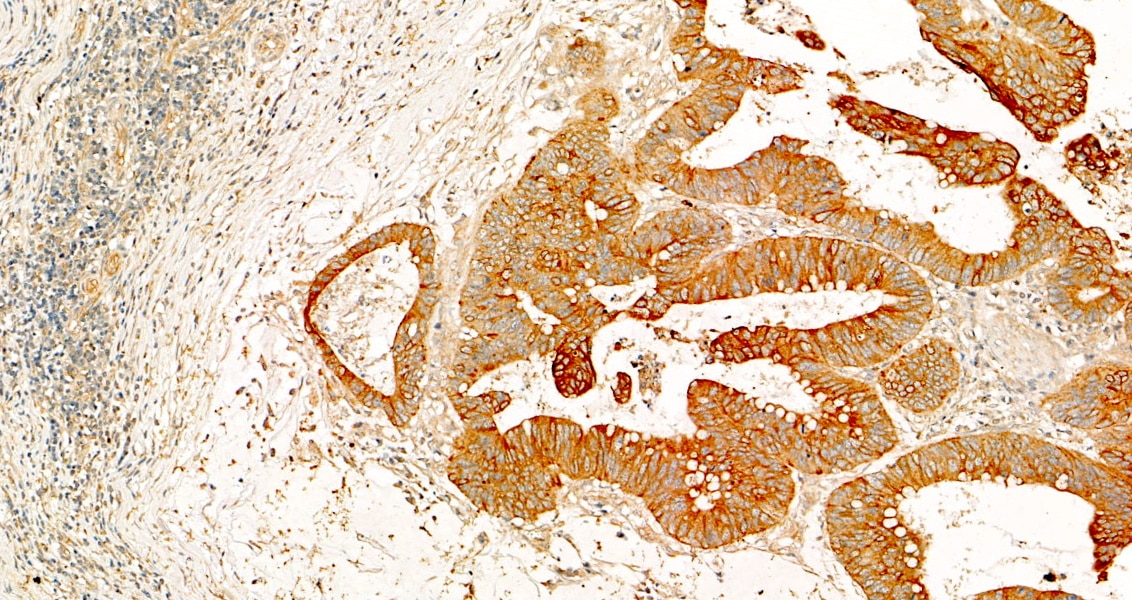
| Positive IHC detected in | human colon tissue, human appendicitis tissue, human colon cancer tissue, human stomach cancer tissue, human urothelial carcinoma tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
| Positive IF-P detected in | Rabbit colon tissue |
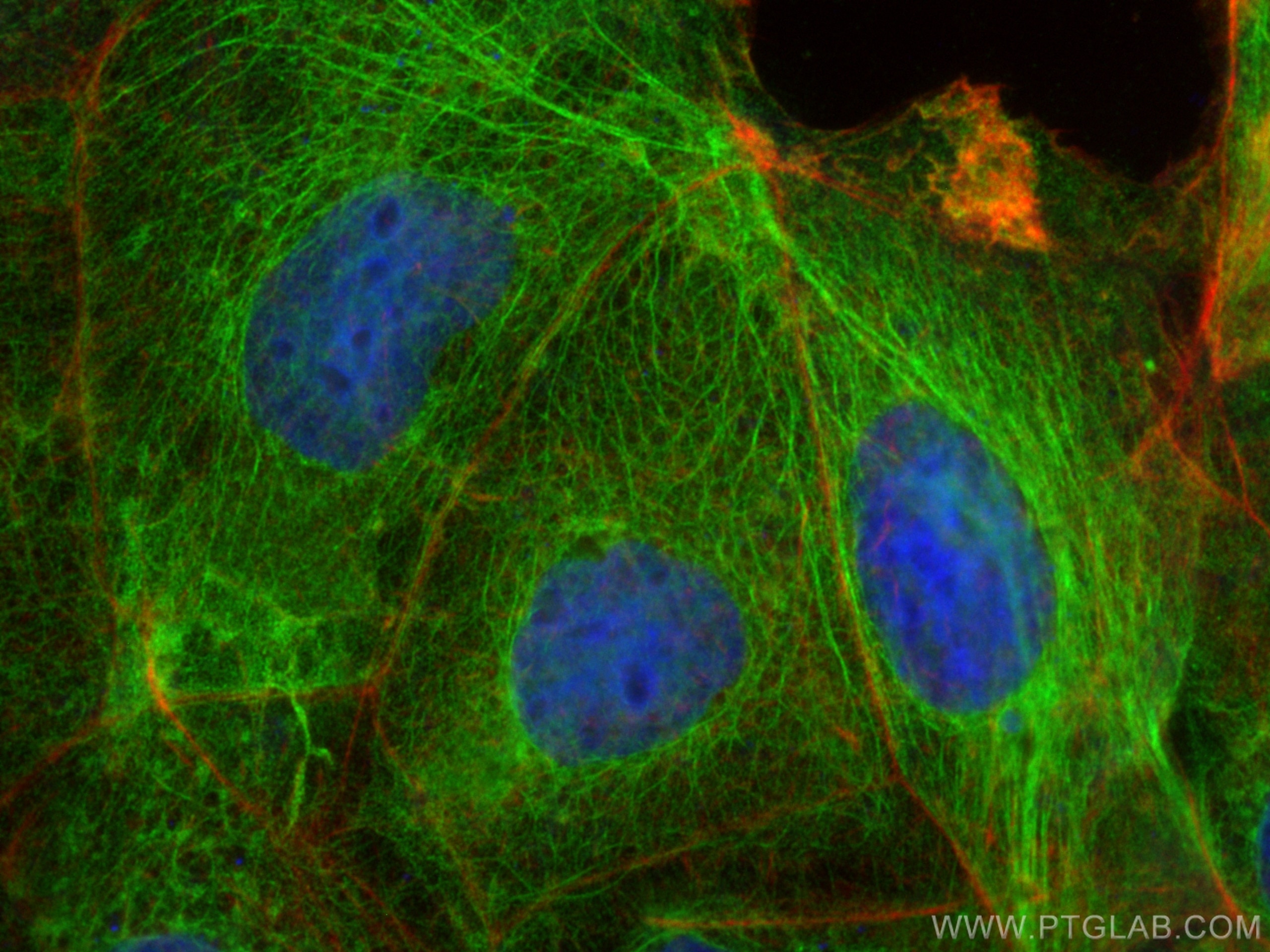
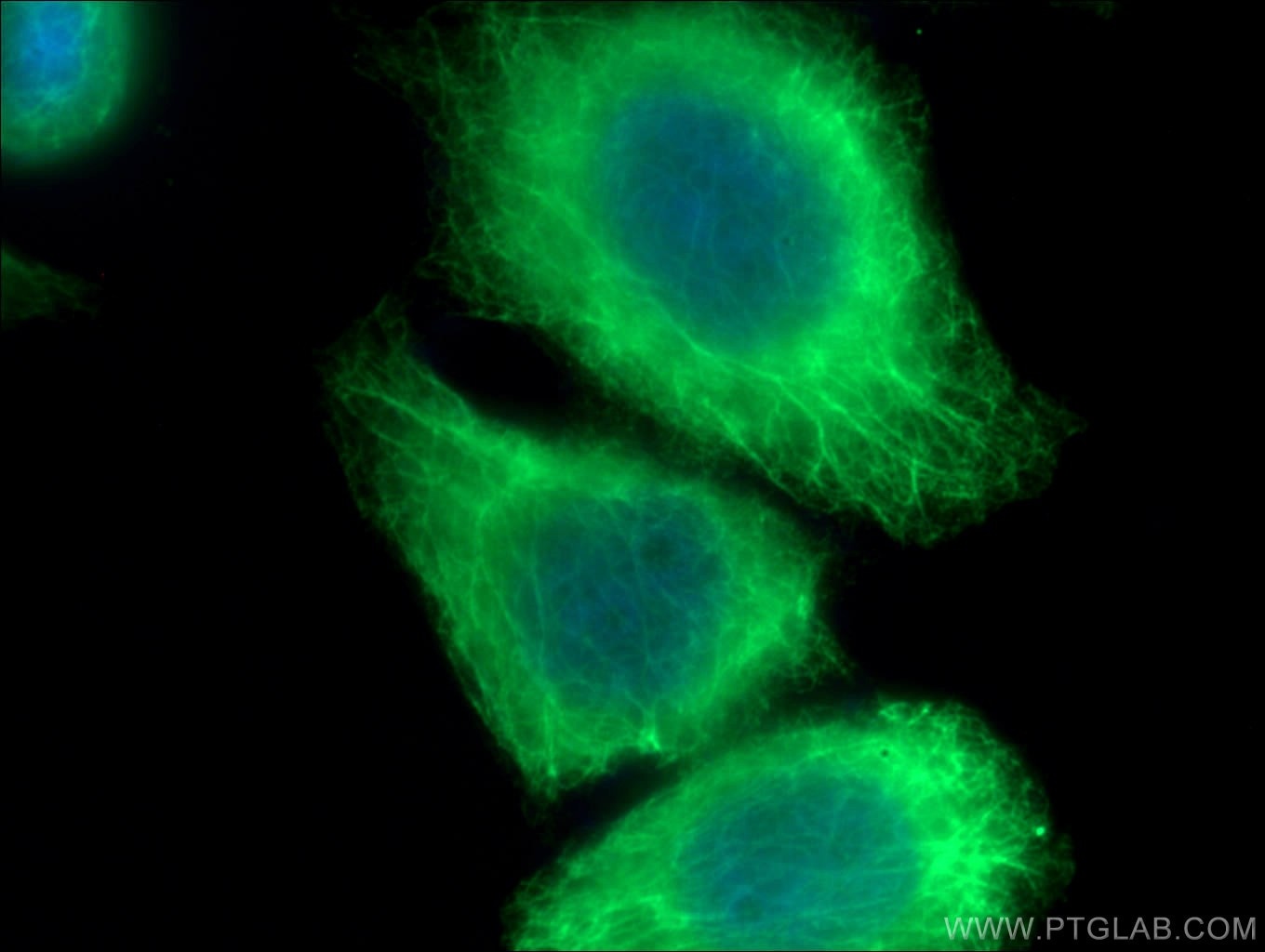
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | Caco-2 cells, HeLa cells |
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HT-29 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:16000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.20 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 9 publications below |
Product Information
17329-1-AP targets Cytokeratin 20 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, FC (Intra), ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, rabbit samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, rabbit |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag11308 Product name: Recombinant human KRT20 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 74-424 aa of BC031559 Sequence: MQNLNDRLASYLEKVRTLEQSNSKLEVQIKQWYETNAPRAGRDYSAYYRQIEELRSQIKDAQLQNARCVLQIDNAKLAAEDFRLKYETERGIRLTVEADLQGLNKVFDDLTLHKTDLEIQIEELNKDLALLKKEHQEEVDGLHKHLGNTVNVEVDAAPGLNLGVIMNEMRQKYEVMAQKNLQEAKEQFERQTAVLQQQVTVNTEELKGTEVQLTELRRTSQSLEIELQSHLSMKESLEHTLEETKARYSSQLANLQSLLSSLEAQLMQIRSNMERQNNEYHILLDIKTRLEQEIATYRRLLEGEDVKTTEYQLSTLEERDIKKTRKIKTVVQEVVDGKVVSSEVKEVEENI Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | keratin 20 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 424 aa, 48 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 46 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC031559 |
| Gene Symbol | Cytokeratin 20 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 54474 |
| RRID | AB_2133592 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P35900 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Keratins are a large family of proteins that form the intermediate filament cytoskeleton of epithelial cells, which are classified into two major sequence types. Type I keratins are a group of acidic intermediate filament proteins, including K9-K23, and the hair keratins Ha1-Ha8. Type II keratins are the basic or neutral courterparts to the acidic type I keratins, including K1-K8, and the hair keratins, Hb1-Hb6. Keratin 20 is a type I cytokeratin. It is a major cellular protein of mature enterocytes and goblet cells and is specifically found in the gastric and intestinal mucosa.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for Cytokeratin 20 antibody 17329-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Cytokeratin 20 antibody 17329-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Cytokeratin 20 antibody 17329-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for Cytokeratin 20 antibody 17329-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Res Gut microbiota drives macrophage-dependent self-renewal of intestinal stem cells via niche enteric serotonergic neurons. | ||
Nat Cell Biol LncGata6 maintains stemness of intestinal stem cells and promotes intestinal tumorigenesis. | ||
Neuron 5-hydroxytryptamine produced by enteric serotonergic neurons initiates colorectal cancer stem cell self-renewal and tumorigenesis. | ||
Biomaterials A microengineered collagen scaffold for generating a polarized crypt-villus architecture of human small intestinal epithelium. | ||
Cancer Lett LGR4 cooperates with PrPc to endow the stemness of colorectal cancer stem cells contributing to tumorigenesis and liver metastasis. | ||
Nutrients Propolis Has an Anticancer Effect on Early Stage Colorectal Cancer by Affecting Epithelial Differentiation and Gut Immunity in the Tumor Microenvironment |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Felletár (Verified Customer) (05-09-2025) | Immunohistochemical staining was performed using a novel, pre-commercial automated staining-covering and scanning system. The protocol included a 30-minute incubation with the primary antibody and utilized a polymer-based horseradish peroxidase (HRP) detection system. Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). scanning under 20x lens.
 |